10-K: Annual report pursuant to Section 13 and 15(d)
Published on February 23, 2012
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
ý |
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011
OR
o |
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
For the transition period from to
Commission File No. 001-02217

(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
|
DELAWARE
(State or other jurisdiction of
incorporation or organization)
|
58-0628465
(IRS Employer
Identification No.)
|
|
|
One Coca-Cola Plaza
Atlanta, Georgia
(Address of principal executive offices)
|
30313
(Zip Code)
|
|
Registrant's telephone number, including area code: (404) 676-2121
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class |
Name of each exchange on which registered |
|
COMMON STOCK, $0.25 PAR VALUE |
NEW YORK STOCK EXCHANGE |
|
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
___________________________________________________
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Exchange Act. Yes o No ý
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of Registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. o
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer," "accelerated filer" and "smaller reporting company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
Large accelerated filer ý
|
Accelerated filer o
|
Non-accelerated filer o
|
Smaller reporting company o
|
|||
(Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | ||||||
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes o No ý
The aggregate market value of the common equity held by non-affiliates of the Registrant (assuming for these purposes, but without conceding, that all executive officers and Directors are "affiliates" of the Registrant) as of July 1, 2011, the last business day of the Registrant's most recently completed second fiscal quarter, was $148,385,503,727 (based on the closing sale price of the Registrant's Common Stock on that date as reported on the New York Stock Exchange).
The number of shares outstanding of the Registrant's Common Stock as of February 20, 2012, was 2,263,204,221.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the Company's Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of Shareowners to be held on April 25, 2012, are incorporated by reference in Part III.
Table of Contents
Page |
||
Part I |
||
Part II |
||
Part III |
||
Part IV |
||
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This report contains information that may constitute "forward-looking statements." Generally, the words "believe," "expect," "intend," "estimate," "anticipate," "project," "will" and similar expressions identify forward-looking statements, which generally are not historical in nature. However, the absence of these words or similar expressions does not mean that a statement is not forward-looking. All statements that address operating performance, events or developments that we expect or anticipate will occur in the future — including statements relating to volume growth, share of sales and earnings per share growth, and statements expressing general views about future operating results — are forward-looking statements. Management believes that these forward-looking statements are reasonable as and when made. However, caution should be taken not to place undue reliance on any such forward-looking statements because such statements speak only as of the date when made. Our Company undertakes no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law. In addition, forward-looking statements are subject to certain risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from our Company's historical experience and our present expectations or projections. These risks and uncertainties include, but are not limited to, those described in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" and elsewhere in this report and those described from time to time in our future reports filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
PART I
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
In this report, the terms "The Coca-Cola Company," "Company," "we," "us" and "our" mean The Coca-Cola Company and all entities included in our consolidated financial statements.
General
The Coca-Cola Company is the world's largest beverage company. We own or license and market more than 500 nonalcoholic beverage brands, primarily sparkling beverages but also a variety of still beverages such as waters, enhanced waters, juices and juice drinks, ready-to-drink teas and coffees, and energy and sports drinks. We own and market four of the world's top five nonalcoholic sparkling beverage brands: Coca-Cola, Diet Coke, Fanta and Sprite. Finished beverage products bearing our trademarks, sold in the United States since 1886, are now sold in more than 200 countries.
We make our branded beverage products available to consumers throughout the world through our network of Company-owned or controlled bottling and distribution operations as well as independently owned bottling partners, distributors, wholesalers and retailers — the world's largest beverage distribution system. Of the approximately 56 billion beverage servings of all types consumed worldwide every day, beverages bearing trademarks owned by or licensed to us account for more than 1.7 billion.
We believe that our success depends on our ability to connect with consumers by providing them with a wide variety of options to meet their desires, needs and lifestyle choices. Our success further depends on the ability of our people to execute effectively, every day.
Our goal is to use our Company's assets — our brands, financial strength, unrivaled distribution system, global reach and the talent and strong commitment of our management and associates — to become more competitive and to accelerate growth in a manner that creates value for our shareowners.
We were incorporated in September 1919 under the laws of the State of Delaware and succeeded to the business of a Georgia corporation with the same name that had been organized in 1892.
Acquisition of Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc.'s North American Business and Related Transactions
On October 2, 2010, we acquired the North American business of Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. ("CCE"), one of our major bottlers, consisting of CCE's production, sales and distribution operations in the United States, Canada, the British Virgin Islands, the United States Virgin Islands and the Cayman Islands, and a substantial majority of CCE's corporate segment. CCE shareowners other than the Company exchanged their CCE common stock for common stock in a new entity named Coca-Cola Enterprises, Inc. ("New CCE"), which after the closing of the transaction continued to hold the European operations that had been held by CCE prior to the acquisition. The Company does not have any ownership interest in New CCE. Upon completion of the CCE transaction, we combined the management of the acquired North American business with the management of our existing foodservice business; Minute Maid and Odwalla juice businesses; North America supply chain operations; and Company-owned bottling operations in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, into a unified bottling and customer service organization called Coca-Cola Refreshments ("CCR"). In addition, we reshaped our remaining Coca-Cola North America ("CCNA") operations into an organization that primarily provides franchise leadership and consumer marketing and innovation for the North American market. As a result of the transaction and related reorganization, our North American businesses operate as aligned and agile organizations with distinct capabilities, responsibilities and strengths.
1
In contemplation of the closing of our acquisition of CCE's North American business, we reached an agreement with Dr Pepper Snapple Group, Inc. ("DPS") to distribute certain DPS brands in territories where DPS brands had been distributed by CCE prior to the CCE transaction. Under the terms of our agreement with DPS, concurrently with the closing of the CCE transaction, we entered into license agreements with DPS to distribute Dr Pepper trademark brands in the U.S., Canada Dry in the Northeast U.S., and Canada Dry and C' Plus in Canada, and we made a net one-time cash payment of $715 million to DPS. Under the license agreements, the Company agreed to meet certain performance obligations to distribute DPS products in retail and foodservice accounts and vending machines. The license agreements have initial terms of 20 years, with automatic 20-year renewal periods unless otherwise terminated under the terms of the agreements. The license agreements replaced agreements between DPS and CCE existing immediately prior to the completion of the CCE transaction. In addition, we entered into an agreement with DPS to include Dr Pepper and Diet Dr Pepper in our Coca-Cola Freestyle fountain dispensers in certain outlets throughout the United States. The Coca-Cola Freestyle agreement has a term of 20 years.
On October 2, 2010, we sold all of our ownership interests in Coca-Cola Drikker AS (the "Norwegian bottling operation") and Coca-Cola Drycker Sverige AB (the "Swedish bottling operation") to New CCE for $0.9 billion in cash. In addition, in connection with the acquisition of CCE's North American business, we granted to New CCE the right to negotiate the acquisition of our majority interest in our German bottler at any time from 18 to 39 months after February 25, 2010, at the then current fair value and subject to terms and conditions as mutually agreed.
Operating Segments
The Company's operating structure is the basis for our internal financial reporting. As of December 31, 2011, our operating structure included the following operating segments, the first six of which are sometimes referred to as "operating groups" or "groups":
• |
Eurasia and Africa |
• |
Europe |
• |
Latin America |
• |
North America |
• |
Pacific |
• |
Bottling Investments |
• |
Corporate |
Our North America operating segment includes the CCE North American business we acquired on October 2, 2010. Except to the extent that differences among operating segments are material to an understanding of our business taken as a whole, the description of our business in this report is presented on a consolidated basis.
For financial information about our operating segments and geographic areas, refer to Note 19 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in Part II, "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" of this report, incorporated herein by reference. For certain risks attendant to our non-U.S. operations, refer to "Item 1A. Risk Factors" below.
Products and Brands
As used in this report:
• |
"concentrates" means flavoring ingredients and, depending on the product, sweeteners used to prepare syrups or finished beverages, and includes powders for purified water products such as Dasani; |
• |
"syrups" means beverage ingredients produced by combining concentrates and, depending on the product, sweeteners and added water; |
• |
"fountain syrups" means syrups that are sold to fountain retailers, such as restaurants and convenience stores, which use dispensing equipment to mix the syrups with sparkling or still water at the time of purchase to produce finished beverages that are served in cups or glasses for immediate consumption; |
• |
"sparkling beverages" means nonalcoholic ready-to-drink beverages with carbonation, including carbonated energy drinks and carbonated waters and flavored waters; |
• |
"still beverages" means nonalcoholic beverages without carbonation, including noncarbonated waters, flavored waters and enhanced waters, noncarbonated energy drinks, juices and juice drinks, ready-to-drink teas and coffees, and sports drinks; |
2
• |
"Company Trademark Beverages" means beverages bearing our trademarks and certain other beverage products bearing trademarks licensed to us by third parties for which we provide marketing support and from the sale of which we derive economic benefit; and |
• |
"Trademark Coca-Cola Beverages" or "Trademark Coca-Cola" means beverages bearing the trademark Coca-Cola or any trademark that includes Coca-Cola or Coke (that is, Coca-Cola, Diet Coke and Coca-Cola Zero and all their variations and line extensions, including Coca-Cola Light, caffeine free Diet Coke, Cherry Coke, etc.). Likewise, when we use the capitalized word "Trademark" together with the name of one of our other beverage products (such as "Trademark Fanta," "Trademark Sprite" or "Trademark Simply"), we mean beverages bearing the indicated trademark (that is, Fanta, Sprite or Simply, respectively) and all its variations and line extensions (such that "Trademark Fanta" includes Fanta Orange, Fanta Zero Orange and Fanta Apple; "Trademark Sprite" includes Sprite, Diet Sprite, Sprite Zero and Sprite Light; and "Trademark Simply" includes Simply Orange, Simply Apple and Simply Grapefruit). |
Our Company markets, manufactures and sells:
• |
beverage concentrates, sometimes referred to as "beverage bases," and syrups, including fountain syrups (we refer to this part of our business as our "concentrate business" or "concentrate operations"); and |
• |
finished sparkling and still beverages (we refer to this part of our business as our "finished products business" or "finished products operations"). |
Generally, finished products operations generate higher net operating revenues but lower gross profit margins than concentrate operations.
In our concentrate operations, we typically generate net operating revenues by selling concentrates and syrups to authorized bottling and canning operations (to which we typically refer as our "bottlers" or our "bottling partners"). Our bottling partners either combine the concentrates with sweeteners (depending on the product), still water and/or sparkling water, or combine the syrups with sparkling water to produce finished beverages. The finished beverages are packaged in authorized containers bearing our trademarks or trademarks licensed to us — such as cans and refillable and nonrefillable glass and plastic bottles — and are then sold to retailers directly or, in some cases, through wholesalers or other bottlers. Outside the United States, we also sell concentrates for fountain beverages to our bottling partners who are typically authorized to manufacture fountain syrups, which they sell to fountain retailers such as restaurants and convenience stores which use the fountain syrups to produce beverages for immediate consumption, or to fountain wholesalers who in turn sell and distribute the fountain syrups to fountain retailers.
Our finished products operations consist primarily of the production, sales and distribution operations managed by CCR and our Company-owned or controlled bottling and distribution operations. CCR is included in our North America operating segment, and our Company-owned or controlled bottling and distribution operations are included in our Bottling Investments operating segment. Our finished products operations generate net operating revenues by selling sparkling beverages and a variety of still beverages, such as juices and juice drinks, energy and sports drinks, ready-to-drink teas and coffees, and certain water products, to retailers or to distributors, wholesalers and bottling partners who distribute them to retailers. In addition, in the United States, we manufacture fountain syrups and sell them to fountain retailers, such as restaurants and convenience stores who use the fountain syrups to produce beverages for immediate consumption, or to authorized fountain wholesalers or bottling partners who resell the fountain syrups to fountain retailers. In the United States, we authorize wholesalers to resell our fountain syrups through nonexclusive appointments that neither restrict us in setting the prices at which we sell fountain syrups to the wholesalers nor restrict the territories in which the wholesalers may resell in the United States.
For information about net operating revenues and unit case volume related to our concentrate operations and finished products operations, respectively, refer to the heading "Our Business — General" in Part II, "Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" of this report, which is incorporated herein by reference.
Most of our branded beverage products, particularly outside of North America, are manufactured, sold and distributed by independently owned and managed bottling partners. However, from time to time we acquire or take control of bottling or canning operations, often in underperforming markets where we believe we can use our resources and expertise to improve performance. Owning such a controlling interest enables us to compensate for limited local resources; help focus the bottler's sales and marketing programs; assist in the development of the bottler's business and information systems; and establish an appropriate capital structure for the bottler. The Company-owned or controlled bottling operations, other than those managed by CCR, are included in our Bottling Investments group.
In line with our long-term bottling strategy, we may periodically consider options for reducing our ownership interest in a Bottling Investments group bottler. One such option is to combine our bottling interests with the bottling interests of others to form strategic business alliances. Another option is to sell our interest in a bottling operation to one of our other bottling
3
partners in which we have an equity method investment. In both of these situations, our Company continues to participate in the bottler's results of operations through our share of the strategic business alliance's or equity method investee's earnings or losses.
The following table sets forth our most significant brands in each of our major beverage categories:
SPARKLING BEVERAGES* |
STILL BEVERAGES* |
|||||||
Core Sparkling |
Energy Drinks†
|
Juices and Juice Drinks |
Coffees and Teas |
Waters |
||||
Coca-Cola |
Burn |
Minute Maid1
|
Nestea teas2
|
Ciel1
|
||||
Sprite |
Nos4
|
Minute Maid Pulpy |
Georgia coffees3
|
Dasani1
|
||||
Fanta5
|
Real Gold3
|
Del Valle9
|
Leão / Matte Leão teas7
|
Ice Dew8
|
||||
Diet Coke / Coca-Cola Light |
Simply4
|
Sokenbicha teas3
|
Bonaqua / Bonaqa1
|
|||||
Coca-Cola Zero |
Hi-C |
Dogadan teas10
|
Kinley11
|
|||||
Schweppes12
|
Dobriy6
|
Ayataka teas3
|
||||||
Thums Up13
|
Cappy1
|
|||||||
Fresca |
||||||||
Inca Kola15
|
Other Still Beverages
|
Sports Drinks
|
||||||
Lift |
glacéau vitaminwater |
Powerade1
|
||||||
Barq's4
|
Fuze4
|
Aquarius14
|
||||||
* |
Includes, for each brand, all flavor variations and line extensions. Unless otherwise indicated in a footnote below, products under the brands are sold in markets across two or more geographic operating groups. |
† |
In some markets, certain of our energy drink products are still beverages. |
1 |
In some markets, certain products sold under this brand are sparkling beverages. |
2 |
Nestea products are distributed in the United States under a sublicense from a subsidiary of Nestlé S.A. ("Nestlé"), and in various other markets worldwide through Beverage Partners Worldwide ("BPW"), the Company's joint venture with Nestlé. The Nestea trademark is owned by Société des Produits Nestlé S.A. In January 2012, the Company and Nestlé announced that they are refocusing BPW on markets in Europe and Canada. In Taiwan and Hong Kong, the Company will enter into a license agreement with Nestlé for Nestea. In all other territories, the joint venture will be phased out by the end of 2012. In addition, the sublicense agreement for Nestea in the United States will terminate at the end of 2012. In some markets, certain Nestea products are sparkling beverages. |
3 |
Sold primarily in Japan. |
4 |
Sold primarily in North America. |
5 |
In some markets, certain Fanta products are still beverages. |
6 |
Dobriy juice products are manufactured, marketed and sold primarily in Russia, Ukraine and Belarus by Multon, a Russian juice business operated as a joint venture with Coca-Cola Hellenic Bottling Company S.A. Certain products sold under this brand are sparkling beverages. |
7 |
The Company manufactures, markets and sells Leão / Matte Leão teas in Brazil through a joint venture with our bottling partners. |
8 |
Sold in China. |
9 |
The Company manufactures, markets and sells juices and juice drinks under the Del Valle trademark through joint ventures with our bottling partners in Mexico and Brazil. |
10 |
Sold in Turkey. |
11 |
Kinley is also a sparkling beverage in certain countries. |
12 |
The Schweppes brand is owned by the Company in some countries (excluding the U.S., among others). In some markets, certain Schweppes products are still beverages. |
13 |
Sold primarily in India. |
14 |
In some markets, we offer water products or sparkling beverages in addition to sports drinks under the brand Aquarius. |
15 |
Sold primarily in Latin America (Chile, Ecuador and Peru). |
Consumer demand determines the optimal menu of Company product offerings. Consumer demand can vary from one locale to another and can change over time within a single locale. Employing our business strategy, and with special focus on core brands, our Company seeks to build its existing brands and, at the same time, to broaden its historical family of brands, products and services in order to create and satisfy consumer demand locale by locale.
4
During 2011, our Company introduced a variety of new brands, brand extensions and new beverage products. The Latin America group launched Frugos Sabores Caseros, a juice nectar targeted to capture the homemade juice category, in Peru, and leveraged its existing portfolio through search and reapply initiatives such as Powerade ION4, glacéau smartwater, Del Valle Limon & Nada and Burn, an energy drink. In the Pacific group, Fanta, a fruit-flavored sparkling beverage, was relaunched in Singapore and Malaysia after a significant period of absence from those markets; Real Leaf, a green tea-based beverage, extended its footprint with launches of two varieties in Vietnam; and in South Korea we introduced three flavor variants of the Georgia Emerald Mountain Blend ready-to-drink coffee beverage and Burn Intense, an energy drink. The Europe group saw the launch of Powerade ION4 in Denmark, Norway, Sweden and France, with France also launching Powerade Zero. In the Eurasia and Africa group, Turkey saw the launch of Cappy Pulpy, and India launched Fanta Powder, an orange-flavored powder formulation. Schweppes Novida, a sparkling malt drink, was launched in Kenya and Uganda; and in Uganda we also launched Coca-Cola Zero. In Egypt, we launched Cappy Fruitbite, the Company's first juice drink with real fruit pieces in that market, and Schweppes Gold, a sparkling flavored malt drink. In addition, in Ghana, we launched Schweppes Malt, a dark malt drink.
In furtherance of our commitments to sustainability and innovation, our PlantBottle technology, which allows us to replace 100 percent petroleum-based PET plastic with PET plastic that contains up to 30 percent material derived from plants, is becoming more widely used around the world. By the end of 2011, PlantBottle packaging was available in 20 countries, and nearly 10 billion PlantBottle packages had been shipped. Also in 2011, the availability of our Coca-Cola Freestyle fountain dispenser expanded in the United States to over 2,000 locations in 44 states. In addition, we added 19 beverages to bring the number of regular and low-calorie beverage choices available on Coca-Cola Freestyle to 125 in honor of the Company's 125th anniversary.
We measure the volume of Company beverage products sold in two ways: (1) unit cases of finished products and (2) concentrate sales. As used in this report, "unit case" means a unit of measurement equal to 192 U.S. fluid ounces of finished beverage (24 eight-ounce servings); and "unit case volume" means the number of unit cases (or unit case equivalents) of Company beverage products directly or indirectly sold by the Company and its bottling partners (the "Coca-Cola system") to customers. Unit case volume primarily consists of beverage products bearing Company trademarks. Also included in unit case volume are certain products licensed to, or distributed by, our Company, and brands owned by Coca-Cola system bottlers for which our Company provides marketing support and from the sale of which we derive economic benefit. In addition, unit case volume includes sales by joint ventures in which the Company has an equity interest. We believe unit case volume is one of the measures of the underlying strength of the Coca-Cola system because it measures trends at the consumer level. The unit case volume numbers used in this report are derived based on estimates received by the Company from its bottling partners and distributors. Concentrate sales volume represents the amount of concentrates and syrups (in all cases expressed in equivalent unit cases) sold by, or used in finished beverages sold by, the Company to its bottling partners or other customers. Unit case volume and concentrate sales volume growth rates are not necessarily equal during any given period. Factors such as seasonality, bottlers' inventory practices, supply point changes, timing of price increases, new product introductions and changes in product mix can impact unit case volume and concentrate sales volume and can create differences between unit case volume and concentrate sales volume growth rates. In addition to the items mentioned above, the impact of unit case volume from certain joint ventures, in which the Company has an equity interest, but to which the Company does not sell concentrates or syrups, may give rise to differences between unit case volume and concentrate sales volume growth rates.
Distribution System and Bottler's Agreements
We make our branded beverage products available to consumers in more than 200 countries through our network of Company-owned or controlled bottling and distribution operations as well as independently owned bottling partners, distributors, wholesalers and retailers — the world's largest beverage distribution system. Consumers enjoy finished beverage products bearing our trademarks at a rate of more than 1.7 billion servings each day. We continue to expand our marketing presence and increase our unit case volume in developed, developing and emerging markets. Our strong and stable system helps us to capture growth by manufacturing, distributing and marketing existing, enhanced and new innovative products to our consumers throughout the world.
The Coca-Cola system sold approximately 26.7 billion, 25.5 billion and 24.4 billion unit cases of our products in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. Sparkling beverages represented approximately 75 percent, 76 percent and 77 percent of our worldwide unit case volume for 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. Trademark Coca-Cola Beverages accounted for approximately 49 percent, 50 percent and 51 percent of our worldwide unit case volume for 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
In 2011, unit case volume in the United States ("U.S. unit case volume") represented approximately 20 percent of the Company's worldwide unit case volume. Of the U.S. unit case volume for 2011, approximately 70 percent was attributable to sparkling beverages and approximately 30 percent to still beverages. Trademark Coca-Cola Beverages accounted for approximately 49 percent of U.S. unit case volume for 2011.
5
Unit case volume outside the United States represented approximately 80 percent of the Company's worldwide unit case volume for 2011. The countries outside the United States in which our unit case volumes were the largest in 2011 were Mexico, China, Brazil and Japan, which together accounted for approximately 31 percent of our worldwide unit case volume. Of the non-U.S. unit case volume for 2011, approximately 77 percent was attributable to sparkling beverages and approximately 23 percent to still beverages. Trademark Coca-Cola Beverages accounted for approximately 49 percent of non-U.S. unit case volume for 2011.
In our concentrate operations, we typically sell concentrates and syrups to our bottling partners, who use the concentrate to manufacture finished products which they sell to distributors and other customers. Separate contracts ("Bottler's Agreements") exist between our Company and each of our bottling partners regarding the manufacture and sale of Company products. Subject to specified terms and conditions and certain variations, the Bottler's Agreements generally authorize the bottlers to prepare specified Company Trademark Beverages, to package the same in authorized containers, and to distribute and sell the same in (but, subject to applicable local law, generally only in) an identified territory. The bottler is obligated to purchase its entire requirement of concentrates or syrups for the designated Company Trademark Beverages from the Company or Company-authorized suppliers. We typically agree to refrain from selling or distributing, or from authorizing third parties to sell or distribute, the designated Company Trademark Beverages throughout the identified territory in the particular authorized containers; however, we typically reserve for ourselves or our designee the right (1) to prepare and package such beverages in such containers in the territory for sale outside the territory, and (2) to prepare, package, distribute and sell such beverages in the territory in any other manner or form. Territorial restrictions on bottlers vary in some cases in accordance with local law.
Being a bottler does not create a legal partnership or joint venture between us and our bottlers. Our bottlers are independent contractors and are not our agents.
While, as described below, under most of our Bottler's Agreements we generally have complete flexibility to determine the price and other terms of sale of the concentrates and syrups we sell to our bottlers, as a practical matter, our Company's ability to exercise its contractual flexibility to determine the price and other terms of sale of its syrups, concentrates and finished beverages is subject, both outside and within the United States, to competitive market conditions.
Bottler's Agreements Outside the United States
The Bottler's Agreements between us and our authorized bottlers outside the United States generally are of stated duration, subject in some cases to possible extensions or renewals of the term of the contract. Generally, these contracts are subject to termination by the Company following the occurrence of certain designated events. These events include defined events of default and certain changes in ownership or control of the bottler.
In certain parts of the world outside the United States, we have not granted comprehensive beverage production rights to the bottlers. In such instances, we or our authorized suppliers sell Company Trademark Beverages to the bottlers for sale and distribution throughout the designated territory, often on a nonexclusive basis. Most of the Bottler's Agreements in force between us and bottlers outside the United States authorize the bottlers to manufacture and distribute fountain syrups, usually on a nonexclusive basis.
Our Company generally has complete flexibility to determine the price and other terms of sale of the concentrates and syrups we sell to bottlers outside the United States. In some instances, however, we have agreed or may in the future agree with a bottler with respect to concentrate pricing on a prospective basis for specified time periods. In some markets, in an effort to allow our Company and our bottling partners to grow together through shared value, aligned incentives and the flexibility necessary to meet consumers' always changing needs and tastes, we worked with our bottling partners to develop and implement an incidence-based pricing model for sparkling and still beverages. Under this model, the concentrate price we charge is impacted by a number of factors, including, but not limited to, bottler pricing, the channels in which the finished products are sold and package mix. Outside the United States, in most cases, we have no obligation to provide marketing support to the bottlers. Nevertheless, we may, at our discretion, contribute toward bottler expenditures for advertising and marketing. We may also elect to undertake independent or cooperative advertising and marketing activities.
Bottler's Agreements Within the United States
During the year ended December 31, 2011, CCR, our bottling and customer service organization for North America, manufactured, sold and distributed approximately 87 percent of our unit case volume in the United States. The discussion below regarding the terms of Bottler's Agreements and other contracts relates to Bottler's Agreements and contracts for territories in the United States that are not covered by CCR.
In the United States, with certain very limited exceptions, the Bottler's Agreements for Trademark Coca-Cola Beverages and other cola-flavored beverages have no stated expiration date. Our standard contracts for other sparkling beverage flavors and for still beverages are of stated duration, subject to bottler renewal rights. The Bottler's Agreements in the United States are
6
subject to termination by the Company for nonperformance or upon the occurrence of certain defined events of default that may vary from contract to contract.
Under the terms of the Bottler's Agreements, bottlers in the United States are authorized to manufacture and distribute Company Trademark Beverages in bottles and cans. However, these bottlers generally are not authorized to manufacture fountain syrups. Rather, in the United States, our Company manufactures and sells fountain syrups to authorized fountain wholesalers (including certain authorized bottlers) and some fountain retailers. These wholesalers in turn sell the syrups or deliver them on our behalf to restaurants and other retailers.
Certain of the Bottler's Agreements for cola-flavored sparkling beverages in effect in the United States give us complete flexibility to determine the price and other terms of sale of concentrates and syrups for Company Trademark Beverages. In some instances, we have agreed or may in the future agree with a bottler with respect to concentrate pricing on a prospective basis for specified time periods. Certain Bottler's Agreements, entered into prior to 1987, provide for concentrates or syrups for certain Trademark Coca-Cola Beverages and other cola-flavored Company Trademark Beverages to be priced pursuant to a stated formula. Bottlers that accounted for approximately 3.7 percent of total unit case volume in the United States in 2011 have contracts for certain Trademark Coca-Cola Beverages and other cola-flavored Company Trademark Beverages with pricing formulas that generally provide for a baseline price. This baseline price may be adjusted periodically by the Company, up to a maximum indexed ceiling price, and is adjusted quarterly based upon changes in certain sugar or sweetener prices, as applicable. Bottlers that accounted for approximately 0.1 percent of total unit case volume in the United States in 2011 operate under our oldest form of contract, which provides for a fixed price for Coca-Cola syrup used in bottles and cans. This price is subject to quarterly adjustments to reflect changes in the quoted price of sugar.
We have standard contracts with bottlers in the United States for the sale of concentrates and syrups for non-cola-flavored sparkling beverages and certain still beverages in bottles and cans, and, in certain cases, for the sale of finished still beverages in bottles and cans. All of these standard contracts give the Company complete flexibility to determine the price and other terms of sale.
In an effort to allow our Company and our bottling partners to grow together through shared value, aligned incentives and the flexibility necessary to meet consumers' always changing needs and tastes, we worked with bottling partners that produce and distribute most of our non-CCR unit case volume in the United States to develop and implement an incidence-based pricing model, primarily for sparkling beverages. Under this model, the concentrate price we charge is impacted by a number of factors, including, but not limited to, bottler pricing, the channels in which the finished products are sold and package mix. We expect to use an incidence-based pricing model in 2012 with bottlers that produce and distribute most of our non-CCR unit case volume in the United States.
Under most of our Bottler's Agreements and other standard beverage contracts with bottlers in the United States, our Company has no obligation to participate with bottlers in expenditures for advertising and marketing. Nevertheless, at our discretion, we may contribute toward such expenditures and undertake independent or cooperative advertising and marketing activities. Some U.S. Bottler's Agreements entered into prior to 1987 impose certain marketing obligations on us with respect to certain Company Trademark Beverages.
Promotions and Marketing Programs
In addition to conducting our own independent advertising and marketing activities, we may provide promotional and marketing services or funds to our bottlers. In most cases, we do this on a discretionary basis under the terms of commitment letters or agreements, even though we are not obligated to do so under the terms of the bottling or distribution agreements between our Company and the bottlers. Also, on a discretionary basis in most cases, our Company may develop and introduce new products, packages and equipment to assist its bottlers. Likewise, in many instances, we provide promotional and marketing services and/or funds and/or dispensing equipment and repair services to fountain and bottle/can retailers, typically pursuant to marketing agreements. The aggregate amount of funds provided by our Company to bottlers, resellers or other customers of our Company's products, principally for participation in promotional and marketing programs, was $5.8 billion in 2011.
Significant Equity Method Investments
We make equity investments in selected bottling operations with the intention of maximizing the strength and efficiency of the Coca-Cola system's production, distribution and marketing capabilities around the world. These investments are intended to result in increases in unit case volume, net revenues and profits at the bottler level, which in turn generate increased concentrate sales for our Company's concentrate and syrup business. When this occurs, both we and our bottling partners benefit from long-term growth in volume, improved cash flows and increased shareowner value. In cases where our investments in bottlers represent noncontrolling interests, our intention is to provide expertise and resources to strengthen those businesses. When our
7
equity investment provides us with the ability to exercise significant influence over the investee bottler's operating and financial policies, we account for the investment under the equity method, and we sometimes refer to such a bottler as an "equity method investee bottler" or "equity method investee."
Our significant equity method investee bottlers include the following:
Coca-Cola Hellenic Bottling Company S.A. ("Coca-Cola Hellenic"). Our ownership interest in Coca-Cola Hellenic was 23 percent at December 31, 2011. Coca-Cola Hellenic has bottling and distribution rights, through direct ownership or joint ventures, in Armenia, Austria, Belarus, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Estonia, the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Moldova, Montenegro, Nigeria, Northern Ireland, Poland, Republic of Ireland, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Switzerland and Ukraine. Coca-Cola Hellenic estimates that the area in these 28 countries which it serves through its bottling and distribution rights has a combined population of 560 million people. In 2011, 46 percent of the unit case volume of Coca-Cola Hellenic consisted of Trademark Coca-Cola Beverages; 50 percent of its unit case volume consisted of other Company Trademark Beverages; and approximately 4 percent of its unit case volume consisted of beverage products of Coca-Cola Hellenic or other companies.
Coca-Cola FEMSA, S.A.B. de C.V. ("Coca-Cola FEMSA"). Our ownership interest in Coca-Cola FEMSA was 29 percent at December 31, 2011. Coca-Cola FEMSA is a Mexican holding company with bottling subsidiaries in a substantial part of central Mexico, including Mexico City and the southeast and northeast parts of Mexico; greater São Paulo, Campinas, Santos, the state of Matto Grosso do Sul, part of the state of Minas Gerais and part of the state of Goias in Brazil; central Guatemala; most of Colombia; all of Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Panama and Venezuela; and greater Buenos Aires, Argentina. Coca-Cola FEMSA estimates that the territories in which it markets beverage products contain 55 percent of the population of Mexico, 22 percent of the population of Brazil, 99 percent of the population of Colombia, 35 percent of the population of Guatemala, 100 percent of the populations of Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Panama and Venezuela, and 32 percent of the population of Argentina. In 2011, 62 percent of the unit case volume of Coca-Cola FEMSA consisted of Trademark Coca-Cola Beverages and 38 percent of its unit case volume consisted of other Company Trademark Beverages.
Coca-Cola Amatil Limited ("Coca-Cola Amatil"). Our ownership interest in Coca-Cola Amatil was 29 percent at December 31, 2011. Coca-Cola Amatil has bottling and distribution rights, through direct ownership or joint ventures, in Australia, New Zealand, Fiji, Papua New Guinea and Indonesia. Coca-Cola Amatil estimates that the territories in which it markets beverage products contain 100 percent of the populations of Australia, New Zealand, Fiji and Papua New Guinea, and 98 percent of the population of Indonesia. In 2011, 45 percent of the unit case volume of Coca-Cola Amatil consisted of Trademark Coca-Cola Beverages; 41 percent of its unit case volume consisted of other Company Trademark Beverages; and 14 percent of its unit case volume consisted of beverage products of Coca-Cola Amatil or other companies.
Seasonality
Sales of our nonalcoholic ready-to-drink beverages are somewhat seasonal, with the second and third calendar quarters accounting for the highest sales volumes. The volume of sales in the beverage business may be affected by weather conditions.
Competition
Our Company competes in the nonalcoholic beverage segment of the commercial beverage industry. The nonalcoholic beverage segment of the commercial beverage industry is highly competitive, consisting of numerous companies. These include companies that, like our Company, compete in multiple geographic areas, as well as businesses that are primarily regional or local in operation. Competitive products include numerous nonalcoholic sparkling beverages; various water products, including packaged, flavored and enhanced waters; juices and nectars; fruit drinks and dilutables (including syrups and powdered drinks); coffees and teas; energy and sports and other performance-enhancing drinks; dairy-based drinks; functional beverages; and various other nonalcoholic beverages. These competitive beverages are sold to consumers in both ready-to-drink and other than ready-to-drink form. In many of the countries in which we do business, including the United States, PepsiCo, Inc., is one of our primary competitors. Other significant competitors include, but are not limited to, Nestlé, Dr Pepper Snapple Group, Inc., Groupe Danone, Kraft Foods Inc. and Unilever. In certain markets, our competition includes beer companies. We also compete against numerous regional and local companies and, in some markets, against retailers that have developed their own store or private label beverage brands.
Competitive factors impacting our business include, but are not limited to, pricing, advertising, sales promotion programs, product innovation, increased efficiency in production techniques, the introduction of new packaging, new vending and dispensing equipment, and brand and trademark development and protection.
Our competitive strengths include leading brands with a high level of consumer acceptance; a worldwide network of bottlers and distributors of Company products; sophisticated marketing capabilities; and a talented group of dedicated associates. Our competitive challenges include strong competition in all geographic regions and, in many countries, a concentrated retail sector
8
with powerful buyers able to freely choose among Company products, products of competitive beverage suppliers and individual retailers' own store or private label beverage brands.
Raw Materials
Water is a main ingredient in substantially all of our products. While historically we have not experienced significant water supply difficulties, water is a limited resource in many parts of the world and our Company recognizes water availability, quality and the sustainability of that natural resource for both our operations and also the communities where we operate as one of the key challenges facing our business.
In addition to water, the principal raw materials used in our business are nutritive and non-nutritive sweeteners. In the United States, the principal nutritive sweetener is high fructose corn syrup ("HFCS"), a form of sugar, which is available from numerous domestic sources and is historically subject to fluctuations in its market price. The principal nutritive sweetener used by our business outside the United States is sucrose, another form of sugar, which is also available from numerous sources and is historically subject to fluctuations in its market price. Our Company generally has not experienced any difficulties in obtaining its requirements for nutritive sweeteners. In the United States, we purchase HFCS to meet our and our bottlers' requirements with the assistance of Coca-Cola Bottlers' Sales & Services Company LLC ("CCBSS"). CCBSS is a limited liability company that is owned by authorized Coca-Cola bottlers doing business in the United States. Among other things, CCBSS provides procurement services to our Company for the purchase of various goods and services in the United States, including HFCS.
The principal non-nutritive sweeteners we use in our business are aspartame, acesulfame potassium, saccharin, cyclamate and sucralose. Generally, these raw materials are readily available from numerous sources. However, our Company purchases aspartame, an important non-nutritive sweetener that is used alone or in combination with other important non-nutritive sweeteners such as saccharin or acesulfame potassium in our low-calorie sparkling beverage products, primarily from The NutraSweet Company and Ajinomoto Co., Inc., which we consider to be our primary sources for the supply of this product. We currently purchase acesulfame potassium from Nutrinova Nutrition Specialties & Food Ingredients GmbH, which we consider to be our primary source for the supply of this product, and from one additional supplier. Our Company generally has not experienced any difficulties in obtaining its requirements for non-nutritive sweeteners.
Our Company sells a number of products sweetened with sucralose, a non-nutritive sweetener. We work closely with Tate & Lyle PLC, our primary sucralose supplier, to maintain continuity of supply, and we do not anticipate difficulties in obtaining our requirements. We also purchase Truvia, a non-nutritive natural sweetener made with rebiana, which is derived from the stevia plant, from Cargill, Incorporated, and we do not anticipate any supply issues with this ingredient.
With regard to juice and juice drink products, juice and juice concentrate from citrus fruit, particularly orange juice and orange juice concentrate, are our principal raw materials. The citrus industry is subject to the variability of weather conditions. In particular, freezing weather or hurricanes in central Florida may result in shortages and higher prices for orange juice and orange juice concentrate throughout the industry. The Company sources our orange juice and orange juice concentrate from both Florida and the Southern Hemisphere (particularly Brazil). Therefore, we typically have an adequate supply of orange juice and orange juice concentrate that meets our Company's standards.
Our Company-owned or consolidated bottling and canning operations and our finished products business also purchase various other raw materials including, but not limited to, PET resin, preforms and bottles; glass and aluminum bottles; aluminum and steel cans; plastic closures; aseptic fiber packaging; labels; cartons; cases; post-mix packaging; and carbon dioxide. We generally purchase these raw materials from multiple suppliers and historically have not experienced material shortages.
Patents, Copyrights, Trade Secrets and Trademarks
Our Company owns numerous patents, copyrights and trade secrets, as well as substantial know-how and technology, which we collectively refer to in this report as "technology." This technology generally relates to our Company's products and the processes for their production; the packages used for our products; the design and operation of various processes and equipment used in our business; and certain quality assurance software. Some of the technology is licensed to suppliers and other parties. Our sparkling beverage and other beverage formulae are among the important trade secrets of our Company.
We own numerous trademarks that are very important to our business. Depending upon the jurisdiction, trademarks are valid as long as they are in use and/or their registrations are properly maintained. Pursuant to our Bottler's Agreements, we authorize our bottlers to use applicable Company trademarks in connection with their manufacture, sale and distribution of Company products. In addition, we grant licenses to third parties from time to time to use certain of our trademarks in conjunction with certain merchandise and food products.
9
Governmental Regulation
Our Company is required to comply, and it is our policy to comply, with applicable laws in the numerous countries throughout the world in which we do business. In many jurisdictions, compliance with competition laws is of special importance to us, and our operations may come under special scrutiny by competition law authorities due to our competitive position in those jurisdictions.
In the United States, the safety, production, transportation, distribution, advertising, labeling and sale of many of our Company's products and their ingredients are subject to the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act; the Federal Trade Commission Act; the Lanham Act; state consumer protection laws; competition laws; federal, state and local workplace health and safety laws; various federal, state and local environmental protection laws; and various other federal, state and local statutes and regulations. Outside the United States, our business is subject to numerous similar statutes and regulations, as well as other legal and regulatory requirements.
A California law known as Proposition 65 requires that a warning appear on any product sold in California that contains a substance that, in the view of the state, causes cancer or birth defects. The state maintains lists of these substances and periodically adds other substances to these lists. Proposition 65 exposes all food and beverage producers to the possibility of having to provide warnings on their products in California because it does not provide for any generally applicable quantitative threshold below which the presence of a listed substance is exempt from the warning requirement. Consequently, the detection of even a trace amount of a listed substance can subject an affected product to the requirement of a warning label. However, Proposition 65 does not require a warning if the manufacturer of a product can demonstrate that the use of that product exposes consumers to a daily quantity of a listed substance that is:
• |
below a "safe harbor" threshold that may be established; |
• |
naturally occurring; |
• |
the result of necessary cooking; or |
• |
subject to another applicable exemption. |
One or more substances that are currently on the Proposition 65 lists, or that may be added in the future, can be detected in Company products at low levels that are safe. With respect to substances that have not yet been listed under Proposition 65, the Company takes the position that listing is not scientifically justified. With respect to substances that are already listed, the Company takes the position that the presence of each such substance in Company products is subject to an applicable exemption from the warning requirement. The State of California or other parties, however, may take a contrary position.
Bottlers of our beverage products presently offer and use nonrefillable, recyclable containers in the United States and various other markets around the world. Some of these bottlers also offer and use refillable containers, which are also recyclable. Legal requirements apply in various jurisdictions in the United States and overseas requiring that deposits or certain ecotaxes or fees be charged for the sale, marketing and use of certain nonrefillable beverage containers. The precise requirements imposed by these measures vary. Other types of statutes and regulations relating to beverage container deposits, recycling, ecotaxes and/or product stewardship also apply in various jurisdictions in the United States and overseas. We anticipate that additional, similar legal requirements may be proposed or enacted in the future at local, state and federal levels, both in the United States and elsewhere.
All of our Company's facilities and other operations in the United States and elsewhere around the world are subject to various environmental protection statutes and regulations, including those relating to the use of water resources and the discharge of wastewater. Our policy is to comply with all such legal requirements. Compliance with these provisions has not had, and we do not expect such compliance to have, any material adverse effect on our Company's capital expenditures, net income or competitive position.
Employees
We refer to our employees as "associates." As of December 31, 2011 and 2010, our Company had approximately 146,200 and 139,600 associates, respectively, of which approximately 4,700 and 4,900, respectively, were employed by consolidated variable interest entities ("VIEs"). The increase in the total number of associates in 2011 was primarily due to an increase in the North America operating segment, mostly related to the Great Plains Coca-Cola Bottling Company acquisition, as well as an increase in the Bottling Investments operating segment. As of December 31, 2011 and 2010, our Company had approximately 67,400 and 64,500 associates, respectively, located in the United States, of which approximately 600 and 700, respectively, were employed by consolidated VIEs.
10
Our Company, through its divisions and subsidiaries, is a party to numerous collective bargaining agreements. As of December 31, 2011, approximately 19,000 associates in North America were covered by collective bargaining agreements. These agreements typically have terms of three to five years. We currently expect that we will be able to renegotiate such agreements on satisfactory terms when they expire.
The Company believes that its relations with its associates are generally satisfactory.
Securities Exchange Act Reports
The Company maintains a website at the following address: www.thecoca-colacompany.com. The information on the Company's website is not incorporated by reference in this annual report on Form 10-K.
We make available on or through our website certain reports and amendments to those reports that we file with or furnish to the Securities and Exchange Commission (the "SEC") in accordance with the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Exchange Act"). These include our annual reports on Form 10-K, our quarterly reports on Form 10-Q and our current reports on Form 8-K. We make this information available on our website free of charge as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file the information with, or furnish it to, the SEC.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
In addition to the other information set forth in this report, you should carefully consider the following factors, which could materially affect our business, financial condition or results of operations in future periods. The risks described below are not the only risks facing our Company. Additional risks not currently known to us or that we currently deem to be immaterial also may materially adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations in future periods.
Obesity and other health concerns may reduce demand for some of our products.
Consumers, public health officials and government officials are highly concerned about the public health consequences associated with obesity, particularly among young people. In addition, some researchers, health advocates and dietary guidelines are encouraging consumers to reduce consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages, including those sweetened with HFCS or other nutritive sweeteners. Increasing public concern about these issues; possible new taxes on sugar-sweetened beverages; additional governmental regulations concerning the marketing, labeling, packaging or sale of our beverages; and negative publicity resulting from actual or threatened legal actions against us or other companies in our industry relating to the marketing, labeling or sale of sugar-sweetened beverages may reduce demand for our beverages, which could affect our profitability.
Water scarcity and poor quality could negatively impact the Coca-Cola system's production costs and capacity.
Water is the main ingredient in substantially all of our products. It is also a limited resource in many parts of the world, facing unprecedented challenges from overexploitation, increasing pollution, poor management and climate change. As demand for water continues to increase around the world, and as water becomes scarcer and the quality of available water deteriorates, our system may incur increasing production costs or face capacity constraints which could adversely affect our profitability or net operating revenues in the long run.
Changes in the nonalcoholic beverage business environment and retail trends could impact our financial results.
The nonalcoholic beverage business environment is rapidly evolving as a result of, among other things, changes in consumer preferences, including changes based on health and nutrition considerations and obesity concerns; shifting consumer tastes and needs; changes in consumer lifestyles; and competitive product and pricing pressures. In addition, the nonalcoholic beverage retail landscape is very dynamic and constantly evolving, not only in emerging and developing markets, where modern trade is growing at a faster pace than traditional trade outlets, but also in developed markets, where new formats such as discounters and value stores, as well as the volume of transactions through e-commerce, are growing at a rapid pace. Our industry is also being affected by the trend toward consolidation in the retail channel, particularly in Europe and the United States. If we are unable to successfully adapt to the rapidly changing environment and retail trends, our share of sales, volume growth and overall financial results could be negatively affected.
If we fail to realize a significant portion of the anticipated benefits of the acquisition of CCE's North American business, the value of your investment in our Company may be adversely affected.
On October 2, 2010, we acquired CCE's North American bottling and distribution operations. We believe the acquisition will enable us to evolve our entire business in North America, including the acquired operations, to more profitably deliver our valuable brands in the largest nonalcoholic ready-to-drink beverage market in the world. When we determined to make the
11
acquisition, we believed that the transaction would, among other things, enhance our ability to create a more fully integrated and adaptable supply chain in the North American market to allow our combined North American business to more efficiently and effectively operate our distribution chain in the North American territories and enhance revenue opportunities; create a unified operating system in North America that will address the unique needs of the North American market; strategically position us to better market and distribute our products in North America; improve efficiencies by streamlining operations and reducing or eliminating the costs, expenses, management time and resources associated with interactions and negotiations between the previously separate organizations; allow us to optimize and improve the efficiencies of manufacturing and logistics operations in North America through economies of scale and geography; generate significant operational synergies; facilitate and increase the pace of innovation and new product introduction in North America; and optimize our operating model and improve the strategic planning process, increasing management focus and streamlining decision making. While we believe that the anticipated benefits of the acquisition are achievable, it is possible that we may not be able to realize some or even a significant portion of such benefits, or may not be able to achieve them within the anticipated time frame. If we are unable to realize a significant portion of the anticipated benefits, or if it takes us significantly longer than expected to realize such benefits, our future results of operations may be adversely affected and we may not be able to meet investors' expectations or achieve our long-term growth objectives, which could negatively affect the value of your investment in our Company.
Our indebtedness increased significantly as a result of the acquisition of CCE's North American business. Our higher level of indebtedness will increase our borrowing costs and interest expense in future periods and, therefore, may adversely affect our financial performance.
As a result of the CCE transaction, we assumed $7.9 billion of debt from CCE. Our increased level of indebtedness and resulting higher borrowing costs and interest expense may reduce amounts available for dividends, stock repurchases, capital expenditures and acquisitions, and may cause rating agencies to downgrade our debt, all of which could have adverse effects on our future financial performance.
Our pension expense increased substantially as a result of the acquisition of CCE's North American business and we may incur multi-employer plan withdrawal liabilities in the future, which could negatively impact our financial performance.
Our total pension expense for 2011 was $249 million compared with $176 million for 2010. Most of the pension expense increase in 2011 was due to the full year impact of our acquisition of CCE's North American business and a decrease in the Company's discount rate compared to 2010. In addition, the Company's expense for U.S. multi-employer pension plans totaled $69 million in 2011, of which $32 million was related to our withdrawal from certain of these plans. The U.S. multi-employer pension plans in which we currently participate have contractual arrangements that extend into 2017. If, in the future, we choose to withdraw from any of the multi-employer pension plans in which we participate, we will likely need to record withdrawal liabilities which could negatively impact our financial performance in the applicable periods.
Continuing uncertainty in the credit and equity markets may adversely affect our financial performance.
The global credit markets experienced unprecedented disruptions during late 2008 and early 2009. While credit market conditions have improved somewhat since the crisis, the improvements have not been uniform. In addition, the sovereign debt crisis affecting various countries in the European Union is creating further uncertainties in the global credit markets. The cost and availability of credit vary by market and are subject to changes in the global or regional economic environment. If the current uncertain conditions in the credit markets continue or worsen, our ability to access credit markets on favorable terms may be negatively affected, which could increase our cost of borrowing. In addition, the current uncertain credit market conditions may make it more difficult for our bottling partners to access financing on terms comparable to those available prior to the global credit crisis, which would affect the Coca-Cola system's profitability as well as our share of the income of bottling partners in which we have equity method investments. The current uncertain global credit market conditions and their actual or perceived effects on our and our major bottling partners' results of operations and financial condition, along with the current unfavorable economic environment in the United States and much of the world, may increase the likelihood that the major independent credit agencies will downgrade our credit ratings, which could have a negative effect on our borrowing costs.
In addition, some of the major financial institutions remain fragile, and the counterparty risk associated with our existing derivative financial instruments remains higher than pre-crisis levels. Therefore, we may be unable to secure creditworthy counterparties for derivative transactions in the future or may incur higher than anticipated costs in our hedging activities. The decrease in availability of consumer credit resulting from the financial crisis, as well as general unfavorable economic conditions, may also cause consumers to reduce their discretionary spending, which would reduce the demand for our beverages and negatively affect our net operating revenues and the Coca-Cola system's profitability.
12
Increased competition could hurt our business.
The nonalcoholic beverage segment of the commercial beverage industry is highly competitive. We compete with major international beverage companies that, like our Company, operate in multiple geographic areas, as well as numerous companies that are primarily local in operation. In many countries in which we do business, including the United States, PepsiCo, Inc. is a primary competitor. Other significant competitors include, but are not limited to, Nestlé, Dr Pepper Snapple Group, Inc., Groupe Danone, Kraft Foods Inc. and Unilever. In certain markets, our competition includes major beer companies. Our beverage products also compete against local or regional brands as well as against store or private label brands developed by retailers, some of which are Coca-Cola system customers. Our ability to gain or maintain share of sales or gross margins in the global market or in various local markets may be limited as a result of actions by competitors.
If we are unable to expand our operations in developing and emerging markets, our growth rate could be negatively affected.
Our success depends in part on our ability to grow our business in developing and emerging markets, which in turn depends on economic and political conditions in those markets and on our ability to acquire bottling operations in those markets or to form strategic business alliances with local bottlers and to make necessary infrastructure enhancements to production facilities, distribution networks, sales equipment and technology. Moreover, the supply of our products in developing and emerging markets must match consumers' demand for those products. Due to product price, limited purchasing power and cultural differences, there can be no assurance that our products will be accepted in any particular developing or emerging market.
Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates could affect our financial results.
We earn revenues, pay expenses, own assets and incur liabilities in countries using currencies other than the U.S. dollar, including the euro, the Japanese yen, the Brazilian real and the Mexican peso. In 2011, we used 72 functional currencies in addition to the U.S. dollar and derived $27.8 billion of net operating revenues from operations outside the United States. Because our consolidated financial statements are presented in U.S. dollars, we must translate revenues, income and expenses, as well as assets and liabilities, into U.S. dollars at exchange rates in effect during or at the end of each reporting period. Therefore, increases or decreases in the value of the U.S. dollar against other major currencies affect our net operating revenues, operating income and the value of balance sheet items denominated in foreign currencies. In addition, unexpected and dramatic devaluations of currencies in developing or emerging markets, such as the devaluation of the Venezuelan bolivar, could negatively affect the value of our earnings from, and of the assets located in, those markets. Because of the geographic diversity of our operations, weaknesses in some currencies might be offset by strengths in others over time. We also use derivative financial instruments to further reduce our net exposure to currency exchange rate fluctuations. However, we cannot assure you that fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates, particularly the strengthening of the U.S. dollar against major currencies or the currencies of large developing countries, would not materially affect our financial results.
If interest rates increase, our net income could be negatively affected.
We maintain levels of debt that we consider prudent based on our cash flows, interest coverage ratio and percentage of debt to capital. We use debt financing to lower our cost of capital, which increases our return on shareowners' equity. This exposes us to adverse changes in interest rates. When appropriate, we use derivative financial instruments to reduce our exposure to interest rate risks. We cannot assure you, however, that our financial risk management program will be successful in reducing the risks inherent in exposures to interest rate fluctuations. In addition, our exposure to fluctuating interest rates has increased as a result of the indebtedness we assumed in connection with the acquisition of CCE's North American business. Our interest expense may also be affected by our credit ratings. In assessing our credit strength, credit rating agencies consider our capital structure and financial policies as well as the consolidated balance sheet and other financial information for the Company. In addition, some credit rating agencies also consider financial information for certain major bottlers. It is our expectation that the credit rating agencies will continue using this methodology. If our credit ratings were to be downgraded as a result of changes in our capital structure; our major bottlers' financial performance; changes in the credit rating agencies' methodology in assessing our credit strength; the credit agencies' perception of the impact of the continuing unfavorable credit conditions on our or our major bottlers' current or future financial performance and financial condition; or for any other reason, our cost of borrowing could increase. Additionally, if the credit ratings of certain bottlers in which we have equity method investments were to be downgraded, such bottlers' interest expense could increase, which would reduce our equity income.
We rely on our bottling partners for a significant portion of our business. If we are unable to maintain good relationships with our bottling partners, our business could suffer.
We generate a significant portion of our net operating revenues by selling concentrates and syrups to independent bottling partners. As independent companies, our bottling partners, some of which are publicly traded companies, make their own business decisions that may not always align with our interests. In addition, many of our bottling partners have the right to
13
manufacture or distribute their own products or certain products of other beverage companies. If we are unable to provide an appropriate mix of incentives to our bottling partners through a combination of pricing and marketing and advertising support, or if our bottling partners are not satisfied with our brand innovation and development efforts, they may take actions that, while maximizing their own short-term profits, may be detrimental to our Company or our brands, or they may devote more of their energy and resources to business opportunities or products other than those of the Company. Such actions could, in the long run, have an adverse effect on our profitability.
If our bottling partners' financial condition deteriorates, our business and financial results could be affected.
We derive a significant portion of our net operating revenues from sales of concentrates and syrups to our bottling partners and, therefore, the success of our business depends on our bottling partners' financial strength and profitability. While under our bottling partners' agreements we generally have the right to unilaterally change the prices we charge for our concentrates and syrups, our ability to do so may be materially limited by our bottling partners' financial condition and their ability to pass price increases along to their customers. In addition, we have investments in certain of our bottling partners, which we account for under the equity method, and our operating results include our proportionate share of such bottling partners' income or loss. Our bottling partners' financial condition is affected in large part by conditions and events that are beyond our and their control, including competitive and general market conditions in the territories in which they operate; the availability of capital and other financing resources on reasonable terms; loss of major customers; or disruptions of bottling operations that may be caused by strikes, work stoppages, labor unrest or natural disasters. A deterioration of the financial condition or results of operations of one or more of our major bottling partners could adversely affect our net operating revenues from sales of concentrates and syrups; could result in a decrease in our equity income; and could negatively affect the carrying values of our investments in bottling partners, resulting in asset write-offs.
Increases in income tax rates or changes in income tax laws could have a material adverse impact on our financial results.
We are subject to income tax in the United States and in numerous other jurisdictions in which we generate net operating revenues. Increases in income tax rates could reduce our after-tax income from affected jurisdictions. In addition, there have been proposals to reform U.S. tax laws that could significantly impact how U.S. multinational corporations are taxed on foreign earnings. We earn a substantial portion of our income in foreign countries. Although we cannot predict whether or in what form these proposals will pass, several of the proposals being considered, if enacted into law, could have a material adverse impact on our tax expense and cash flow.
Increased or new indirect taxes in the United States or in one or more of our other major markets could negatively affect our business.
Our business operations are subject to numerous duties or taxes that are not based on income, sometimes referred to as "indirect taxes," including import duties, excise taxes, sales or value-added taxes, property taxes and payroll taxes, in many of the jurisdictions in which we operate, including indirect taxes imposed by state and local governments. In addition, in the past, the United States Congress considered imposing a federal excise tax on beverages sweetened with sugar, HFCS or other nutritive sweeteners and may consider similar proposals in the future. As federal, state and local governments experience significant budget deficits, some lawmakers have proposed singling out beverages among a plethora of revenue-raising items. Increases in or the imposition of new indirect taxes on our business operations or products would increase the cost of products or, to the extent levied directly on consumers, make our products less affordable, which may negatively impact our net operating revenues.
If we are unable to renew collective bargaining agreements on satisfactory terms, or we or our bottling partners experience strikes, work stoppages or labor unrest, our business could suffer.
Many of our associates at our key manufacturing locations and bottling plants are covered by collective bargaining agreements. With the acquisition of CCE's North American business on October 2, 2010, the number of our associates in North America represented by labor unions substantially increased to approximately 19,000 as of December 31, 2011. While we generally have been able to renegotiate collective bargaining agreements on satisfactory terms when they expire and regard our relations with associates and their representatives as generally satisfactory, negotiations in the current environment remain challenging, as the Company must have competitive cost structures in each market while meeting the compensation and benefits needs of our associates. If we are unable to renew collective bargaining agreements on satisfactory terms, our labor costs could increase, which would affect our profit margins. In addition, many of our bottling partners' employees are represented by labor unions. Strikes, work stoppages or other forms of labor unrest at any of our major manufacturing facilities or at our or our major bottlers' plants could impair our ability to supply concentrates and syrups to our bottling partners or our bottlers' ability to supply finished beverages to customers, which would reduce our net operating revenues and could expose us to customer claims.
14
Increase in the cost, disruption of supply or shortage of energy could affect our profitability.
CCR, our North America bottling and customer service organization, and our Company-owned or controlled bottlers operate a large fleet of trucks and other motor vehicles to distribute and deliver beverage products to customers. In addition, we use a significant amount of electricity, natural gas and other energy sources to operate our concentrate plants and the bottling plants and distribution facilities operated by CCR and our Company-owned or controlled bottlers. An increase in the price, disruption of supply or shortage of fuel and other energy sources in North America, in other countries in which we have concentrate plants, or in any of the major markets in which our Company-owned or controlled bottlers operate that may be caused by increasing demand or by events such as natural disasters, power outages or the like would increase our operating costs and negatively impact our profitability.
Our bottling partners also operate large fleets of trucks and other motor vehicles to distribute and deliver beverage products to their own customers and use a significant amount of electricity, natural gas and other energy sources to operate their own bottling plants and distribution facilities. Increases in the price, disruption of supply or shortage of fuel and other energy sources in any of the major markets in which our bottling partners operate would increase the affected bottling partners' operating costs and could indirectly negatively impact our results of operations.
Increase in the cost, disruption of supply or shortage of ingredients, other raw materials or packaging materials could harm our business.
We and our bottling partners use various ingredients in our business, including HFCS, sucrose, aspartame, saccharin, acesulfame potassium, sucralose, ascorbic acid, citric acid, phosphoric acid and caramel color, other raw materials such as orange and other citrus fruit juice and juice concentrates, as well as packaging materials such as PET for bottles and aluminum for cans. The prices for these ingredients, other raw materials and packaging materials fluctuate depending on market conditions. Substantial increases in the prices of our or our bottling partners' ingredients, other raw materials and packaging materials, to the extent they cannot be recouped through increases in the prices of finished beverage products, would increase our and the Coca-Cola system's operating costs and could reduce our profitability. Increases in the prices of our finished products resulting from a higher cost of ingredients, other raw materials and packaging materials could affect affordability in some markets and reduce Coca-Cola system sales. In addition, some of our ingredients, such as aspartame, acesulfame potassium, sucralose, saccharin and ascorbic acid, as well as some of the packaging containers, such as aluminum cans, are available from a limited number of suppliers, some of which are located in countries experiencing political or other risks. We cannot assure you that we and our bottling partners will be able to maintain favorable arrangements and relationships with these suppliers.
The citrus industry is subject to the variability of weather conditions, which affect the supply of orange juice and orange juice concentrate, which are important raw materials for our business. In particular, freezing weather or hurricanes in central Florida may result in shortages and higher prices for orange juice and orange juice concentrate throughout the industry. In addition, in December 2011, we learned that orange juice from Brazil contained residues of carbendazim, a fungicide that is not registered in the U.S. for use on food products. The Company uses Brazilian orange juice and orange juice concentrate to make various orange juice products for distribution in the U.S. under the Simply Orange and Minute Maid brands. The Company disclosed to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (the "FDA") that carbendazim had been detected in orange juice from Brazil. The Company also informed the FDA that orange juice and orange juice concentrate from all or most suppliers in Brazil contained the prohibited residues. The FDA subsequently issued a letter stating that carbendazim at the low levels reported as present in finished orange juice products in the U.S. "does not raise safety concerns." In addition, however, the FDA stated that it "will deny entry into the U.S. to shipments [of orange juice] that test positive for carbendazim." Because the FDA will refuse admission of orange juice and orange juice concentrate containing carbendazim, the supply of orange juice and orange juice concentrate from Brazil and other exporting countries to the U.S. will be reduced in 2012 and may be negatively affected beyond 2012. This has required us to make additional purchases of Florida juice at a higher cost than Brazilian juice. Depending on consumer demand, additional purchases of Florida juice may be necessary in the future.
An increase in the cost, a sustained interruption in the supply, or a shortage of some of these ingredients, other raw materials, packaging materials or cans and other containers that may be caused by a deterioration of our or our bottling partners' relationships with suppliers; by supplier quality and reliability issues; or by events such as natural disasters, power outages, labor strikes, political uncertainties or governmental instability, or the like, could negatively impact our net revenues and profits. Because manufacturing and bottling operations are heavy users of ingredients and packaging materials, our Company's direct exposure to the risk of an increase in the cost, disruption of supply or shortage of ingredients or packaging materials has increased as a result of our acquisition of CCE's North American business.
15
Changes in laws and regulations relating to beverage containers and packaging could increase our costs and reduce demand for our products.
We and our bottlers currently offer nonrefillable, recyclable containers in the United States and in various other markets around the world. Legal requirements have been enacted in various jurisdictions in the United States and overseas requiring that deposits or certain ecotaxes or fees be charged for the sale, marketing and use of certain nonrefillable beverage containers. Other proposals relating to beverage container deposits, recycling, ecotax and/or product stewardship have been introduced in various jurisdictions in the United States and overseas, and we anticipate that similar legislation or regulations may be proposed in the future at local, state and federal levels, both in the United States and elsewhere. Consumers' increased concerns and changing attitudes about solid waste streams and environmental responsibility and related publicity could result in the adoption of such legislation or regulations. If these types of requirements are adopted and implemented on a large scale in any of the major markets in which we operate, they could affect our costs or require changes in our distribution model, which could reduce our net operating revenues or profitability.
Significant additional labeling or warning requirements may inhibit sales of affected products.
Various jurisdictions may seek to adopt significant additional product labeling or warning requirements relating to the content or perceived adverse health consequences of certain of our products. If these types of requirements become applicable to one or more of our major products under current or future environmental or health laws or regulations, they may inhibit sales of such products. One such law, which is in effect in California and is known as Proposition 65, requires that a warning appear on any product sold in California that contains a substance that, in the view of the state, causes cancer or birth defects. The state maintains lists of these substances and periodically adds other substances to these lists. Proposition 65 exposes all food and beverage producers to the possibility of having to provide warnings on their products in California because it does not provide for any generally applicable quantitative threshold below which the presence of a listed substance is exempt from the warning requirement. Consequently, the detection of even a trace amount of a listed substance can subject an affected product to the requirement of a warning label. However, Proposition 65 does not require a warning if the manufacturer of a product can demonstrate that the use of the product in question exposes consumers to a daily quantity of a listed substance that is below a "safe harbor" threshold that may be established, is naturally occurring, is the result of necessary cooking, or is subject to another applicable exception. One or more substances that are currently on the Proposition 65 lists, or that may be added to the lists in the future, can be detected in Company products at low levels that are safe. With respect to substances that have not yet been listed under Proposition 65, the Company takes the position that listing is not scientifically justified. With respect to substances that are already listed, the Company takes the position that the presence of each such substance in Company products is subject to an applicable exemption from the warning requirement. The State of California or other parties, however, may take a contrary position. If we were required to add Proposition 65 warnings on the labels of one or more of our beverage products produced for sale in California, the resulting consumer reaction to the warnings and possible adverse publicity could negatively affect our sales both in California and in other markets.
Unfavorable general economic conditions in the United States or in other major markets could negatively impact our financial performance.
Unfavorable general economic conditions, such as a recession or economic slowdown in the United States or in one or more of our other major markets, could negatively affect the affordability of, and consumer demand for, some of our beverages. Under difficult economic conditions, consumers may seek to reduce discretionary spending by forgoing purchases of our products or by shifting away from our beverages to lower-priced products offered by other companies, including private label brands. Softer consumer demand for our beverages in the United States or in other major markets could reduce the Coca-Cola system's profitability and could negatively affect our financial performance.
Unfavorable economic and political conditions in international markets could hurt our business.
We derive a significant portion of our net operating revenues from sales of our products in international markets. In 2011, our operations outside the United States accounted for $27.8 billion of our net operating revenues. Unfavorable economic and political conditions, including civil unrest and governmental changes, in certain of our international markets, as well as the financial uncertainties in the euro zone, could undermine consumer confidence and reduce consumers' purchasing power, thereby reducing demand for our products. In addition, product boycotts resulting from political activism could reduce demand for our products, while restrictions on our ability to transfer earnings or capital across borders which may be imposed or expanded as a result of political and economic instability could impact our profitability. Without limiting the generality of the preceding sentences, the unfavorable business environment in Venezuela; the current unstable economic and political conditions and civil unrest and political activism in the Middle East, India, Pakistan or the Philippines; the civil unrest and instability in Egypt and other countries in North Africa; the unstable situation in Iraq; or the continuation or escalation of terrorist activities could adversely impact our international business.
16
Litigation or legal proceedings could expose us to significant liabilities and damage our reputation.
We are party to various litigation claims and legal proceedings. We evaluate these litigation claims and legal proceedings to assess the likelihood of unfavorable outcomes and to estimate, if possible, the amount of potential losses. Based on these assessments and estimates, we establish reserves and/or disclose the relevant litigation claims or legal proceedings, as appropriate. These assessments and estimates are based on the information available to management at the time and involve a significant amount of management judgment. We caution you that actual outcomes or losses may differ materially from those envisioned by our current assessments and estimates. In addition, we have bottling and other business operations in markets with high-risk legal compliance environments. Our policies and procedures require strict compliance by our associates and agents with all United States and local laws and regulations and consent orders applicable to our business operations, including those prohibiting improper payments to government officials. Nonetheless, we cannot assure you that our policies, procedures and related training programs will always ensure full compliance by our associates and agents with all applicable legal requirements. Improper conduct by our associates or agents could damage our reputation in the United States and internationally or lead to litigation or legal proceedings that could result in civil or criminal penalties, including substantial monetary fines, as well as disgorgement of profits.
Adverse weather conditions could reduce the demand for our products.
The sales of our products are influenced to some extent by weather conditions in the markets in which we operate. Unusually cold or rainy weather during the summer months may have a temporary effect on the demand for our products and contribute to lower sales, which could have an adverse effect on our results of operations for such periods.
If product safety or quality issues, or negative publicity, even if unwarranted, damage our brand image and corporate reputation, our business may suffer.
Our success depends on our ability to maintain consumer confidence in the safety and quality of our products. Our success also depends on our ability to maintain the brand image of our existing products, build up brand image for new products and brand extensions, and maintain our corporate reputation. We cannot assure you, however, that our commitment to product safety and quality and our continuing investment in advertising and marketing will have the desired impact on our products' brand image and on consumer preferences. Product safety or quality issues, actual or perceived, or allegations of product contamination, even when false or unfounded, could tarnish the image of the affected brands and may cause consumers to choose other products. Allegations of product safety or quality issues or contamination, even if untrue, may require us from time to time to recall a beverage or other product from all of the markets in which the affected production was distributed. Such issues or recalls could negatively affect our profitability and brand image. In some emerging markets, the production and sale of counterfeit or "spurious" products, which we and our bottling partners may not be able to fully combat, may damage the image and reputation of our products. In addition, campaigns by activists attempting to connect us or our bottling system with human and workplace rights issues in certain emerging markets could adversely impact our corporate image and reputation. For example, in June 2011, the United Nations Human Rights Council endorsed the Guiding Principles for Business and Human Rights, which outlines how businesses should implement the corporate responsibility to respect human rights principles included in the UN "Protect, Respect and Remedy" framework on human rights. Through our Human Rights Statement and Workplace Rights Policy and Supplier Guiding Principles, and our participation in the United Nations Global Compact and its LEAD program, as well as our active participation in the Global Business Initiative on Human Rights, we have made a number of commitments to respect all human rights. Allegations that we are not respecting any of the 30 human rights found in the United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights, even if untrue, could have a significant impact on our corporate reputation and long-term financial results. Also, adverse publicity surrounding obesity and health concerns related to our products, water usage, environmental concerns, labor relations and the like, could negatively affect our Company's overall reputation and our products' acceptance by consumers.
Changes in, or failure to comply with, the laws and regulations applicable to our products or our business operations could increase our costs or reduce our net operating revenues.
Our Company's business is subject to various laws and regulations in the numerous countries throughout the world in which we do business, including laws and regulations relating to competition, product safety, advertising and labeling, container deposits, recycling or stewardship, the protection of the environment, and employment and labor practices. In the United States, the production, distribution and sale of many of our products are subject to, among others, the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, the Federal Trade Commission Act, the Lanham Act, state consumer protection laws, the Occupational Safety and Health Act, and various environmental statutes, as well as various state and local statutes and regulations. Outside the United States, the production, distribution, sale, advertising and labeling of many of our products are also subject to various laws and regulations. Changes in applicable laws or regulations or evolving interpretations thereof, including increased government regulations to limit carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gas emissions as a result of concern over climate change or to limit or
17
eliminate the use of bisphenol-A, or BPA (an odorless, tasteless food-grade chemical commonly used in the food and beverage industries as a component in the coating of the interior of cans), may result in increased compliance costs, capital expenditures and other financial obligations for us and our bottling partners, which could affect our profitability or impede the production or distribution of our products, which could affect our net operating revenues. In addition, failure to comply with environmental, health or safety requirements and other applicable laws or regulations could result in the assessment of damages, the imposition of penalties, suspension of production, changes to equipment or processes, or a cessation of operations at our or our bottling partners' facilities, as well as damage to our and the Coca-Cola system's image and reputation, all of which could harm our and the Coca-Cola system's profitability.
Changes in accounting standards could affect our reported financial results.
New accounting standards or pronouncements that may become applicable to our Company from time to time, or changes in the interpretation of existing standards and pronouncements, could have a significant effect on our reported results for the affected periods.
If we are not able to achieve our overall long-term goals, the value of an investment in our Company could be negatively affected.
We have established and publicly announced certain long-term growth objectives. These objectives were based on our evaluation of our growth prospects, which are generally based on volume and sales potential of many product types, some of which are more profitable than others, and on an assessment of the potential price and product mix. There can be no assurance that we will achieve the required volume or revenue growth or the mix of products necessary to achieve our long-term growth objectives.
If we are unable to realize the significant benefits from our productivity and reinvestment program, our financial results could be negatively affected.
We believe that productivity gains are essential to achieving our long-term growth objectives and, therefore, a leading priority of our Company is to design and implement the most effective and efficient business system possible. As part of our efforts to become more efficient, leaner and adaptive to changing market conditions, we recently announced a productivity and reinvestment program consisting of (i) a new productivity initiative focused on global supply chain optimization, global marketing and innovation effectiveness, operating expense leverage, operational excellence and data and information technology systems standardization; and (ii) an expansion of our initiative to capture CCR integration synergies in North America, focused primarily on our North American product supply. We expect to incur significant costs to capture these savings and additional synergies. We intend to invest the savings generated by this program to enhance ongoing systemwide brand-building initiatives and also to mitigate potential incremental near-term commodity costs. If we are unable to successfully implement our productivity and reinvestment program, or if we are unable to capture the anticipated savings and additional synergies, our financial results could be negatively affected.
If we are unable to protect our information systems against service interruption, misappropriation of data or breaches of security, our operations could be disrupted and our reputation may be damaged.
We rely on networks and information systems and other technology ("information systems"), including the Internet and third-party hosted services, to support a variety of business processes and activities, including procurement and supply chain, manufacturing, distribution, invoicing and collection of payments. We use information systems to process financial information and results of operations for internal reporting purposes and to comply with regulatory financial reporting, legal and tax requirements. In addition, we depend on information systems for digital marketing activities and electronic communications among our locations around the world and between Company personnel and our bottlers and other customers, suppliers and consumers. Because information systems are critical to many of the Company's operating activities, our business processes may be impacted by system shutdowns or service disruptions. These disruptions may be caused by failures during routine operations such as system upgrades or user errors, as well as network or hardware failures, malicious or disruptive software, computer hackers, geopolitical events, natural disasters, failures or impairments of telecommunications networks, or other catastrophic events. In addition, such events could result in unauthorized disclosure of confidential information. If our information systems suffer severe damage, disruption or shutdown and our business continuity plans do not effectively resolve the issues in a timely manner, we could experience delays in reporting our financial results and we may lose revenue and profits as a result of our inability to timely manufacture, distribute, invoice and collect payments for concentrate or finished products. Misuse, leakage or falsification of information could result in a violation of data privacy laws and regulations and damage the reputation and credibility of the Company and have a negative impact on net operating revenues. In addition, we may suffer financial and reputational damage because of lost or misappropriated confidential information belonging to us or to our bottling partners, other customers, suppliers or consumers. The Company could also be required to spend significant financial and other
18
resources to remedy the damage caused by a security breach or to repair or replace networks and information systems.
Like most major corporations, the Company's information systems are a target of attacks. In order to address potential risks to our information systems, we continue to make investments in personnel, technologies, cyberinsurance, training of Company personnel, bottlers and third parties. The Company maintains an information risk management program which is supervised by information technology management and reviewed by a cross-functional committee. As part of this program, reports which include analysis of emerging risks as well as the Company's plans and strategies to address them are regularly prepared and presented to senior management.
We may be required to recognize additional impairment charges which could materially affect our financial results.
We assess our goodwill, trademarks and other intangible assets as well as our other long-lived assets as and when required by accounting principles generally accepted in the United States to determine whether they are impaired and, if they are, we record appropriate impairment charges. Our equity method investees also perform impairment tests, and we record our proportionate share of impairment charges recorded by them adjusted, as appropriate, for the impact of items such as basis differences, deferred taxes and deferred gains. It is possible that we may be required to record significant impairment charges or our proportionate share of significant charges recorded by equity method investees in the future and, if we do so, our operating or equity income could be materially adversely affected.
If we do not successfully integrate and manage our Company-owned or controlled bottling operations, our results could suffer.
From time to time we acquire or take control of bottling operations, often in underperforming markets where we believe we can use our resources and expertise to improve performance. We may incur unforeseen liabilities and obligations in connection with acquiring, taking control of or managing bottling operations and may encounter unexpected difficulties and costs in restructuring and integrating them into our Company's operating and internal control structures. We may also experience delays in extending our Company's internal control over financial reporting to newly acquired or controlled bottling operations, which may increase the risk of failure to prevent misstatements in such operations' financial records and in our consolidated financial statements. In 2011, net operating revenues generated by our Bottling Investments group (which includes Company-owned or controlled bottling operations other than those managed by CCR) represented approximately 18 percent of our Company's consolidated net operating revenues. Our financial performance depends in large part on how well we can manage and improve the performance of Company-owned or controlled bottling operations. We cannot assure you, however, that we will be able to achieve our strategic and financial objectives for such bottling operations. If we are unable to achieve such objectives, our consolidated results could be negatively affected.
Climate change may negatively affect our business.
There is increasing concern that a gradual increase in global average temperatures due to increased concentration of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere will cause significant changes in weather patterns around the globe and an increase in the frequency and severity of natural disasters. Decreased agricultural productivity in certain regions as a result of changing weather patterns may limit availability or increase the cost of key agricultural commodities, such as sugarcane, corn, beets, citrus, coffee and tea, which are important ingredients for our products. Increased frequency or duration of extreme weather conditions could also impair production capabilities, disrupt our supply chain or impact demand for our products. Climate change may also exacerbate water scarcity and cause a further deterioration of water quality in affected regions, which could limit water availability for our system's bottling operations. As a result, the effects of climate change could have a long-term adverse impact on our business and results of operations.
Global or regional catastrophic events could impact our operations and financial results.
Because of our global presence and worldwide operations, our business can be affected by large-scale terrorist acts, especially those directed against the United States or other major industrialized countries; the outbreak or escalation of armed hostilities; major natural disasters; or widespread outbreaks of infectious diseases. Such events could impair our ability to manage our business around the world, could disrupt our supply of raw materials and ingredients, and could impact production, transportation and delivery of concentrates, syrups and finished products. In addition, such events could cause disruption of regional or global economic activity, which can affect consumers' purchasing power in the affected areas and, therefore, reduce demand for our products.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
Not applicable.
19
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
Our worldwide headquarters is located on a 35-acre office complex in Atlanta, Georgia. The complex includes the approximately 621,000 square foot headquarters building and an approximately 870,000 square foot building in which CCNA's and CCR's main offices are located. The complex also includes several other buildings, including the approximately 264,000 square foot Coca-Cola Plaza building, technical and engineering facilities, a learning center and a reception center. We also own an office and retail building at 711 Fifth Avenue in New York, New York. These properties are primarily included in the Corporate operating segment.
We own or lease additional facilities, real estate and office space throughout the world which we use for administrative, manufacturing, processing, packaging, packing, storage, warehousing, distribution and retail operations. These properties are generally included in the geographic operating segment in which they are located.
In North America, as of December 31, 2011, we owned 69 beverage production facilities, 10 principal beverage concentrate and/or syrup manufacturing plants, one facility that manufactures juice concentrates for foodservice use and two bottled water facilities; we leased one bottled water facility, one beverage production facility and six container manufacturing facilities; and we operated 287 principal beverage distribution warehouses, of which 104 were leased and the rest were owned. Also included in the North America operating segment is a portion of the Atlanta office complex.
Additionally, as of December 31, 2011, our Company owned and operated 20 principal beverage concentrate manufacturing plants outside of North America, of which four are included in the Eurasia and Africa operating segment; three are included in the Europe operating segment; five are included in the Latin America operating segment; and eight are included in the Pacific operating segment.
We own or hold a majority interest in or otherwise consolidate under applicable accounting rules bottling operations that, as of December 31, 2011, owned 97 principal beverage bottling and canning plants located throughout the world. These plants are included in the Bottling Investments operating segment.
Management believes that our Company's facilities for the production of our products are suitable and adequate, that they are being appropriately utilized in line with past experience, and that they have sufficient production capacity for their present intended purposes. The extent of utilization of such facilities varies based upon seasonal demand for our products. However, management believes that additional production can be obtained at the existing facilities by adding personnel and capital equipment and, at some facilities, by adding shifts of personnel or expanding the facilities. We continuously review our anticipated requirements for facilities and, on the basis of that review, may from time to time acquire additional facilities and/or dispose of existing facilities.
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
The Company is involved in various legal proceedings, including the proceedings specifically discussed below. Management believes that the total liabilities to the Company that may arise as a result of currently pending legal proceedings will not have a material adverse effect on the Company taken as a whole.
Aqua-Chem Litigation
On December 20, 2002, the Company filed a lawsuit (The Coca-Cola Company v. Aqua-Chem, Inc., Civil Action No. 2002CV631-50) in the Superior Court of Fulton County, Georgia (the "Georgia Case"), seeking a declaratory judgment that the Company has no obligation to its former subsidiary, Aqua-Chem, Inc., now known as Cleaver-Brooks, Inc. ("Aqua-Chem"), for any past, present or future liabilities or expenses in connection with any claims or lawsuits against Aqua-Chem. Subsequent to the Company's filing but on the same day, Aqua-Chem filed a lawsuit (Aqua-Chem, Inc. v. The Coca-Cola Company, Civil Action No. 02CV012179) in the Circuit Court, Civil Division of Milwaukee County, Wisconsin (the "Wisconsin Case"). In the Wisconsin Case, Aqua-Chem sought a declaratory judgment that the Company is responsible for all liabilities and expenses not covered by insurance in connection with certain of Aqua-Chem's general and product liability claims arising from occurrences prior to the Company's sale of Aqua-Chem in 1981, and a judgment for breach of contract in an amount exceeding $9 million for costs incurred by Aqua-Chem to date in connection with such claims. The Wisconsin Case initially was stayed, pending final resolution of the Georgia Case, and later was voluntarily dismissed without prejudice by Aqua-Chem.
The Company owned Aqua-Chem from 1970 to 1981. During that time, the Company purchased over $400 million of insurance coverage, which also insures Aqua-Chem for some of its prior and future costs for certain product liability and other claims. The Company sold Aqua-Chem to Lyonnaise American Holding, Inc., in 1981 under the terms of a stock sale agreement. The 1981 agreement, and a subsequent 1983 settlement agreement, outlined the parties' rights and obligations concerning past and future claims and lawsuits involving Aqua-Chem. Cleaver-Brooks, a division of Aqua-Chem, manufactured boilers, some of which contained asbestos gaskets. Aqua-Chem was first named as a defendant in asbestos lawsuits in or around 1985 and
20
currently has approximately 40,000 active claims pending against it.
The parties agreed in 2004 to stay the Georgia Case pending the outcome of insurance coverage litigation filed by certain Aqua-Chem insurers on March 26, 2004. In the coverage action, five plaintiff insurance companies filed suit (Century Indemnity Company, et al. v. Aqua-Chem, Inc., The Coca-Cola Company, et al., Case No. 04CV002852) in the Circuit Court, Civil Division of Milwaukee County, Wisconsin, against the Company, Aqua-Chem and 16 insurance companies. Several of the policies that were the subject of the coverage action had been issued to the Company during the period (1970 to 1981) when the Company owned Aqua-Chem. The complaint sought a determination of the respective rights and obligations under the insurance policies issued with regard to asbestos-related claims against Aqua-Chem. The action also sought a monetary judgment reimbursing any amounts paid by the plaintiffs in excess of their obligations. Two of the insurers, one with a $15 million policy limit and one with a $25 million policy limit, asserted cross-claims against the Company, alleging that the Company and/or its insurers are responsible for Aqua-Chem's asbestos liabilities before any obligation is triggered on the part of the cross-claimant insurers to pay for such costs under their policies.
Aqua-Chem and the Company filed and obtained a partial summary judgment determination in the coverage action that the insurers for Aqua-Chem and the Company were jointly and severally liable for coverage amounts, but reserving judgment on other defenses that might apply. During the course of the Wisconsin insurance coverage litigation, Aqua-Chem and the Company reached settlements with several of the insurers, including plaintiffs, who have paid or will pay funds into an escrow account for payment of costs arising from the asbestos claims against Aqua-Chem. On July 24, 2007, the Wisconsin trial court entered a final declaratory judgment regarding the rights and obligations of the parties under the insurance policies issued by the remaining defendant insurers, which judgment was not appealed. The judgment directs, among other things, that each insurer whose policy is triggered is jointly and severally liable for 100 percent of Aqua-Chem's losses up to policy limits. The court's judgment concluded the Wisconsin insurance coverage litigation.
The Company and Aqua-Chem continued to pursue and obtain coverage agreements for the asbestos-related claims against Aqua-Chem with those insurance companies that did not settle in the Wisconsin insurance coverage litigation. The Company anticipated that a final settlement with three of those insurers would be finalized in May 2011, but such insurers repudiated their settlement commitments and, as a result, Aqua-Chem and the Company filed suit against them in Wisconsin state court to enforce the coverage-in-place settlement or, in the alternative, to obtain a declaratory judgment validating Aqua-Chem and the Company's interpretation of the court's judgment in the Wisconsin coverage litigation. Whether or not Aqua-Chem and the Company prevail in the coverage-in-place settlement litigation, these three insurance companies will remain subject to the court's judgment in the Wisconsin insurance coverage litigation.
The Georgia Case remains subject to the stay agreed to in 2004.
Chapman
On June 30, 2005, Maryann Chapman filed a purported shareholder derivative action (Chapman v. Isdell, et al.) in the Superior Court of Fulton County, Georgia, alleging violations of state law by certain individual current and former members of the Board of Directors of the Company and senior management, including breaches of fiduciary duties, abuse of control, gross mismanagement, waste of corporate assets and unjust enrichment, between January 2003 and the date of filing of the complaint that have caused substantial losses to the Company and other damages, such as to its reputation and goodwill. The defendants named in the lawsuit include Neville Isdell, Douglas Daft, Gary Fayard, Ronald Allen, Cathleen Black, Warren Buffett, Herbert Allen, Barry Diller, Donald McHenry, Sam Nunn, James Robinson, Peter Ueberroth, James Williams, Donald Keough, Maria Lagomasino, Pedro Reinhard, Robert Nardelli and Susan Bennett King. The Company is also named a nominal defendant. The complaint further alleges that the September 2004 earnings warning issued by the Company resulted from factors known by the individual defendants as early as January 2003 that were not adequately disclosed to the investing public until the earnings warning. The factors cited in the complaint include (i) a flawed business strategy and a business model that was not working; (ii) a workforce so depleted by layoffs that it was unable to properly react to changing market conditions; (iii) impaired relationships with key bottlers; and (iv) the fact that the foregoing conditions would lead to diminished earnings. The plaintiff, purportedly on behalf of the Company, seeks damages in an unspecified amount, extraordinary equitable and/or injunctive relief, restitution and disgorgement of profits, reimbursement for costs and disbursements of the action, and such other and further relief as the Court deems just and proper. The Company's motion to dismiss the complaint and the plaintiff's response were filed and fully briefed. The Court heard oral argument on the Company's motion to dismiss on June 6, 2006. Following the hearing, the Court took the matter under advisement and the parties are awaiting a ruling. There were no material developments in this case during 2011.
The Company intends to vigorously defend its interests in this matter.
21
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
ITEM X. EXECUTIVE OFFICERS OF THE COMPANY
The following are the executive officers of our Company as of February 22, 2012:
Harry L. Anderson, 49, is Senior Vice President, Global Business and Technology Services of the Company. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Anderson served as Executive Vice President, Finance and Operations, Turner Entertainment Group; Executive Vice President, Finance and Administration, Turner Sales and Distribution Group; and Vice President and Group Controller, Turner Sales and Distribution Group. Before joining Turner Broadcasting, Mr. Anderson was with Price Waterhouse in Audit and Accounting Services. Mr. Anderson joined the Company in 2001 as Senior Vice President, Coca-Cola Ventures. In 2002, he was named Director of Supply Chain and Manufacturing Management. Mr. Anderson served as Chief Financial Officer of Coca-Cola North America from 2004 until 2007. In 2007, he was appointed Vice President and Controller of the Company and served in that capacity until August 2009. In June 2009, Mr. Anderson was named to lead the newly formed Global Business and Technology Services organization, effective July 1, 2009. In July 2009, he was elected Senior Vice President of the Company.
Ahmet C. Bozer, 51, is President of the Eurasia and Africa Group. Mr. Bozer joined the Company in 1990 as a Financial Control Manager for Coca-Cola USA and held a number of other roles in the finance organization. In 1992, he became the Region Finance Manager for Coca-Cola Turkey. In 1994, he joined Coca-Cola Bottlers of Turkey (now Coca-Cola Icecek A.S.) as Finance Director and was named Managing Director in 1998. In 2000, Mr. Bozer rejoined the Company as President of the Eurasia Division, which became Eurasia and Middle East Division in 2003, covering 36 countries and including the Adriatic and Balkans Region. In 2006, Mr Bozer assumed the additional leadership responsibility for the Russia, Ukraine and Belarus Division. Effective January 1, 2007, with the addition of the India and South West Asia Division under his responsibilities, Mr. Bozer was named President of the Eurasia Group. Effective July 1, 2008, Mr. Bozer became President of the Eurasia and Africa Group.
Steven A. Cahillane, 46, is President and Chief Executive Officer of Coca-Cola Refreshments, the Company's bottling and customer service organization for North America. Prior to joining the Company, from August 2003 until August 2005, Mr. Cahillane served as the Chief Executive for Interbrew UK and Ireland, a division of InBev S.A. In August 2005, he became Chief Commercial Officer of InBev S.A. and served in that capacity until August 2007. In October 2007, Mr. Cahillane joined CCE and served as President of CCE's Europe Group until July 2008 and then as President of the North America Business Unit of CCE from July 2008 until October 2010. Mr. Cahillane was appointed to his current position effective October 2, 2010.
Alexander B. Cummings, Jr., 55, is Executive Vice President and Chief Administrative Officer of the Company. Mr. Cummings began his career in 1982 with The Pillsbury Company and held various positions within Pillsbury, the last position being Vice President of Finance and Chief Financial Officer for all of Pillsbury's international businesses. Mr. Cummings joined the Company in 1997 as Deputy Region Manager, Nigeria, based in Lagos, Nigeria. In 1998, Mr. Cummings was named Managing Director/Region Manager, Nigeria, and in 2000, he became President of the North West Africa Division based in Morocco. In March 2001, Mr. Cummings became President of the Africa Group overseeing the Company's business in the entire African continent, and served in this capacity until June 2008. Mr. Cummings was appointed Chief Administrative Officer of the Company effective July 1, 2008, and was elected Executive Vice President of the Company effective October 15, 2008.
J. Alexander M. Douglas, Jr., 50, is President of the North America Group. Mr. Douglas joined the Company in January 1988 as a District Sales Manager for the Foodservice Division of Coca-Cola USA. In May 1994, he was named Vice President of Coca-Cola USA, initially assuming leadership of the CCE Sales and Marketing Group and eventually assuming leadership of the entire North American Field Sales and Marketing Groups. In January 2000, Mr. Douglas was appointed President of the North American Division within the North America Group. He served as Senior Vice President and Chief Customer Officer of the Company from February 2003 until August 2006 and continued serving as Senior Vice President until April 2007. Mr. Douglas was appointed President of the North America Group in August 2006.
Ceree Eberly, 49, is Senior Vice President and Chief People Officer of the Company, with responsibility for leading the Company's global People Function (formerly Human Resources). Ms. Eberly joined the Company in February 1990, serving in staffing, compensation and other roles supporting the Company's business units around the world. From October 1998 until January 2003, she served as Human Resources Director for the Latin Center Business Unit. From February 2003 until June 2007, Ms. Eberly served as Vice President of the McDonald's Division. She was appointed Group Human Resources Director for Europe in July 2007 and served in that capacity until she was appointed Chief People Officer effective December 1, 2009. Ms. Eberly was elected Senior Vice President of the Company effective April 1, 2010.
22
Gary P. Fayard, 59, is Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of the Company. Mr. Fayard joined the Company in April 1994. In July 1994, he was elected Vice President and Controller. In December 1999, he was elected Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer. Mr. Fayard was elected Executive Vice President of the Company in February 2003.
Irial Finan, 54, is Executive Vice President of the Company and President, Bottling Investments and Supply Chain. Mr. Finan joined the Coca-Cola system in 1981 with Coca-Cola Bottlers Ireland, Ltd., where for several years he held a variety of accounting positions. From 1987 until 1990, Mr. Finan served as Finance Director of Coca-Cola Bottlers Ireland, Ltd. From 1991 to 1993, he served as Managing Director of Coca-Cola Bottlers Ulster, Ltd. He was Managing Director of Coca-Cola bottlers in Romania and Bulgaria until late 1994. From 1995 to 1999, he served as Managing Director of Molino Beverages, with responsibility for expanding markets, including the Republic of Ireland, Northern Ireland, Romania, Moldova, Russia and Nigeria. Mr. Finan served from May 2001 until 2003 as Chief Executive Officer of Coca-Cola Hellenic. Mr. Finan joined the Company and was named President, Bottling Investments in August 2004. He was elected Executive Vice President of the Company in October 2004.
Bernhard Goepelt, 49, is Senior Vice President, General Counsel and Chief Legal Counsel of the Company. Mr. Goepelt joined the Company in 1992 as Legal Counsel for the German Division. In 1997, he was appointed Legal Counsel for the Middle and Far East Group and in 1999 was promoted to Division Counsel, Southeast and West Asia Division, based in Thailand. In January 2003, Mr. Goepelt was appointed Group Counsel for the Central Europe, Eurasia and Middle East Group. In 2005, he assumed the position of General Counsel for Japan and China and in 2007 Mr. Goepelt was appointed General Counsel, Pacific Group. In April 2010, he moved to Atlanta to become Associate General Counsel, Global Marketing, Commercial Leadership & Strategy. In September 2010, Mr. Goepelt took on the additional responsibility of General Counsel for the Pacific Group. In addition to his functional responsibilities, he also managed the administration of the Legal Division. Mr. Goepelt was elected Senior Vice President, General Counsel and Chief Legal Counsel of the Company in December 2011.
Glenn G. Jordan S., 55, is President of the Pacific Group. Mr. Jordan joined the Company in 1978 as a field representative for Coca-Cola de Colombia where, for several years, he held various positions, including Region Manager from 1985 to 1989. Mr. Jordan served as Marketing Operations Manager, Pacific Group from 1989 to 1990 and as Vice President of Coca-Cola International and Executive Assistant to the Pacific Group President from 1990 to 1991. Mr. Jordan served as Senior Vice President, Marketing and Operations, for the Brazil Division from 1991 to 1995; as President of the River Plate Division, which comprised Argentina, Uruguay and Paraguay, from 1995 to 2000; and as President of the South Latin America Division, comprising Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Ecuador, Paraguay, Peru and Uruguay, from 2000 to 2003. In February 2003, Mr. Jordan was appointed Executive Vice President and Director of Operations for the Latin America Group and served in that capacity until February 2006. Mr. Jordan was appointed President of the East, South Asia and Pacific Rim Group in February 2006. The East, South Asia and Pacific Rim Group was reconfigured and renamed the Pacific Group, effective January 1, 2007.
Geoffrey J. Kelly, 67, served as General Counsel of the Company until December 2011 and will continue to serve as Senior Vice President until his retirement in February 2012. Mr. Kelly joined the Company in 1970 in Australia as manager of the Legal Department for the Australasia Area. From 1970 until 2000, Mr. Kelly held a number of key roles, including Senior Counsel for the Pacific Group and subsequently for the Middle and Far East Group. In 2000, Mr. Kelly was appointed Senior Counsel for International Operations. He became Chief Deputy General Counsel in 2003 and was elected Senior Vice President of the Company in February 2004. In January 2005, he assumed the role of Acting General Counsel to the Company, and in July 2005, he was elected General Counsel of the Company.
Muhtar Kent, 59, is Chairman of the Board of Directors, Chief Executive Officer and President of the Company. Mr. Kent joined the Company in 1978 and held a variety of marketing and operations roles throughout his career with the Company. In 1985, he was appointed General Manager of Coca-Cola Turkey and Central Asia. From 1989 to 1995, Mr. Kent served as President of the East Central Europe Division and Senior Vice President of Coca-Cola International. Between 1995 and 1998, he served as Managing Director of Coca-Cola Amatil-Europe covering bottling operations in 12 countries, and from 1999 until 2005, he served as President and Chief Executive Officer of Efes Beverage Group, a diversified beverage company with Coca-Cola and beer operations across Southeast Europe, Turkey and Central Asia. Mr. Kent rejoined the Company in May 2005 as President and Chief Operating Officer, North Asia, Eurasia and Middle East Group, an organization serving a broad and diverse region that included China, Japan and Russia. He was appointed President, Coca-Cola International in January 2006 and was elected Executive Vice President of the Company in February 2006. He was elected President and Chief Operating Officer of the Company in December 2006 and was elected to the Board of Directors in April 2008. Mr. Kent was elected Chief Executive Officer of the Company effective July 1, 2008. Mr. Kent was elected Chairman of the Board of Directors of the Company in April 2009.
Dominique Reiniche, 56, is President of the Europe Group. Ms. Reiniche joined the Company in May 2005 as President of the European Union Group, which was reconfigured effective July 1, 2008, to include the Adriatic and Balkans Business Unit and renamed the Europe Group. Prior to joining the Company, Ms. Reiniche held a number of marketing, sales and general
23
management positions with CCE. From May 1998 until December 2002, she served as General Manager of France for CCE, and from January 2003 until May 2005, Ms. Reiniche was President of CCE Europe. Before joining the Coca-Cola system, she was Director of Marketing and Strategy with Kraft Jacobs-Suchard and Associate Advertising Manager at Procter & Gamble.
José Octavio Reyes, 59, is President of the Latin America Group. Mr. Reyes began his career with the Company in 1980 at Coca-Cola de México as Manager of Strategic Planning. In 1987, he was appointed Manager of the Sprite and Diet Coke brands at Corporate Headquarters. In 1990, he was appointed Marketing Director for the Brazil Division, and later became Marketing and Operations Vice President for the Mexico Division. Mr. Reyes assumed the role of Deputy Division President for the Mexico Division in January 1996 and was named Division President for the Mexico Division in May 1996. He assumed his position as President of the Latin America Group in December 2002.
Joseph V. Tripodi, 56, is Executive Vice President and Chief Marketing and Commercial Officer of the Company. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Tripodi served as Senior Vice President and Chief Marketing Officer for Allstate Insurance Co. Prior to joining Allstate in November 2003, Mr. Tripodi was Chief Marketing Officer for The Bank of New York. From 1999 until April 2002, he served as Chief Marketing Officer for Seagram Spirits & Wine Group. From 1989 to 1998, he was the Executive Vice President for Global Marketing, Products and Services for MasterCard International. Previously, Mr. Tripodi spent seven years with the Mobil Oil Corporation in roles of increasing responsibility in planning, marketing, business development and operations in New York, Paris, Hong Kong and Guam. Mr. Tripodi joined the Company as Chief Marketing and Commercial Officer effective September 2007 and was elected Senior Vice President of the Company in October 2007, a capacity in which he served until July 2009 when he was elected Executive Vice President of the Company.
Clyde C. Tuggle, 49, is Senior Vice President, Global Public Affairs and Communications Officer of the Company. Mr. Tuggle joined the Company in January 1989 in the Corporate Issues Communications Department. In June 1992, he was named Executive Assistant to Roberto C. Goizueta, then Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of the Company, where he managed external affairs and communications for the Office of the Chairman. In 1998, Mr. Tuggle transferred to the Company's Central European Division Office in Vienna where he held a variety of positions, including Director of Operations Development, Deputy to the Division President and Region Manager for Austria. In January 2000, Mr. Tuggle returned to Atlanta as Executive Assistant to then Chairman and Chief Executive Officer Douglas N. Daft and was elected Vice President of the Company. In February 2003, he was elected Senior Vice President of the Company and appointed Director of Worldwide Public Affairs and Communications. From 2005 until September 2008, Mr. Tuggle served as President of the Russia, Ukraine & Belarus Business Unit. In September 2008, he returned to Atlanta as Senior Vice President, Corporate Affairs and Productivity. In May 2009, Mr. Tuggle was named Senior Vice President, Global Public Affairs and Communications of the Company.
Jerry S. Wilson, 57, is Senior Vice President and Chief Customer and Commercial Officer of the Company. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Wilson held various positions in roles of increasing responsibility in distribution, district management, franchise leadership and brand management within Volkswagen of America from 1981 to 1988. Mr. Wilson joined the Company in 1988 as an Area Account Executive for the Foodservice Division of Coca-Cola USA. From 1990 to 1992, he served as Manager of Account Executives, and from 1992 to 1994, he served as Manager of Sales Development. Mr. Wilson was promoted to Director of Sales Operations in 1994 and later that year became Director of Strategic Marketing. In 1995, Mr. Wilson was named Director of Strategic Planning for Coca-Cola USA. In 1996, he was promoted to Vice President, Coca-Cola USA Foodservice, West Area, and in 1999, Mr. Wilson was named Vice President of the North America operations within the McDonald's Division. In April 2003, he was promoted to global Chief Operating Officer of the McDonald's Division, and in December 2005, Mr. Wilson was promoted to President of the global McDonald's Division and was elected Vice President of the Company. Mr. Wilson was elected Senior Vice President of the Company in October 2006 and was appointed global Chief Customer and Commercial Officer effective March 1, 2009.
Guy Wollaert, 52, is Senior Vice President and Chief Technical Officer of the Company. Mr. Wollaert joined the Company in 1992 in Brussels as a Project Manager and has held various positions of increasing responsibility in the technical and supply chain fields. From 1997 to 1999, he served as Technical Director for the Indonesia region based in Jakarta. In 1999, Mr. Wollaert relocated to Atlanta where he held the position of Value Chain Account Manager for the Asia Pacific region. In late 2000, he joined Coca-Cola Tea Products Co. Ltd. ("CCTPC"), a Company subsidiary based in Tokyo. Mr. Wollaert became President of CCTPC in January 2002. From 2003 to 2006, he was President of Coca-Cola National Beverages Ltd., a national supply management Company subsidiary that managed the Company's Japan supply business. In 2006, Mr. Wollaert returned to Atlanta as Vice President, Global Supply Chain Development, and from January 2008 until December 2010, he served as General Manager, Global Juice Center. Mr. Wollaert was appointed Chief Technical Officer effective January 1, 2011, and was elected Senior Vice President of the Company in February 2011.
All executive officers serve at the pleasure of the Board of Directors. There is no family relationship between any of the Directors or executive officers of the Company.
24
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT'S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
The principal United States market in which the Company's common stock is listed and traded is the New York Stock Exchange.
The following table sets forth, for the quarterly periods indicated, the high and low market prices per share for the Company's common stock, as reported on the New York Stock Exchange composite tape, and dividend per share information:
|
Common Stock
Market Prices
|
|||||||||||
High |
Low |
Dividends
Declared
|
|||||||||
2011 |
|||||||||||
Fourth quarter |
$ |
70.29 |
$ |
63.34 |
$ |
0.47 |
|||||
Third quarter |
71.77 |
63.59 |
0.47 |
||||||||
Second quarter |
68.77 |
64.43 |
0.47 |
||||||||
First quarter |
67.48 |
61.29 |
0.47 |
||||||||
2010 |
|||||||||||
Fourth quarter |
$ |
65.88 |
$ |
58.55 |
$ |
0.44 |
|||||
Third quarter |
59.24 |
50.02 |
0.44 |
||||||||
Second quarter |
55.56 |
49.47 |
0.44 |
||||||||
First quarter |
57.43 |
52.23 |
0.44 |
||||||||
While we have historically paid dividends to holders of our common stock on a quarterly basis, the declaration and payment of future dividends will depend on many factors, including, but not limited to, our earnings, financial condition, business development needs and regulatory considerations, and is at the discretion of our Board of Directors.
As of February 20, 2012, there were 250,275 shareowner accounts of record. This figure does not include a substantially greater number of "street name" holders or beneficial holders of our common stock, whose shares are held of record by banks, brokers and other financial institutions.
The information under the principal heading "EQUITY COMPENSATION PLAN INFORMATION" in the Company's definitive Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of Shareowners to be held on April 25, 2012, to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the "Company's 2012 Proxy Statement"), is incorporated herein by reference.
During the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011, no equity securities of the Company were sold by the Company that were not registered under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended.
25
The following table presents information with respect to purchases of common stock of the Company made during the three months ended December 31, 2011, by the Company or any "affiliated purchaser" of the Company as defined in Rule 10b-18(a)(3) under the Exchange Act.
Period |
Total Number of
Shares Purchased1
|
Average
Price Paid
Per Share
|
Total Number of
Shares Purchased
as Part of Publicly
Announced Plans
or Programs 2
|
Maximum Number of
Shares That May
Yet Be Purchased
Under the Publicly
Announced Plans
or Programs
|
||||||||
October 1, 2011 through October 28, 2011 |
1,370,988 |
$ |
66.42 |
1,350,000 |
93,759,148 |
|||||||
October 29, 2011 through November 25, 2011 |
3,926,672 |
67.33 |
3,800,000 |
89,959,148 |
||||||||
November 26, 2011 through December 31, 2011 |
8,244,042 |
67.83 |
7,979,076 |
81,980,072 |
||||||||
Total |
13,541,702 |
$ |
67.54 |
13,129,076 |
||||||||
1 |
The total number of shares purchased includes: (i) shares purchased pursuant to the 2006 Plan described in footnote 2 below and (ii) shares surrendered to the Company to pay the exercise price and/or to satisfy tax withholding obligations in connection with so-called stock swap exercises of employee stock options and/or the vesting of restricted stock issued to employees, totaling 20,988 shares, 126,672 shares and 264,966 shares for the fiscal months of October, November and December 2011, respectively. |
2 |
On July 20, 2006, we publicly announced that our Board of Directors had authorized a plan (the "2006 Plan") for the Company to purchase up to 300 million shares of our Company's common stock. This column discloses the number of shares purchased pursuant to the 2006 Plan during the indicated time periods. |
26
Performance Graph
Comparison of Five-Year Cumulative Total Return Among
The Coca-Cola Company, the Peer Group Index and the S&P 500 Index
Total Return
Stock Price Plus Reinvested Dividends
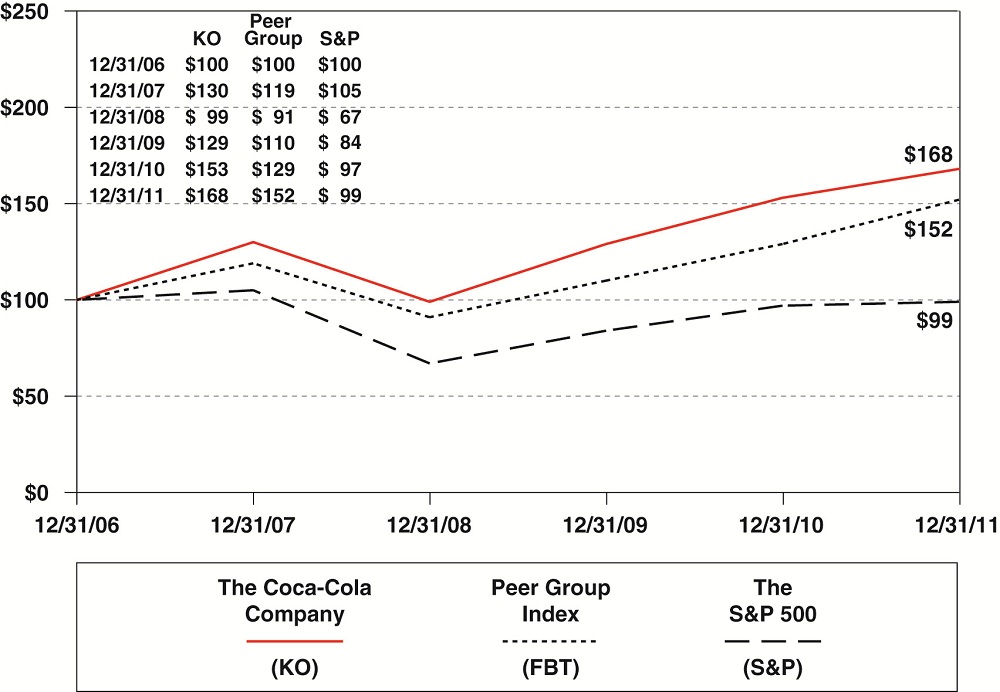
The total return assumes that dividends were reinvested quarterly and is based on a $100 investment on December 31, 2006.
The Peer Group Index is a self-constructed peer group of companies that are included in the Dow Jones Food and Beverage Group and the Dow Jones Tobacco Group of companies, from which the Company has been excluded.
The Peer Group Index consists of the following companies: Altria Group, Inc., Archer-Daniels-Midland Company, Beam Inc., Brown-Forman Corporation (Class B Stock), Bunge Limited, Campbell Soup Company, Coca-Cola Enterprises, Inc., ConAgra Foods, Inc., Constellation Brands, Inc., Corn Products International, Inc., Darling International Inc., Dean Foods Company, Diamond Foods, Inc., Dr Pepper Snapple Group, Inc., Flowers Foods, Inc., Fresh Del Monte Produce Inc., General Mills, Inc., Green Mountain Coffee Roasters, Inc., Herbalife Ltd., H.J. Heinz Company, Hormel Foods Corporation, Kellogg Company, Kraft Foods Inc., Lancaster Colony Corporation, Lorillard, Inc., McCormick & Company, Inc., Mead Johnson Nutrition Company, Molson Coors Brewing Company, Monsanto Company, Monster Beverage Corporation (formerly known as Hansen Natural Corporation), PepsiCo, Inc., Philip Morris International Inc., Ralcorp Holdings, Inc., Reynolds American Inc., Sara Lee Corporation, Smithfield Foods, Inc., The Hain Celestial Group, Inc., The Hershey Company, The J.M. Smucker Company, Tootsie Roll Industries, Inc., TreeHouse Foods, Inc., Tyson Foods, Inc., and Universal Corporation.
Companies included in the Dow Jones Food and Beverage Group and the Dow Jones Tobacco Group change periodically. This year, the groups include Beam Inc. and Diamond Foods, Inc., both of which were not included in the groups last year. Additionally, this year the groups do not include Central European Distribution Corporation, Chiquita Brands International, Inc., Del Monte Foods Company, and Martek Biosciences Corporation, all of which were included in the groups last year.
27
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
The following selected financial data should be read in conjunction with "Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" and consolidated financial statements and notes thereto contained in "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" of this report.
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 1
|
2009 |
2008 |
2007 |
||||||||||||||
(In millions except per share data) |
|||||||||||||||||||
SUMMARY OF OPERATIONS |
|||||||||||||||||||
Net operating revenues |
$ |
46,542 |
$ |
35,119 |
$ |
30,990 |
$ |
31,944 |
$ |
28,857 |
|||||||||
|
Net income attributable to shareowners of
The Coca-Cola Company
|
8,572 |
11,809 |
6,824 |
5,807 |
5,981 |
||||||||||||||
PER SHARE DATA |
|||||||||||||||||||
Basic net income |
$ |
3.75 |
$ |
5.12 |
$ |
2.95 |
$ |
2.51 |
$ |
2.59 |
|||||||||
Diluted net income |
3.69 |
5.06 |
2.93 |
2.49 |
2.57 |
||||||||||||||
Cash dividends |
1.88 |
1.76 |
1.64 |
1.52 |
1.36 |
||||||||||||||
BALANCE SHEET DATA |
|||||||||||||||||||
Total assets |
$ |
79,974 |
$ |
72,921 |
$ |
48,671 |
$ |
40,519 |
$ |
43,269 |
|||||||||
Long-term debt |
13,656 |
14,041 |
5,059 |
2,781 |
3,277 |
||||||||||||||
1 |
Includes the impact of the Company's acquisition of CCE's North American business and the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE. Both of these transactions occurred on October 2, 2010. This information also includes the impact of the deconsolidation of certain entities, primarily bottling operations, on January 1, 2010, as a result of the Company's adoption of new accounting guidance issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB"). Refer to Note 1 and Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
|
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Overview
The following Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations ("MD&A") is intended to help the reader understand The Coca-Cola Company, our operations and our present business environment. MD&A is provided as a supplement to — and should be read in conjunction with — our consolidated financial statements and the accompanying notes thereto contained in "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" of this report. This overview summarizes the MD&A, which includes the following sections:
• |
Our Business — a general description of our business and the nonalcoholic beverage segment of the commercial beverage industry, our objective, our strategic priorities, our core capabilities, and challenges and risks of our business.
|
• |
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates — a discussion of accounting policies that require critical judgments and estimates.
|
• |
Operations Review — an analysis of our Company's consolidated results of operations for the three years presented in our consolidated financial statements. Except to the extent that differences among our operating segments are material to an understanding of our business as a whole, we present the discussion in the MD&A on a consolidated basis.
|
• |
Liquidity, Capital Resources and Financial Position — an analysis of cash flows; off-balance sheet arrangements and aggregate contractual obligations; foreign exchange; an overview of financial position; and the impact of inflation and changing prices.
|
28
Our Business
General
The Coca-Cola Company is the world's largest beverage company. We own or license and market more than 500 nonalcoholic beverage brands, primarily sparkling beverages but also a variety of still beverages such as waters, enhanced waters, juices and juice drinks, ready-to-drink teas and coffees, and energy and sports drinks. We own and market four of the world's top five nonalcoholic sparkling beverage brands: Coca-Cola, Diet Coke, Fanta and Sprite. Finished beverage products bearing our trademarks, sold in the United States since 1886, are now sold in more than 200 countries.
We make our branded beverage products available to consumers throughout the world through our network of Company-owned or controlled bottling and distribution operations as well as independently owned bottling partners, distributors, wholesalers and retailers — the world's largest beverage distribution system. Of the approximately 56 billion beverage servings of all types consumed worldwide every day, beverages bearing trademarks owned by or licensed to us account for more than 1.7 billion.
We believe our success depends on our ability to connect with consumers by providing them with a wide variety of choices to meet their desires, needs and lifestyle choices. Our success further depends on the ability of our people to execute effectively, every day.
Our goal is to use our Company's assets — our brands, financial strength, unrivaled distribution system, global reach and the talent and strong commitment of our management and associates — to become more competitive and to accelerate growth in a manner that creates value for our shareowners.
Our Company markets, manufactures and sells:
• |
beverage concentrates, sometimes referred to as "beverage bases," and syrups, including fountain syrups (we refer to this part of our business as our "concentrate business" or "concentrate operations"); and |
• |
finished sparkling and still beverages (we refer to this part of our business as our "finished products business" or "finished products operations"). |
Generally, finished products operations generate higher net operating revenues but lower gross profit margins than concentrate operations.
In our concentrate operations, we typically generate net operating revenues by selling concentrates and syrups to authorized bottling and canning operations (to which we typically refer as our "bottlers" or our "bottling partners"). Our bottling partners either combine the concentrates with sweeteners (depending on the product), still water and/or sparkling water, or combine the syrups with sparkling water to produce finished beverages. The finished beverages are packaged in authorized containers bearing our trademarks or trademarks licensed to us — such as cans and refillable and nonrefillable glass and plastic bottles — and are then sold to retailers directly or, in some cases, through wholesalers or other bottlers. Outside the United States, we also sell concentrates for fountain beverages to our bottling partners who are typically authorized to manufacture fountain syrups, which they sell to fountain retailers such as restaurants and convenience stores which use the fountain syrups to produce beverages for immediate consumption, or to fountain wholesalers who in turn sell and distribute the fountain syrups to fountain retailers.
Our finished products operations consist primarily of the production, sales and distribution operations managed by CCR and our Company-owned or controlled bottling and distribution operations. CCR is included in our North America operating segment, and our Company-owned or controlled bottling and distribution operations are included in our Bottling Investments operating segment. Our finished products operations generate net operating revenues by selling sparkling beverages and a variety of still beverages, such as juices and juice drinks, energy and sports drinks, ready-to-drink teas and coffees, and certain water products, to retailers or to distributors, wholesalers and bottling partners who distribute them to retailers. In addition, in the United States, we manufacture fountain syrups and sell them to fountain retailers such as restaurants and convenience stores who use the fountain syrups to produce beverages for immediate consumption or to authorized fountain wholesalers or bottling partners who resell the fountain syrups to fountain retailers. In the United States, we authorize wholesalers to resell our fountain syrups through nonexclusive appointments that neither restrict us in setting the prices at which we sell fountain syrups to the wholesalers nor restrict the territories in which the wholesalers may resell in the United States.
29
The following table sets forth the percentage of total net operating revenues related to concentrate operations and finished products operations:
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
|||||
Concentrate operations1
|
39 |
% |
51 |
% |
54 |
% |
||
Finished products operations2
|
61 |
3 |
49 |
3 |
46 |
|||
Net operating revenues |
100 |
% |
100 |
% |
100 |
% |
||
1 |
Includes concentrates sold by the Company to authorized bottling partners for the manufacture of fountain syrups. The bottlers then typically sell the fountain syrups to wholesalers or directly to fountain retailers. |
2 |
Includes fountain syrups manufactured by the Company, including consolidated bottling operations, and sold to fountain retailers or to authorized fountain wholesalers or bottling partners who resell the fountain syrups to fountain retailers. |
3 |
Includes net operating revenues related to the acquired CCE North American business for the full year in 2011. In 2010, the percentage includes net operating revenues from the date of the CCE acquisition on October 2, 2010. |
The following table sets forth the percentage of total worldwide unit case volume related to concentrate operations and finished products operations:
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
|||||
Concentrate operations1
|
70 |
% |
76 |
% |
78 |
% |
||
Finished products operations2
|
30 |
3 |
24 |
3 |
22 |
|||
Total worldwide unit case volume |
100 |
% |
100 |
% |
100 |
% |
||
1 |
Includes unit case volume related to concentrates sold by the Company to authorized bottling partners for the manufacture of fountain syrups. The bottlers then typically sell the fountain syrups to wholesalers or directly to fountain retailers. |
2 |
Includes unit case volume related to fountain syrups manufactured by the Company, including consolidated bottling operations, and sold to fountain retailers or to authorized fountain wholesalers or bottling partners who resell the fountain syrups to fountain retailers. |
3 |
Includes unit case volume related to the acquired CCE North American business for the full year in 2011. In 2010, the percentage includes unit case volume from the date of the CCE acquisition on October 2, 2010. |
Acquisition of CCE's North American Business and Related Transactions
Pursuant to the terms of the business separation and merger agreement entered into on February 25, 2010, as amended (the "merger agreement"), on October 2, 2010 (the "acquisition date"), we acquired CCE's North American business, consisting of CCE's production, sales and distribution operations in the United States, Canada, the British Virgin Islands, the United States Virgin Islands and the Cayman Islands, and a substantial majority of CCE's corporate segment. We believe this acquisition will result in an evolved franchise system that will enable us to better serve the unique needs of the North American market. The creation of a unified operating system will strategically position us to better market and distribute our nonalcoholic beverage brands in North America.
Under the terms of the merger agreement, the Company acquired the 67 percent of CCE's North American business that was not already owned by the Company for consideration that included: (1) the Company's 33 percent indirect ownership interest in CCE's European operations; (2) cash consideration; and (3) replacement awards issued to certain current and former employees of CCE's North American and corporate operations. At closing, CCE shareowners other than the Company exchanged their CCE common stock for common stock in a new entity, which was renamed Coca-Cola Enterprises, Inc. (which is referred to herein as "New CCE") and which continues to hold the European operations held by CCE prior to the acquisition. At closing, New CCE became 100 percent owned by shareowners that held shares of common stock of CCE immediately prior to the closing, other than the Company. As a result of this transaction, the Company does not own any interest in New CCE.
As of October 1, 2010, our Company owned 33 percent of the outstanding common stock of CCE. Based on the closing price of CCE's common stock on the last day of trading prior to the acquisition date, the fair value of our investment in CCE was $5,373 million, which reflected the fair value of our ownership in both CCE's North American business and its European operations. We remeasured our equity interest in CCE to fair value upon the close of the transaction. As a result, we recognized a gain of $4,978 million, which was classified in the line item other income (loss) — net in our consolidated statement of income. The gain included a $137 million reclassification adjustment related to foreign currency translation gains recognized upon the disposal of our indirect investment in CCE's European operations. The Company relinquished its indirect ownership interest in CCE's European operations to New CCE as part of the consideration to acquire the 67 percent of CCE's North American business that was not already owned by the Company.
30
Although the CCE transaction was structured to be primarily cashless, under the terms of the merger agreement, we agreed to assume $8.9 billion of CCE debt. In the event the actual CCE debt on the acquisition date was less than the agreed amount, we agreed to make a cash payment to New CCE for the difference. As of the acquisition date, the debt assumed by the Company was $7.9 billion. The total cash consideration paid to New CCE as part of the transaction was $1.4 billion, which included $1.0 billion related to the debt shortfall.
In contemplation of the closing of our acquisition of CCE's North American business, we reached an agreement with DPS to distribute certain DPS brands in territories where DPS brands had been distributed by CCE prior to the CCE transaction. Under the terms of our agreement with DPS, concurrently with the closing of the CCE transaction, we entered into license agreements with DPS to distribute Dr Pepper trademark brands in the U.S., Canada Dry in the Northeast U.S., and Canada Dry and C' Plus in Canada, and we made a net one-time cash payment of $715 million to DPS. Under the license agreements, the Company agreed to meet certain performance obligations to distribute DPS products in retail and foodservice accounts and vending machines. The license agreements have initial terms of 20 years, with automatic 20-year renewal periods unless otherwise terminated under the terms of the agreements. The license agreements replaced agreements between DPS and CCE existing immediately prior to the completion of the CCE transaction. In addition, we entered into an agreement with DPS to include Dr Pepper and Diet Dr Pepper in our Coca-Cola Freestyle fountain dispensers in certain outlets throughout the United States. The Coca-Cola Freestyle agreement has a term of 20 years.
On October 2, 2010, we sold all of our ownership interests in our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE for $0.9 billion in cash. In addition, in connection with the acquisition of CCE's North American business, we granted to New CCE the right to negotiate the acquisition of our majority interest in our German bottler at any time from 18 to 39 months after February 25, 2010, at the then current fair value and subject to terms and conditions as mutually agreed.
The Nonalcoholic Beverage Segment of the Commercial Beverage Industry
We operate in the highly competitive nonalcoholic beverage segment of the commercial beverage industry. We face strong competition from numerous other general and specialty beverage companies. We, along with other beverage companies, are affected by a number of factors, including, but not limited to, cost to manufacture and distribute products, consumer spending, economic conditions, availability and quality of water, consumer preferences, inflation, political climate, local and national laws and regulations, foreign currency exchange fluctuations, fuel prices and weather patterns.
Our Objective
Our objective is to use our formidable assets — brands, financial strength, unrivaled distribution system, global reach, and the talent and strong commitment of our management and associates — to achieve long-term sustainable growth. Our vision for sustainable growth includes the following:
• |
People: Being a great place to work where people are inspired to be the best they can be. |
• |
Portfolio: Bringing to the world a portfolio of beverage brands that anticipates and satisfies people's desires and needs. |
• |
Partners: Nurturing a winning network of partners and building mutual loyalty. |
• |
Planet: Being a responsible global citizen that makes a difference. |
• |
Profit: Maximizing return to shareowners while being mindful of our overall responsibilities. |
• |
Productivity: Managing our people, time and money for greatest effectiveness. |
Strategic Priorities
We have four strategic priorities designed to create long-term sustainable growth for our Company and the Coca-Cola system and value for our shareowners. These strategic priorities are driving global beverage leadership; accelerating innovation; leveraging our balanced geographic portfolio; and leading the Coca-Cola system for growth. To enable the entire Coca-Cola system so that we can deliver on these strategic priorities, we must further enhance our core capabilities of consumer marketing; commercial leadership; franchise leadership; and bottling and distribution operations.
31
Core Capabilities
Consumer Marketing
Marketing investments are designed to enhance consumer awareness of and increase consumer preference for our brands. This produces long-term growth in unit case volume, per capita consumption and our share of worldwide nonalcoholic beverage sales. Through our relationships with our bottling partners and those who sell our products in the marketplace, we create and implement integrated marketing programs, both globally and locally, that are designed to heighten consumer awareness of and product appeal for our brands. In developing a strategy for a Company brand, we conduct product and packaging research, establish brand positioning, develop precise consumer communications and solicit consumer feedback. Our integrated marketing activities include, but are not limited to, advertising, point-of-sale merchandising and sales promotions.
We have disciplined marketing strategies that focus on driving volume in emerging markets, increasing our brand value in developing markets and growing profit in our developed markets. In emerging markets, we are investing in infrastructure programs that drive volume through increased access to consumers. In developing markets, where consumer access has largely been established, our focus is on differentiating our brands. In our developed markets, we continue to invest in brands and infrastructure programs, but at a slower rate than revenue growth.
We are focused on affordability and ensuring we are communicating the appropriate message based on the current economic environment.
Commercial Leadership
The Coca-Cola system has millions of customers around the world who sell or serve our products directly to consumers. We focus on enhancing value for our customers and providing solutions to grow their beverage businesses. Our approach includes understanding each customer's business and needs — whether that customer is a sophisticated retailer in a developed market or a kiosk owner in an emerging market. We focus on ensuring that our customers have the right product and package offerings and the right promotional tools to deliver enhanced value to themselves and the Company. We are constantly looking to build new beverage consumption occasions in our customers' outlets through unique and innovative consumer experiences, product availability and delivery systems, and beverage merchandising and displays. We participate in joint brand-building initiatives with our customers in order to drive customer preference for our brands. Through our commercial leadership initiatives, we embed ourselves further into our retail customers' businesses while developing strategies for better execution at the point of sale.
Franchise Leadership
We must continue to improve our franchise leadership capabilities to give our Company and our bottling partners the ability to grow together through shared values, aligned incentives and a sense of urgency and flexibility that supports consumers' always changing needs and tastes. The financial health and success of our bottling partners are critical components of the Company's success. We work with our bottling partners to identify system requirements that enable us to quickly achieve scale and efficiencies, and we share best practices throughout the bottling system. Our system leadership allows us to leverage recent acquisitions to expand our volume base and enhance margins. With our bottling partners, we work to produce differentiated beverages and packages that are appropriate for the right channels and consumers. We also design business models for sparkling and still beverages in specific markets to ensure that we appropriately share the value created by these beverages with our bottling partners. We will continue to build a supply chain network that leverages the size and scale of the Coca-Cola system to gain a competitive advantage.
Bottling and Distribution Operations
Most of our Company beverage products are manufactured, sold and distributed by independently owned and managed bottling partners. However, over the past several years the amount of Company beverage products that are manufactured, sold and distributed by consolidated bottling and distribution operations has increased. We often acquire bottlers in underperforming markets where we believe we can use our resources and expertise to improve performance. Owning such a controlling interest enables us to compensate for limited local resources; help focus the bottler's sales and marketing programs; assist in the development of the bottler's business and information systems; and establish an appropriate capital structure for the bottler.
Our Company has a long history of providing world-class customer service, demonstrating leadership in the marketplace and leveraging the talent of our global workforce. In addition, we have an experienced bottler management team. All of these factors are critical to build upon as we manage our growing bottling and distribution operations.
The Company has a deep commitment to continuously improving our business. This includes our efforts to develop innovative packaging and merchandising solutions which help drive demand for our beverages and meet the growing needs of our consumers. As we further transform the way we go to market the Company continues to seek out ways to be more efficient.
32
Challenges and Risks
Being a global company provides unique opportunities for our Company. Challenges and risks accompany those opportunities.
Our management has identified certain challenges and risks that demand the attention of the nonalcoholic beverage segment of the commercial beverage industry and our Company. Of these, four key challenges and risks are discussed below.
Obesity and Inactive Lifestyles. Increasing concern among consumers, public health professionals and government agencies of the potential health problems associated with obesity and inactive lifestyles represents a significant challenge to our industry. We recognize that obesity is a complex public health problem. Our commitment to consumers begins with our broad product line, which includes a wide selection of diet and light beverages, juices and juice drinks, sports drinks and water products. Our commitment also includes adhering to responsible policies in schools and in the marketplace; supporting programs to encourage physical activity and promote nutrition education; and continuously meeting changing consumer needs through beverage innovation, choice and variety. We are committed to playing an appropriate role in helping address this issue in cooperation with governments, educators and consumers through science-based solutions and programs.
Water Quality and Quantity. Water quality and quantity is an issue that increasingly requires our Company's attention and collaboration with the nonalcoholic beverage segment of the commercial beverage industry, governments, nongovernmental organizations and communities where we operate. Water is the main ingredient in substantially all of our products. It is also a limited natural resource facing unprecedented challenges from overexploitation, increasing pollution and poor management. Our Company is in an excellent position to share the water-related knowledge we have developed in the communities we serve — water resource management, water treatment, wastewater treatment systems, and models for working with communities and partners in addressing water and sanitation needs. We are actively engaged in assessing the specific water-related risks that we and many of our bottling partners face and have implemented a formal water risk management program. We are working with our global partners to develop water sustainability projects. We are actively encouraging improved water efficiency and conservation efforts throughout our system. As demand for water continues to increase around the world, we expect commitment and continued action on our part will be crucial to the successful long-term stewardship of this critical natural resource.
Evolving Consumer Preferences. Consumers want more choices. We are impacted by shifting consumer demographics and needs, on-the-go lifestyles, aging populations in developed markets and consumers who are empowered with more information than ever. We are committed to generating new avenues for growth through our core brands with a focus on diet and light products. We are also committed to continuing to expand the variety of choices we provide to consumers to meet their needs, desires and lifestyle choices.
Increased Competition and Capabilities in the Marketplace. Our Company is facing strong competition from some well-established global companies and many local participants. We must continue to selectively expand into other profitable segments of the nonalcoholic beverage segment of the commercial beverage industry and strengthen our capabilities in marketing and innovation in order to maintain our brand loyalty and market share.
All four of these challenges and risks — obesity and inactive lifestyles, water quality and quantity, evolving consumer preferences, and increased competition and capabilities in the marketplace — have the potential to have a material adverse effect on the nonalcoholic beverage segment of the commercial beverage industry and on our Company; however, we believe our Company is well positioned to appropriately address these challenges and risks.
See also "Item 1A. Risk Factors" in Part I of this report for additional information about risks and uncertainties facing our Company.
33
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our consolidated financial statements are prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, which require management to make estimates, judgments and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in our consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. We believe our most critical accounting policies and estimates relate to the following:
• |
Principles of Consolidation |
• |
Purchase Accounting for Acquisitions |
• |
Recoverability of Noncurrent Assets |
• |
Pension Plan Valuations |
• |
Revenue Recognition |
• |
Income Taxes |
Management has discussed the development, selection and disclosure of critical accounting policies and estimates with the Audit Committee of the Company's Board of Directors. While our estimates and assumptions are based on our knowledge of current events and actions we may undertake in the future, actual results may ultimately differ from these estimates and assumptions. For a discussion of the Company's significant accounting policies, refer to Note 1 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Principles of Consolidation
Our Company consolidates all entities that we control by ownership of a majority voting interest as well as VIEs for which our Company is the primary beneficiary. Generally, we consolidate only business enterprises that we control by ownership of a majority voting interest. However, there are situations in which consolidation is required even though the usual condition of consolidation (ownership of a majority voting interest) does not apply. Generally, this occurs when an entity holds an interest in another business enterprise that was achieved through arrangements that do not involve voting interests, which results in a disproportionate relationship between such entity's voting interests in, and its exposure to the economic risks and potential rewards of, the other business enterprise. This disproportionate relationship results in what is known as a variable interest, and the entity in which we have the variable interest is referred to as a "VIE". An enterprise must consolidate a VIE if it is determined to be the primary beneficiary of the VIE. The primary beneficiary has both (a) the power to direct the activities of the VIE that most significantly impact the entity's economic performance, and (b) the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive benefits from the VIE that could potentially be significant to the VIE.
Our Company holds interests in certain VIEs, primarily bottling and container manufacturing operations, for which we were not determined to be the primary beneficiary. Our variable interests in these VIEs primarily relate to profit guarantees or subordinated financial support. Refer to Note 11 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. Although these financial arrangements resulted in us holding variable interests in these entities, the majority of these arrangements did not empower us to direct the activities of the VIEs that most significantly impact the VIEs' economic performance. Our Company's investments, plus any loans and guarantees, related to these VIEs totaled $1,183 million and $1,274 million as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively, representing our maximum exposures to loss. The Company's investments, plus any loans and guarantees, related to these VIEs were not significant to the Company's consolidated financial statements.
In addition, our Company holds interests in certain VIEs, primarily bottling and container manufacturing operations, for which we were determined to be the primary beneficiary. As a result, we have consolidated these entities. Our Company's investments, plus any loans and guarantees, related to these VIEs totaled $199 million and $191 million as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively, representing our maximum exposures to loss. The assets and liabilities of VIEs for which we are the primary beneficiary were not significant to the Company's consolidated financial statements.
Creditors of our VIEs do not have recourse against the general credit of the Company, regardless of whether they are accounted for as consolidated entities.
The information presented above reflects the impact of the Company's adoption of accounting guidance issued by the FASB related to VIEs in June 2009. This accounting guidance resulted in a change in our accounting policy effective January 1, 2010. Among other things, the guidance requires more qualitative than quantitative analyses to determine the primary beneficiary of a VIE, requires continuous assessments of whether an enterprise is the primary beneficiary of a VIE, enhances disclosures about an enterprise's involvement with a VIE, and amends certain guidance for determining whether an entity is a VIE.
Beginning January 1, 2010, we deconsolidated certain entities as a result of this change in accounting policy. These entities are primarily bottling operations and had previously been consolidated due to certain loan guarantees and/or other financial support
34
given by the Company. These financial arrangements, although not significant to our consolidated financial statements, resulted in a disproportionate relationship between our voting interests in these entities and our exposure to the economic risks and potential rewards of the entities. As a result, we determined that we held a majority of the variable interests in these entities and, therefore, were deemed to be the primary beneficiary in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States as of December 31, 2009. Although these financial arrangements resulted in us holding a majority of the variable interests in these VIEs, the majority of these arrangements did not empower us to direct the activities of the VIEs that most significantly impact the VIEs' economic performance. Consequently, subsequent to the change in accounting policy, the Company deconsolidated the majority of these VIEs.
The entities that have been deconsolidated accounted for less than 1 percent of net income attributable to shareowners of The Coca-Cola Company in 2009. On January 1, 2010, the Company began to account for these entities under the equity method of accounting. Although the deconsolidation of these entities impacted individual line items in our consolidated financial statements, the impact on net income attributable to shareowners of The Coca-Cola Company in future periods will be nominal. The equity method of accounting is intended to be a single line consolidation and, therefore, generally should result in the same net income attributable to the investor as would be the case if the investee had been consolidated. The main impact on our consolidated financial statements in 2010 was that, instead of these entities' results of operations and balance sheets affecting our consolidated line items, our proportionate share of net income or loss from these entities was reported in equity income (loss) — net in our consolidated statements of income, and our investment in these entities was reported as equity method investments in our consolidated balance sheets. Refer to the heading "Operations Review — Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" below for additional information.
Purchase Accounting for Acquisitions
The Company adopted new guidance issued by the FASB on January 1, 2009, which changed the application of the acquisition method of accounting in a business combination and also modified the way assets acquired and liabilities assumed are recognized on a prospective basis. In general, the acquisition method of accounting requires companies to record assets acquired and liabilities assumed at their respective fair market values at the date of acquisition. We estimate fair value using the exit price approach, which is defined as the price that would be received if we sold an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly market. The value of an exit price is determined from the viewpoint of all market participants as a whole and may result in the Company valuing assets at a fair value that is not reflective of our intended use of the assets. Any amount of the purchase price paid that is in excess of the estimated fair values of net assets acquired is recorded in the line item goodwill in our consolidated balance sheets. Management's judgment is used to determine the estimated fair values assigned to assets acquired and liabilities assumed, as well as asset lives for property, plant and equipment and amortization periods for intangible assets, and can materially affect the Company's results of operations.
Transaction costs, as well as costs to reorganize acquired companies, are expensed as incurred in the Company's consolidated statements of income.
On October 2, 2010, the Company acquired CCE's North American business and recorded total assets of $22.2 billion as of the acquisition date. The assets we acquired included a material amount of intangible assets that were subject to the significant estimates described above. During our purchase accounting measurement period, which concluded during the third quarter of 2011, the Company made adjustments to certain amounts that resulted in a final balance of $22.0 billion of total assets being recorded in our consolidated balance sheets related to the CCE acquisition. Refer to the heading "Recoverability of Noncurrent Assets" below and Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for further information related to this acquisition.
Recoverability of Noncurrent Assets
We perform recoverability and impairment tests of noncurrent assets in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States. For certain assets, recoverability and/or impairment tests are required only when conditions exist that indicate the carrying value may not be recoverable. For other assets, impairment tests are required at least annually, or more frequently, if events or circumstances indicate that an asset may be impaired.
Our equity method investees also perform such recoverability and/or impairment tests. If an impairment charge was recorded by one of our equity method investees, the Company would record its proportionate share of such charge as a reduction of equity income (loss) — net in our consolidated statements of income. However, the actual amount we record with respect to our proportionate share of such charges may be impacted by items such as basis differences, deferred taxes and deferred gains.
Management's assessments of the recoverability and impairment tests of noncurrent assets involve critical accounting estimates. These estimates require significant management judgment, include inherent uncertainties and are often interdependent; therefore, they do not change in isolation. Factors that management must estimate include, among others, the economic life of the asset, sales volume, pricing, cost of raw materials, inflation, cost of capital, marketing spending, foreign currency exchange
35
rates, tax rates and capital spending. These factors are even more difficult to predict when global financial markets are highly volatile. The estimates we use when assessing the recoverability of noncurrent assets are consistent with those we use in our internal planning. When performing impairment tests, we estimate the fair values of the assets using management's best assumptions, which we believe would be consistent with what a hypothetical marketplace participant would use. Estimates and assumptions used in these tests are evaluated and updated as appropriate. The variability of these factors depends on a number of conditions, including uncertainty about future events, and thus our accounting estimates may change from period to period. If other assumptions and estimates had been used when these tests were performed, impairment charges could have resulted. As mentioned above, these factors do not change in isolation and, therefore, we do not believe it is practicable or meaningful to present the impact of changing a single factor. Furthermore, if management uses different assumptions or if different conditions occur in future periods, future impairment charges could result. Refer to the heading "Operations Review" below for additional information related to our present business environment. Certain factors discussed above are impacted by our current business environment and are discussed throughout this report, as appropriate.
Our Company faces many uncertainties and risks related to various economic, political and regulatory environments in the countries in which we operate, particularly in developing or emerging markets. Refer to the heading "Our Business — Challenges and Risks" above and "Item 1A. Risk Factors" in Part I of this report. As a result, management must make numerous assumptions which involve a significant amount of judgment when completing recoverability and impairment tests of noncurrent assets in various regions around the world.
Investments in Equity and Debt Securities
The carrying values of our investments in equity securities are determined using the equity method, the cost method or the fair value method. We account for investments in companies that we do not control or account for under the equity method either at fair value or under the cost method, as applicable. Investments in equity securities are carried at fair value, if the fair value of the security is readily determinable. Equity investments carried at fair value are classified as either trading or available-for-sale securities. Realized and unrealized gains and losses on trading securities and realized gains and losses on available-for-sale securities are included in net income. Unrealized gains and losses, net of deferred taxes, on available-for-sale securities are included in our consolidated balance sheets as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) ("AOCI"). Trading securities are reported as either marketable securities or other assets in our consolidated balance sheets. Securities classified as available-for-sale are reported as either marketable securities or other investments in our consolidated balance sheets, depending on the length of time we intend to hold the investment. Investments in equity securities that do not qualify for fair value accounting are accounted for under the cost method. In accordance with the cost method, our initial investment is recorded at cost and we record dividend income when applicable dividends are declared. Cost method investments are reported as other investments in our consolidated balance sheets.
Our investments in debt securities are carried at either amortized cost or fair value. Investments in debt securities that the Company has the positive intent and ability to hold to maturity are carried at amortized cost and classified as held-to-maturity. Investments in debt securities that are not classified as held-to-maturity are carried at fair value and classified as either trading or available-for-sale.
The following table presents the carrying values of our investments in equity and debt securities (in millions):
December 31, 2011 |
Carrying
Value
|
Percentage
of Total
Assets
|
||||
Equity method investments |
$ |
7,233 |
9 |
% |
||
Securities classified as available-for-sale |
1,401 |
2 |
||||
Securities classified as trading |
211 |
* |
||||
Cost method investments |
155 |
* |
||||
Securities classified as held-to-maturity |
113 |
* |
||||
Total |
$ |
9,113 |
11 |
% |
||
* |
Accounts for less than 1 percent of the Company's total assets. |
36
Investments classified as trading securities are not assessed for impairment, since they are carried at fair value with the change in fair value included in net income. We review our investments in equity and debt securities that are accounted for using the equity method or cost method or that are classified as available-for-sale or held-to-maturity each reporting period to determine whether a significant event or change in circumstances has occurred that may have an adverse effect on the fair value of each investment. When such events or changes occur, we evaluate the fair value compared to our cost basis in the investment. We also perform this evaluation every reporting period for each investment for which our cost basis has exceeded the fair value in the prior period. The fair values of most of our Company's investments in publicly traded companies are often readily available based on quoted market prices. For investments in nonpublicly traded companies, management's assessment of fair value is based on valuation methodologies including discounted cash flows, estimates of sales proceeds and appraisals, as appropriate. We consider the assumptions that we believe hypothetical marketplace participants would use in evaluating estimated future cash flows when employing the discounted cash flow or estimates of sales proceeds valuation methodologies. The ability to accurately predict future cash flows, especially in developing and emerging markets, may impact the determination of fair value.
In the event the fair value of an investment declines below our cost basis, management is required to determine if the decline in fair value is other than temporary. If management determines the decline is other than temporary, an impairment charge is recorded. Management's assessment as to the nature of a decline in fair value is based on, among other things, the length of time and the extent to which the market value has been less than our cost basis, the financial condition and near-term prospects of the issuer, and our intent and ability to retain the investment for a period of time sufficient to allow for any anticipated recovery in market value.
In 2011, the Company recognized impairment charges of $17 million as a result of the other-than-temporary decline in the fair value of available-for-sale securities. In addition, the Company recognized charges of $41 million during 2011 related to the impairment of an investment in an entity accounted for under the equity method of accounting. Each of the impairment charges mentioned above impacted the Corporate operating segment and was recorded in other income (loss) — net. Refer to the heading "Operations Review — Other Income (Loss) — Net" below and Note 16 and Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
In 2010, the Company recognized other-than-temporary impairments of $41 million related to certain available-for-sale securities and an equity method investment. These impairment charges were recorded in other income (loss) — net and impacted the Bottling Investments and Corporate operating segments. Refer to Note 16 and Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
In 2009, the Company recorded a charge of $27 million in other income (loss) — net as a result of an other-than-temporary decline in the fair value of a cost method investment. As of December 31, 2008, the estimated fair value of this investment approximated the Company's carrying value in the investment. However, in 2009, the Company was informed by the investee of its intent to reorganize its capital structure in 2009, which resulted in the Company's shares in the investee being canceled. As a result, the Company determined that the decline in fair value of this cost method investment was other than temporary. This impairment charge impacted the Corporate operating segment. Refer to Note 16 and Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
The following table presents the difference between calculated fair values, based on quoted closing prices of publicly traded shares, and our Company's cost basis in publicly traded bottlers accounted for as equity method investments (in millions):
December 31, 2011 |
Fair
Value
|
Carrying
Value
|
Difference |
||||||||
Coca-Cola FEMSA, S.A.B. de C.V. |
$ |
5,532 |
$ |
1,569 |
$ |
3,963 |
|||||
Coca-Cola Amatil Limited |
2,551 |
999 |
1,552 |
||||||||
Coca-Cola Hellenic Bottling Company S.A. |
1,506 |
1,442 |
64 |
||||||||
Coca-Cola Icecek A.S. |
622 |
155 |
467 |
||||||||
Coca-Cola Central Japan |
183 |
186 |
(3 |
) |
|||||||
Embotelladoras Coca-Cola Polar S.A. |
154 |
86 |
68 |
||||||||
Coca-Cola Bottling Co. Consolidated |
145 |
84 |
61 |
||||||||
Total |
$ |
10,693 |
$ |
4,521 |
$ |
6,172 |
|||||
37
Other Assets
Our Company invests in infrastructure programs with our bottlers that are directed at strengthening our bottling system and increasing unit case volume. Additionally, our Company advances payments to certain customers to fund future marketing activities intended to generate profitable volume and expenses such payments over the periods benefited. Advance payments are also made to certain customers for distribution rights. Payments under these programs are generally capitalized and reported in the line items prepaid expenses and other assets or other assets, as appropriate, in our consolidated balance sheets. When facts and circumstances indicate that the carrying value of these assets (or asset groups) may not be recoverable, management assesses the recoverability of the carrying value by preparing estimates of sales volume and the resulting gross profit and cash flows. These estimated future cash flows are consistent with those we use in our internal planning. If the sum of the expected future cash flows (undiscounted and without interest charges) is less than the carrying amount, we recognize an impairment loss. The impairment loss recognized is the amount by which the carrying amount exceeds the fair value.
As a result of our acquisition of CCE's North American business, the Company recorded charges of $266 million related to preexisting relationships. These charges were primarily related to the write-off of our investment in infrastructure programs with CCE. Our investment in these infrastructure programs with CCE did not meet the criteria to be recognized as an asset subsequent to the acquisition. Refer to Note 2 and Note 6 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Property, Plant and Equipment
As of December 31, 2011, the carrying value of our property, plant and equipment, net of depreciation, was $14,939 million, or 19 percent of our total assets. Certain events or changes in circumstances may indicate that the recoverability of the carrying amount or remaining useful life of property, plant and equipment should be assessed, including, among others, the manner or length of time in which the Company intends to use the asset, a significant decrease in market value, a significant change in the business climate in a particular market, or a current period operating or cash flow loss combined with historical losses or projected future losses. When such events or changes in circumstances are present and an impairment review is performed, we estimate the future cash flows expected to result from the use of the asset (or asset group) and its eventual disposition. These estimated future cash flows are consistent with those we use in our internal planning. If the sum of the expected future cash flows (undiscounted and without interest charges) is less than the carrying amount, we recognize an impairment loss. The impairment loss recognized is the amount by which the carrying amount exceeds the fair value. We use a variety of methodologies to determine the fair value of property, plant and equipment, including appraisals and discounted cash flow models, which are consistent with the assumptions we believe hypothetical marketplace participants would use.
Goodwill, Trademarks and Other Intangible Assets
Intangible assets are classified into one of three categories: (1) intangible assets with definite lives subject to amortization; (2) intangible assets with indefinite lives not subject to amortization; and (3) goodwill. For intangible assets with definite lives, tests for impairment must be performed if conditions exist that indicate the carrying value may not be recoverable. For intangible assets with indefinite lives and goodwill, tests for impairment must be performed at least annually or more frequently if events or circumstances indicate that assets might be impaired. The following table presents the carrying values of intangible assets included in our consolidated balance sheet (in millions):
December 31, 2011 |
Carrying
Value
|
Percentage
of Total
Assets
|
||||
Goodwill |
$ |
12,219 |
15 |
% |
||
Bottlers' franchise rights with indefinite lives |
7,770 |
10 |
||||
Trademarks with indefinite lives |
6,430 |
8 |
||||
Definite-lived intangible assets, net |
1,137 |
1 |
||||
Other intangible assets not subject to amortization |
113 |
* |
||||
Total |
$ |
27,669 |
35 |
% |
||
* |
Accounts for less than 1 percent of the Company's total assets. |
38
When facts and circumstances indicate that the carrying value of definite-lived intangible assets may not be recoverable, management assesses the recoverability of the carrying value by preparing estimates of sales volume and the resulting gross profit and cash flows. These estimated future cash flows are consistent with those we use in our internal planning. If the sum of the expected future cash flows (undiscounted and without interest charges) is less than the carrying amount of the asset (or asset group), we recognize an impairment loss. The impairment loss recognized is the amount by which the carrying amount exceeds the fair value. We use a variety of methodologies to determine the fair value of these assets, including discounted cash flow models, which are consistent with the assumptions we believe hypothetical marketplace participants would use.
We test intangible assets determined to have indefinite useful lives, including trademarks, franchise rights and goodwill, for impairment annually, or more frequently if events or circumstances indicate that assets might be impaired. Our Company performs these annual impairment reviews as of the first day of our third fiscal quarter. We use a variety of methodologies in conducting impairment assessments of indefinite-lived intangible assets, including, but not limited to, discounted cash flow models, which are based on the assumptions we believe hypothetical marketplace participants would use. For indefinite-lived intangible assets, other than goodwill, if the carrying amount exceeds the fair value, an impairment charge is recognized in an amount equal to that excess.
We perform impairment tests of goodwill at our reporting unit level, which is one level below our operating segments. Our operating segments are primarily based on geographic responsibility, which is consistent with the way management runs our business. Our operating segments are subdivided into smaller geographic regions or territories that we sometimes refer to as "business units." These business units are also our reporting units. The Bottling Investments operating segment includes all Company-owned or consolidated bottling operations, regardless of geographic location, except for bottling operations managed by CCR, which are included in our North America operating segment. Generally, each Company-owned or consolidated bottling operation within our Bottling Investments operating segment is its own reporting unit. Goodwill is assigned to the reporting unit or units that benefit from the synergies arising from each business combination.
The goodwill impairment test consists of a two-step process, if necessary. The first step is to compare the fair value of a reporting unit to its carrying value, including goodwill. We typically use discounted cash flow models to determine the fair value of a reporting unit. The assumptions used in these models are consistent with those we believe hypothetical marketplace participants would use. If the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying value, the second step of the impairment test must be performed in order to determine the amount of impairment loss, if any. The second step compares the implied fair value of the reporting unit's goodwill with the carrying amount of that goodwill. If the carrying amount of the reporting unit's goodwill exceeds its implied fair value, an impairment charge is recognized in an amount equal to that excess. The loss recognized cannot exceed the carrying amount of goodwill.
Intangible assets acquired in recent transactions are naturally more susceptible to impairment, primarily due to the fact that they are recorded at fair value based on recent operating plans and macroeconomic conditions present at the time of acquisition. Consequently, if operating results and/or macroeconomic conditions deteriorate shortly after an acquisition, it could result in the impairment of the acquired assets. A deterioration of macroeconomic conditions may not only negatively impact the estimated operating cash flows used in our cash flow models, but may also negatively impact other assumptions used in our analyses, including, but not limited to, the estimated cost of capital and/or discount rates. Additionally, as discussed above, in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, we are required to ensure that assumptions used to determine fair value in our analyses are consistent with the assumptions a hypothetical marketplace participant would use. As a result, the cost of capital and/or discount rates used in our analyses may increase or decrease based on market conditions and trends, regardless of whether our Company's actual cost of capital has changed. Therefore, if the cost of capital and/or discount rates change, our Company may recognize an impairment of an intangible asset in spite of realizing actual cash flows that are approximately equal to, or greater than, our previously forecasted amounts.
As of our most recent annual impairment review, the Company had no significant impairments of its intangible assets, individually or in the aggregate. In addition, as of December 31, 2011, we did not have any reporting units with a material amount of goodwill for which it is reasonably likely that they will fail step one of a goodwill impairment test in the near term. However, if macroeconomic conditions worsen, it is possible that we may experience significant impairments of some of our intangible assets, which would require us to recognize impairment charges. Management will continue to monitor the fair value of our intangible assets in future periods.
In 2010, the Company had no significant impairments of its intangible assets, individually or in the aggregate. We acquired CCE's North American business on October 2, 2010, which resulted in the Company recording $14,327 million of intangible assets, including goodwill. Refer to Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. The acquired intangible assets included $5,850 million of bottler franchise rights, which consisted of $5,200 million of franchise rights with indefinite lives and $650 million of franchise rights with definite lives. The franchise rights with indefinite lives represent franchise rights that had previously provided CCE with exclusive and perpetual rights to manufacture and/or distribute certain beverages in
39
specified territories. The franchise rights with definite lives relate to franchise rights that had previously provided CCE with exclusive rights to manufacture and/or distribute certain beverages in specified territories for a finite period of time and, therefore, have been classified as definite-lived intangible assets.
The Company recorded $8,050 million of goodwill in connection with this acquisition that was assigned to the North America operating segment, of which $170 million is tax deductible. This goodwill is primarily related to synergistic value created from having a unified operating system that will strategically position us to better market and distribute our nonalcoholic beverage brands in North America. It also includes certain other intangible assets that do not qualify for separate recognition, such as an assembled workforce.
In 2009, the Company recognized a $23 million impairment charge due to a change in the expected useful life of an intangible asset, which was previously determined to have an indefinite life. Refer to the heading "Operations Review — Other Operating Charges" below and Note 16 and Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Hyperinflationary Economies
Our Company conducts business in more than 200 countries, some of which have been deemed to be hyperinflationary economies due to excessively high inflation rates in recent years. These economies create financial exposure to the Company. Venezuela was deemed to be a hyperinflationary economy subsequent to December 31, 2009.
As of December 31, 2009, two main exchange rate mechanisms existed in Venezuela. The first exchange rate mechanism is known as the official rate of exchange ("official rate"), which is set by the Venezuelan government. In order to utilize the official rate, entities must seek approval from the government-operated Foreign Exchange Administration Board ("CADIVI"). As of December 31, 2009, the official rate set by the Venezuelan government was 2.15 bolivars per U.S. dollar. The second exchange rate mechanism was known as the parallel rate, which in some circumstances provided entities with a more liquid exchange through the use of a series of transactions via a broker.
Subsequent to December 31, 2009, Venezuela was determined to be a hyperinflationary economy, and the Venezuelan government devalued the bolivar by resetting the official rate to 2.6 bolivars per U.S. dollar for essential goods and 4.3 bolivars per U.S. dollar for nonessential goods. In accordance with hyperinflationary accounting under accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, our local subsidiary was required to use the U.S. dollar as its functional currency. As a result, we remeasured the net assets of our Venezuelan subsidiary using the official rate for nonessential goods of 4.3 bolivars per U.S. dollar. During the first quarter of 2010, we recorded a loss of $103 million related to the remeasurement of our Venezuelan subsidiary's net assets. The loss was recorded in the line item other income (loss) — net in our consolidated statement of income. We classified the impact of the remeasurement loss in the line item effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents in our consolidated statement of cash flows.
In early June 2010, the Venezuelan government introduced a newly regulated foreign currency exchange system known as the Transaction System for Foreign Currency Denominated Securities ("SITME"). This new system, which is subject to annual limits, replaced the parallel market whereby entities domiciled in Venezuela are able to exchange their bolivars to U.S. dollars through authorized financial institutions (commercial banks, savings and lending institutions, etc.).
In December 2010, the Venezuelan government announced that it was eliminating the official rate of 2.6 bolivars per U.S. dollar for essential goods. As a result, there are currently only two exchange rates available for remeasuring bolivar-denominated transactions, the official rate of 4.3 bolivars per U.S. dollar for nonessential goods and the SITME rate. As discussed above, the Company has remeasured the net assets of our Venezuelan subsidiary using the official rate for nonessential goods of 4.3 bolivars per U.S. dollar since January 1, 2010. Therefore, the elimination of the official rate for essential goods had no impact on the remeasurement of the net assets of our Venezuelan subsidiary. We continue to use the official exchange rate for nonessential goods to remeasure the financial statements of our Venezuelan subsidiary. If the official exchange rate devalues further, it would result in our Company recognizing additional foreign currency exchange losses in our consolidated financial statements. As of December 31, 2011, our Venezuelan subsidiary held monetary assets of $300 million.
In addition to the foreign currency exchange exposure related to our Venezuelan subsidiary's net assets, we also sell concentrate to our bottling partner in Venezuela from outside the country. These sales are denominated in U.S. dollars. Some of our concentrate sales were approved by the CADIVI to receive the official rate for essential goods of 2.6 bolivars per U.S. dollar prior to the elimination of the official rate for essential goods in December 2010. Prior to the elimination of the official rate for essential goods, our bottling partner in Venezuela was able to convert bolivars to U.S. dollars to settle our receivables related to sales approved by the CADIVI. However, if we are unable to utilize a government-approved exchange rate mechanism to settle future concentrate sales to our bottling partner in Venezuela, the Company's outstanding receivables balance related to these sales will continue to increase. In addition, we have certain intangible assets associated with products sold in Venezuela. If we are unable to utilize a government-approved exchange rate mechanism for concentrate sales, or if the bolivar further devalues, it could result in the impairment of these intangible assets. As of December 31, 2011, the carrying value of our accounts
40
receivable from our bottling partner in Venezuela and intangible assets associated with products sold in Venezuela was $147 million. The revenues and cash flows associated with concentrate sales to our bottling partner in Venezuela in 2012 are not anticipated to be significant to the Company's consolidated financial statements.
Pension Plan Valuations
Our Company sponsors and/or contributes to pension and postretirement health care and life insurance benefit plans covering substantially all U.S. employees. We also sponsor nonqualified, unfunded defined benefit pension plans for certain associates and participate in multi-employer pension plans in the United States. In addition, our Company and its subsidiaries have various pension plans and other forms of postretirement arrangements outside the United States.
Management is required to make certain critical estimates related to actuarial assumptions used to determine our pension expense and related obligation. We believe the most critical assumptions are related to (1) the discount rate used to determine the present value of the liabilities and (2) the expected long-term rate of return on plan assets. All of our actuarial assumptions are reviewed annually. Changes in these assumptions could have a material impact on the measurement of our pension expense and related obligation.
At each measurement date, we determine the discount rate by reference to rates of high-quality, long-term corporate bonds that mature in a pattern similar to the future payments we anticipate making under the plans. As of December 31, 2011 and 2010, the weighted-average discount rate used to compute our benefit obligation was 4.75 percent and 5.5 percent, respectively.
The expected long-term rate of return on plan assets is based upon the long-term outlook of our investment strategy as well as our historical returns and volatilities for each asset class. We also review current levels of interest rates and inflation to assess the reasonableness of our long-term rates. Our pension plan investment objective is to ensure all of our plans have sufficient funds to meet their benefit obligations when they become due. As a result, the Company periodically revises asset allocations, where appropriate, to improve returns and manage risk. The weighted-average expected long-term rate of return used to calculate our net periodic benefit cost was 8.25 percent and 8.0 percent in 2011 and 2010, respectively.
In 2011, the Company's total pension expense related to defined benefit plans was $249 million. In 2012, we expect our total pension expense to be approximately $200 million. The anticipated decrease is primarily due to approximately $953 million of contributions the Company expects to make to various plans in 2012, of which $900 million was contributed to the Company's U.S. pension plans during the first quarter of 2012. The expected favorable impact of this item will be partially offset by the expected unfavorable impact of a decrease in the weighted-average discount rate used to calculate the Company's benefit obligation. The estimated impact of an additional 50-basis-point decrease in the discount rate on our 2012 pension expense is an increase to our pension expense of approximately $39 million. Additionally, the estimated impact of a 50-basis-point decrease in the expected long-term rate of return on plan assets on our 2012 pension expense is an increase to our pension expense of approximately $25 million.
The sensitivity information provided above is based only on changes to the actuarial assumptions used for our U.S. pension plans. As of December 31, 2011, the Company's primary U.S. plans represented 58 percent and 60 percent of the Company's consolidated projected pension benefit obligation and pension assets, respectively. Refer to Note 13 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information about our pension plans and related actuarial assumptions.
Revenue Recognition
We recognize revenue when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, delivery of products has occurred, the sales price is fixed or determinable, and collectibility is reasonably assured. For our Company, this generally means that we recognize revenue when title to our products is transferred to our bottling partners, resellers or other customers. Title usually transfers upon shipment to or receipt at our customers' locations, as determined by the specific sales terms of each transaction. Our sales terms do not allow for a right of return except for matters related to any manufacturing defects on our part.
Our customers can earn certain incentives, which are included in deductions from revenue, a component of net operating revenues in our consolidated statements of income. These incentives include, but are not limited to, cash discounts, funds for promotional and marketing activities, volume-based incentive programs and support for infrastructure programs. Refer to Note 1 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. The aggregate deductions from revenue recorded by the Company in relation to these programs, including amortization expense on infrastructure programs, were $5.8 billion, $5.0 billion and $4.5 billion in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. In preparing the financial statements, management must make estimates related to the contractual terms, customer performance and sales volume to determine the total amounts recorded as deductions from revenue. Management also considers past results in making such estimates. The actual amounts ultimately paid may be different from our estimates. Such differences are recorded once they have been determined, and have historically not been significant.
41
Income Taxes
Our annual tax rate is based on our income, statutory tax rates and tax planning opportunities available to us in the various jurisdictions in which we operate. Significant judgment is required in determining our annual tax expense and in evaluating our tax positions. We establish reserves to remove some or all of the tax benefit of any of our tax positions at the time we determine that the positions become uncertain based upon one of the following: (1) the tax position is not "more likely than not" to be sustained, (2) the tax position is "more likely than not" to be sustained, but for a lesser amount, or (3) the tax position is "more likely than not" to be sustained, but not in the financial period in which the tax position was originally taken. For purposes of evaluating whether or not a tax position is uncertain, (1) we presume the tax position will be examined by the relevant taxing authority that has full knowledge of all relevant information, (2) the technical merits of a tax position are derived from authorities such as legislation and statutes, legislative intent, regulations, rulings and case law and their applicability to the facts and circumstances of the tax position, and (3) each tax position is evaluated without considerations of the possibility of offset or aggregation with other tax positions taken. We adjust these reserves, including any impact on the related interest and penalties, in light of changing facts and circumstances, such as the progress of a tax audit. Refer to the heading "Operations Review — Income Taxes" below.
A number of years may elapse before a particular matter for which we have established a reserve is audited and finally resolved. The number of years with open tax audits varies depending on the tax jurisdiction. The tax benefit that has been previously reserved because of a failure to meet the "more likely than not" recognition threshold would be recognized in our income tax expense in the first interim period when the uncertainty disappears under any one of the following conditions: (1) the tax position is "more likely than not" to be sustained, (2) the tax position, amount, and/or timing is ultimately settled through negotiation or litigation, or (3) the statute of limitations for the tax position has expired. Settlement of any particular issue would usually require the use of cash.
Tax law requires items to be included in the tax return at different times than when these items are reflected in the consolidated financial statements. As a result, the annual tax rate reflected in our consolidated financial statements is different from that reported in our tax return (our cash tax rate). Some of these differences are permanent, such as expenses that are not deductible in our tax return, and some differences reverse over time, such as depreciation expense. These timing differences create deferred tax assets and liabilities. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on temporary differences between the financial reporting and tax bases of assets and liabilities. The tax rates used to determine deferred tax assets or liabilities are the enacted tax rates in effect for the year and manner in which the differences are expected to reverse. Based on the evaluation of all available information, the Company recognizes future tax benefits, such as net operating loss carryforwards, to the extent that realizing these benefits is considered more likely than not.
We evaluate our ability to realize the tax benefits associated with deferred tax assets by analyzing our forecasted taxable income using both historical and projected future operating results; the reversal of existing taxable temporary differences; taxable income in prior carryback years (if permitted); and the availability of tax planning strategies. A valuation allowance is required to be established unless management determines that it is more likely than not that the Company will ultimately realize the tax benefit associated with a deferred tax asset. As of December 31, 2011, the Company's valuation allowances on deferred tax assets were $859 million and are primarily related to uncertainties regarding the future realization of recorded tax benefits on tax loss carryforwards generated in various jurisdictions. Current evidence does not suggest we will realize sufficient taxable income of the appropriate character (e.g., capital gain versus ordinary income) within the carryforward period to allow us to realize these deferred tax benefits. If we were to identify and implement tax planning strategies to recover these deferred tax assets or generate sufficient income of the appropriate character in these jurisdictions in the future, it could lead to the reversal of these valuation allowances and a reduction of income tax expense. The Company believes it will generate sufficient future taxable income to realize the tax benefits related to the remaining net deferred tax assets in our consolidated balance sheets.
The Company does not record a U.S. deferred tax liability for the excess of the book basis over the tax basis of its investments in foreign corporations to the extent that the basis difference results from earnings that meet the indefinite reversal criteria. This criteria is met if the foreign subsidiary has invested, or will invest, the undistributed earnings indefinitely. The decision as to the amount of undistributed earnings that the Company intends to maintain in non-U.S. subsidiaries takes into account items including, but not limited to, forecasts and budgets of financial needs of cash for working capital, liquidity plans, capital improvement programs, merger and acquisition plans, and planned loans to other non-U.S. subsidiaries. The Company also evaluates its expected cash requirements in the United States. Other factors that can influence that determination are local restrictions on remittances (for example, in some countries a central bank application and approval are required in order for the Company's local country subsidiary to pay a dividend), economic stability and asset risk. As of December 31, 2011, undistributed earnings of the Company's foreign subsidiaries that met the indefinite reversal criteria amounted to $23.5 billion. Refer to Note 14 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
The Company's effective tax rate is expected to be approximately 24.0 percent to 25.0 percent in 2012. This estimated tax rate does not reflect the impact of any unusual or special items that may affect our tax rate in 2012.
42
Recent Accounting Standards and Pronouncements
Refer to Note 1 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for a discussion of recent accounting standards and pronouncements.
Operations Review
Our organizational structure as of December 31, 2011, consisted of the following operating segments, the first six of which are sometimes referred to as "operating groups" or "groups": Eurasia and Africa; Europe; Latin America; North America; Pacific; Bottling Investments; and Corporate. For further information regarding our operating segments, refer to Note 19 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements
In order to continually improve upon the Company's operating performance, from time to time, we engage in buying and selling ownership interests in bottling partners and other manufacturing operations. In addition, we also acquire brands or enter into license agreements for certain brands to supplement our beverage offerings. These items impact our operating results and certain key metrics used by management in assessing the Company's performance.
Unit case volume growth is a key metric used by management to evaluate the Company's performance because it measures demand for our products at the consumer level. The Company's unit case volume represents the number of unit cases (or unit case equivalents) of Company beverage products directly or indirectly sold by the Company and its bottling partners to customers and, therefore, reflects unit case volume for consolidated and unconsolidated bottlers. Refer to the heading "Beverage Volume" below.
Concentrate sales volume represents the amount of concentrates and syrups (in all cases expressed in equivalent unit cases) sold by, or used in finished products sold by, the Company to its bottling partners or other customers. Refer to the heading "Beverage Volume" below.
Our Bottling Investments segment and our other finished products operations, including those managed by CCR, typically generate net operating revenues by selling sparkling beverages and a variety of still beverages, such as juices and juice drinks, energy and sports drinks, ready-to-drink teas and coffees, and certain water products, to retailers or to distributors, wholesalers and bottling partners who distribute them to retailers. In addition, in the United States, we manufacture fountain syrups and sell them to fountain retailers such as restaurants and convenience stores who use the fountain syrups to produce beverages for immediate consumption, or to authorized fountain wholesalers or bottling partners who resell the fountain syrups to fountain retailers. For these finished products operations, we recognize the associated concentrate sales volume at the time the unit case or unit case equivalent is sold to the customer. Our concentrate operations typically generate net operating revenues by selling concentrates and syrups to authorized bottling and canning operations. For these concentrate operations, we recognize concentrate revenue and concentrate sales volume when we sell concentrate to the authorized unconsolidated bottling and canning operations, and we typically report unit case volume when finished products manufactured from the concentrates and syrups are sold to the customer. When we analyze our net operating revenues we generally consider the following four factors: (1) volume growth (unit case volume or concentrate sales volume, as appropriate), (2) structural changes, (3) changes in price, product and geographic mix and (4) foreign currency fluctuations. Refer to the heading "Net Operating Revenues" below.
"Structural changes" generally refers to acquisitions or dispositions of bottling, distribution or canning operations and consolidation or deconsolidation of bottling and distribution entities for accounting purposes. Typically, structural changes do not impact the Company's unit case volume on a consolidated basis or at the geographic operating segment level. We recognize unit case volume for all sales of Company beverage products regardless of our ownership interest in the bottling partner, if any. However, our Bottling Investments operating segment is generally impacted by structural changes because it only includes the unit case volume of consolidated bottlers.
The Company sells concentrates and syrups to both consolidated and unconsolidated bottling partners. The ownership structure of our bottling partners impacts the timing of recognizing concentrate revenue and concentrate sales volume. When we sell concentrates or syrups to our consolidated bottling partners, we are not able to recognize the concentrate revenue or concentrate sales volume until the bottling partner has sold finished products manufactured from the concentrates or syrups to a customer. When we sell concentrates or syrups to our unconsolidated bottling partners, we recognize the concentrate revenue and concentrate sales volume when the concentrates or syrups are sold to the bottling partner. The subsequent sale of the finished products manufactured from the concentrates or syrups to a customer does not impact the timing of recognizing the concentrate revenue or concentrate sales volume.
43
"Acquired brands" refers to brands acquired during the past 12 months. Typically, the Company has not reported unit case volume or recognized concentrate sales volume related to acquired brands in periods prior to the closing of the transaction. Therefore, the unit case volume and concentrate sales volume from the sale of these brands is incremental to prior year volume. We do not generally consider acquired brands to be structural changes.
"License agreements" refers to brands not owned by the Company, but for which we hold certain rights, generally including, but not limited to, distribution rights, and we derive an economic benefit from the ultimate sale of these brands. Typically, the Company has not reported unit case volume or recognized concentrate sales volume related to these brands in periods prior to the beginning of the term of the license agreement. Therefore, the unit case volume and concentrate sales volume from the sale of these brands is incremental to prior year volume. We do not generally consider new license agreements to be structural changes.
Although there were no significant transactions that occurred during 2011, the following transactions and agreements impacted the Company's operating results during both 2011 and 2010:
• |
on October 2, 2010, in legally separate transactions, we acquired CCE's North American business and entered into a license agreement with DPS; |
• |
on October 2, 2010, we sold all of our ownership interests in our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE; and |
• |
on January 1, 2010, we deconsolidated certain entities, primarily bottling operations, as a result of the Company's adoption of new accounting guidance issued by the FASB. |
The impact that each of the aforementioned items had on the Company's consolidated financial statements is discussed throughout this report, as appropriate. The sections below are intended to provide an overview of the impact these items had on our 2011 and 2010 operating results and are expected to have on key metrics used by management.
Acquisition of CCE's North American Business and the DPS License Agreements
Immediately prior to our October 2, 2010, acquisition of CCE's North American business, the Company owned 33 percent of CCE's outstanding common stock. This ownership represented our indirect ownership interest in both CCE's North American business and its European operations. On October 2, 2010, the Company acquired the remaining 67 percent of CCE's North American business not already owned by the Company for consideration that included the Company's indirect ownership interest in CCE's European operations. As a result of this transaction, the Company now owns 100 percent of CCE's North American business and does not own any interest in New CCE's European operations. The operating results of CCE's North American business were included in our consolidated financial statements starting October 2, 2010. The operating results of New CCE do not directly impact the Company's consolidated financial statements, since we have no ownership interest in this entity. Refer to the heading "Our Business — General" above and Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional details related to the acquisition.
On October 2, 2010, the Company also entered into an agreement with DPS to distribute certain DPS brands in territories where these brands were distributed by CCE prior to our acquisition of CCE's North American business. The license agreements replaced agreements between DPS and CCE existing immediately prior to our acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to the heading "Our Business — General" above and Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional details related to these new license agreements.
Prior to the acquisition of CCE's North American business and entering into the DPS license agreements, the Company's North America operating segment was predominantly a concentrate operation. As a result of the acquisition of CCE's North American business and the DPS license agreements, the North America operating segment is now predominantly a finished products operation. Generally, finished products operations produce higher net operating revenues but lower gross profit margins and operating margins compared to concentrate operations. Refer to "Item 1. Business — Products and Brands" for additional discussion of the differences between the Company's concentrate operations and our finished products operations. These transactions resulted in higher net operating revenues but lower gross profit margins and operating margins for the North America operating segment and our consolidated operating results.
Prior to the acquisition of CCE's North American business, the Company reported unit case volume for the sale of Company beverage products sold by CCE. After the transaction closing, we reported unit case volume of Company beverage products just as we had prior to the transaction.
Prior to the acquisition of CCE's North American business, the Company recognized concentrate sales volume at the time we sold the concentrate to CCE. Upon the closing of the transaction, we do not recognize the concentrate sales volume until CCR has sold finished products manufactured from concentrate to a customer.
44
The DPS license agreements impact both the Company's unit case and concentrate sales volume. Sales made pursuant to these license agreements represent acquired volume and are incremental unit case volume and concentrate sales volume to the Company only during the 12-month period following the acquisition. Prior to entering into the license agreements, the Company did not include the DPS brands as unit case volume or concentrate sales volume, as these brands were not Company beverage products. Refer to the heading "Unit Case Volume" below for additional information.
Prior to the acquisition, we recognized the revenues and profits associated with concentrate sales when the concentrate was sold to CCE, excluding the portion that was deemed to be intercompany due to our previous ownership interest in CCE. However, subsequent to the acquisition, the Company does not recognize the revenues and profits associated with concentrate sold to CCE's North American business until the finished products manufactured from those concentrates are sold. For example, in 2010, most of our pre-Easter concentrate sales to CCE impacted our first quarter operating results. In 2011, our Easter-related finished product sales had a greater impact on our second quarter operating results. As a result of this transaction, the Company does not have an indirect ownership interest in New CCE's European operations. Therefore, we are no longer required to defer the portion of revenues and profits associated with concentrate sales to New CCE.
The acquisition of CCE's North American business has resulted in a significant adjustment to our overall cost structure, especially in North America. The following inputs represent a substantial portion of the Company's total cost of goods sold: (1) sweeteners, (2) metals, (3) juices and (4) polyethylene terephthalate ("PET"). The bulk of these costs resides within our North America and Bottling Investments operating segments. The cost to purchase these inputs increased significantly in 2011 when compared to 2010. As a result, the Company incurred incremental costs of $800 million related to these inputs during 2011. The Company increased our hedging activities related to certain commodities in order to mitigate a portion of the price risk associated with forecasted purchases. Many of the derivative financial instruments used by the Company to mitigate the risk associated with these commodity exposures do not qualify for hedge accounting. As a result, the changes in fair value of these derivative instruments have been, and will continue to be, included as a component of net income in each reporting period. Refer to the heading "Gross Profit Margin" below and Note 5 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding our commodity hedging activity. The Company anticipates that the cost of underlying commodities will continue to face upward pressure in 2012. We currently expect the incremental impact of commodity costs related to the inputs described above, primarily juices and sweeteners, to range between $350 million and $450 million on our full year 2012 consolidated results.
In 2010, the gross profit for our North America operating segment was negatively impacted by $235 million, primarily due to the elimination of gross profit in inventory on intercompany sales and an inventory fair value adjustment as a result of the acquisition. Refer to the headings "Gross Profit Margin" and "Operating Income and Operating Margin" below.
The acquisition of CCE's North American business increased the Company's selling, general and administrative expenses in 2011 and 2010, primarily due to delivery-related expenses. Selling, general and administrative expenses are typically higher, as a percentage of net operating revenues, for finished products operations compared to concentrate operations. Selling, general and administrative expenses were also negatively impacted by the amortization of definite-lived intangible assets acquired in the acquisition. The Company recorded $650 million of definite-lived acquired franchise rights that are being amortized over a weighted-average life of approximately eight years from the date of acquisition, which is equal to the weighted-average remaining contractual term of the acquired franchise rights. In addition, the Company recorded $380 million of customer rights that are being amortized over 20 years. We estimate the amortization expense related to these definite-lived intangible assets to be approximately $100 million per year for the next several years, which will be recorded in selling, general and administrative expenses.
In connection with the Company's acquisition of CCE's North American business, we assumed $7,602 million of long-term debt, which had an estimated fair value of $9,345 million as of the acquisition date. In accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, we recorded the assumed debt at its fair value as of the acquisition date. Refer to Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
During 2011, the Company issued $2,979 million of long-term debt. We used $979 million of this newly issued debt and paid a premium of $208 million to exchange $1,022 million of existing long-term debt that was assumed in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business in the fourth quarter of 2010. The remaining cash from the issuance was used to reduce the Company's outstanding commercial paper balance and exchange a certain amount of short-term debt.
45
During the fourth quarter of 2011, the Company extinguished long-term debt that had a carrying value of $20 million and was not scheduled to mature until 2012. This debt was outstanding prior to the Company's acquisition of CCE's North American business. In addition, the Company repurchased long-term debt during 2011 that was assumed in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. The repurchased debt included $99 million in unamortized fair value adjustments recorded as part of our purchase accounting for the CCE transaction and was settled throughout the year as follows:
• |
During the first quarter of 2011, the Company repurchased all of our outstanding U.K. pound sterling notes that had a carrying value of $674 million;
|
• |
During the second quarter of 2011, the Company repurchased long-term debt that had a carrying value of $42 million; and
|
• |
During the third quarter of 2011, the Company repurchased long-term debt that had a carrying value of $19 million.
|
The Company recorded a net charge of $9 million in the line item interest expense in our consolidated statement of income during the year ended December 31, 2011. This net charge was due to the exchange, repurchase and/or extinguishment of long-term debt described above.
On November 15, 2010, the Company issued $4,500 million of long-term notes and used some of the proceeds to repurchase $2,910 million of long-term debt. The Company used the remaining cash from the issuance to reduce our outstanding commercial paper balance. The repurchased debt consisted of $1,827 million of debt assumed in our acquisition of CCE's North American business and $1,083 million of the Company's debt that was outstanding prior to the acquisition. The Company recorded a charge of $342 million in 2010 related to the premiums paid to repurchase the long-term debt and the costs associated with the settlement of treasury rate locks issued in connection with the debt tender offer.
Refer to the heading "Interest Expense" below and Note 10 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information related to the Company's long-term debt balance.
In 2010, we recognized a gain of $4,978 million due to the remeasurement of our equity interest in CCE to fair value upon the close of the transaction. This gain was classified in the line item other income (loss) — net in our consolidated statement of income.
Although our 2010 operating results and certain key metrics were affected by these structural changes, our 2011 consolidated financial statements reflect 12 months of operating results of the acquired CCE North American business and DPS license agreements compared to three months in 2010. Therefore, these structural changes had a much larger impact on our operating results and certain key metrics in 2011, when compared to 2010.
Prior to the closing of this acquisition, we had accounted for our investment in CCE under the equity method of accounting. Under the equity method of accounting, we recorded our proportionate share of CCE's net income or loss in the line item equity income (loss) — net in our consolidated statements of income. However, as a result of this transaction, beginning October 2, 2010, the Company no longer records equity income or loss related to CCE; and therefore, this transaction negatively impacted the amount of equity income the Company recorded during both 2011 and 2010. Refer to the heading "Equity Income (Loss) — Net" below.
Divestiture of Norwegian and Swedish Bottling Operations
The divestiture of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations had no impact on our consolidated unit case volume and consolidated concentrate sales volume, for the same reasons discussed above in relation to our acquisition of CCE's North American business. The divestiture of these bottling operations reduced unit case volume for the Bottling Investments operating segment. In addition, the divestiture reduced net operating revenues and net income for our consolidated operating results and the Bottling Investments operating segment. However, since we divested a finished products business, it had a positive impact on our gross profit margins and operating margins. Furthermore, the impact these divestitures had on the Company's net operating revenues was partially offset by the concentrate revenues that were recognized on sales to these bottling operations. These concentrate sales had previously been eliminated because they were intercompany transactions. The net impact to net operating revenues was included as a structural change in our analysis of changes to net operating revenues. Refer to the heading "Net Operating Revenues" below.
This divestiture resulted in a gain of $597 million in 2010, which was classified in the line item other income (loss) — net in our consolidated statement of income. In 2011, the Company recorded charges of $5 million related to the finalization of working capital adjustments in connection with the divestiture of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations. These charges reduced the transaction gain the Company previously reported in 2010.
46
Impact of New Accounting Guidance
Beginning January 1, 2010, we deconsolidated certain entities as a result of the Company's adoption of new accounting guidance issued by the FASB. These entities are primarily bottling operations, and the Company accounted for them under the equity method of accounting upon deconsolidation. The entities that were deconsolidated as a result of this change in accounting guidance accounted for 3 percent of the Company's consolidated net operating revenues and less than 1 percent of net income attributable to shareowners of The Coca-Cola Company in 2009. Refer to the heading "Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates — Principles of Consolidation" above. These entities accounted for 4 percent of the Company's equity income in 2010. Refer to the heading "Equity Income (Loss) — Net" below. The impact that the deconsolidation of these entities had on net operating revenues was included as a structural change. Refer to the heading "Net Operating Revenues" below.
Beverage Volume
We measure the volume of Company beverage products sold in two ways: (1) unit cases of finished products and (2) concentrate sales. As used in this report, "unit case" means a unit of measurement equal to 192 U.S. fluid ounces of finished beverage (24 eight-ounce servings); and "unit case volume" means the number of unit cases (or unit case equivalents) of Company beverage products directly or indirectly sold by the Company and its bottling partners to customers. Unit case volume primarily consists of beverage products bearing Company trademarks. Also included in unit case volume are certain products licensed to, or distributed by, our Company, and brands owned by Coca-Cola system bottlers for which our Company provides marketing support and from the sale of which we derive economic benefit. In addition, unit case volume includes sales by joint ventures in which the Company has an equity interest. We believe unit case volume is one of the measures of the underlying strength of the Coca-Cola system because it measures trends at the consumer level. The unit case volume numbers used in this report are derived based on estimates received by the Company from its bottling partners and distributors. Concentrate sales volume represents the amount of concentrates and syrups (in all cases expressed in equivalent unit cases) sold by, or used in finished beverages sold by, the Company to its bottling partners or other customers. Unit case volume and concentrate sales volume growth rates are not necessarily equal during any given period. Factors such as seasonality, bottlers' inventory practices, supply point changes, timing of price increases, new product introductions and changes in product mix can impact unit case volume and concentrate sales volume and can create differences between unit case volume and concentrate sales volume growth rates. In addition to the items mentioned above, the impact of unit case volume from certain joint ventures, in which the Company has an equity interest, but to which the Company does not sell concentrates or syrups, may give rise to differences between unit case volume and concentrate sales volume growth rates.
Information about our volume growth by operating segment is as follows:
Percent Change
|
|||||||||||
2011 vs. 2010 |
2010 vs. 2009 |
||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, |
Unit Cases1,2
|
Concentrate
Sales
|
Unit Cases1,2
|
Concentrate
Sales
|
|||||||
Worldwide |
5 |
% |
5 |
% |
5 |
% |
5 |
% |
|||
Eurasia & Africa |
6 |
% |
5 |
% |
12 |
% |
12 |
% |
|||
Europe |
2 |
1 |
— |
— |
|||||||
Latin America |
6 |
5 |
5 |
7 |
|||||||
North America |
4 |
4 |
2 |
2 |
|||||||
Pacific |
5 |
6 |
6 |
6 |
|||||||
Bottling Investments |
— |
N/A |
(1 |
) |
N/A |
||||||
1 |
Bottling Investments operating segment data reflects unit case volume growth for consolidated bottlers only. |
2 |
Geographic segment data reflects unit case volume growth for all bottlers in the applicable geographic areas, both consolidated and unconsolidated. |
47
Unit Case Volume
The Coca-Cola system sold approximately 26.7 billion unit cases of our products in 2011, approximately 25.5 billion unit cases in 2010 and approximately 24.4 billion unit cases in 2009.
Year Ended December 31, 2011, versus Year Ended December 31, 2010
In Eurasia and Africa, unit case volume increased 6 percent, which consisted of 5 percent growth in sparkling beverages and 13 percent growth in still beverages. The group's unit case volume growth was largely due to growth in our key markets, including India and Turkey. India experienced 12 percent unit case volume growth, which consisted of 12 percent growth in sparkling beverages and 11 percent growth in still beverages. India's growth in sparkling beverages was primarily due to 17 percent growth in Trademark Sprite, 15 percent growth in Trademark Thums Up and 11 percent growth in Trademark Coca-Cola. Still beverages in India benefited from 14 percent growth in our Kinley water brand and 11 percent growth in Maaza, a component of our juice portfolio in India. The group also benefited from unit case volume growth of 10 percent in Turkey, which included strong growth in brand Coca-Cola. Unit case volume grew 5 percent in Russia, primarily due to our acquisition of Nidan in the third quarter of 2010. Excluding the impact of the acquired Nidan juice, Russia's overall unit case volume declined 2 percent in 2011. Eurasia and Africa also benefited from unit case volume growth of 8 percent in the Company's Middle East and North Africa Business Unit despite ongoing geopolitical challenges in the region. The group's unit case volume growth in the markets described above was partially offset by a 2 percent unit case volume decline in South Africa. This decline was primarily due to the impact of unfavorable weather conditions during our peak summer selling season as well as higher pricing in the marketplace.
Unit case volume in Europe increased 2 percent, despite an unseasonably cold and rainy summer selling season and moderate consumer confidence. The Company achieved these results by strategically tailoring our price and package offerings to meet the needs of each market with consideration for the current economic environment. The group benefited from the Company's successful launch of our 125th anniversary marketing campaign as well as other integrated marketing campaigns. The group had 2 percent growth in sparkling beverages, including 3 percent growth in Trademark Coca-Cola and growth of 14 percent in Coca-Cola Zero. Unit case volume for still beverages increased 2 percent, led by growth in energy drinks and tea. Germany's unit case volume increased 6 percent, primarily attributable to 6 percent growth in Trademark Coca-Cola and 13 percent growth in Trademark Fanta. Our German business continued to benefit from the Company's bottler restructuring efforts and our effective marketing campaigns. In addition, France and Great Britain had growth of 5 percent and 4 percent, respectively, each led by growth in Trademark Coca-Cola.
In Latin America, unit case volume increased 6 percent, which consisted of 4 percent growth in sparkling beverages and 15 percent growth in still beverages. The group's sparkling beverage unit case volume growth was led by 4 percent growth in brand Coca-Cola. Still beverages benefited from the successful performance of Del Valle as well as strong growth in other still beverages, including water and tea. Mexico had unit case volume growth of 9 percent, led by 7 percent growth in sparkling beverages, which included 7 percent growth in Trademark Coca-Cola. In addition, Argentina had 10 percent growth in Trademark Coca-Cola which contributed to its overall unit case volume growth of 10 percent. Argentina's unit case volume growth benefited from strong integrated marketing campaigns, including sponsorship of the Copa America soccer tournament in July. Brazil's unit case volume increased 1 percent despite a general slowdown in the country's economy. The group's unit case volume growth in the markets described above was partially offset by a 10 percent volume decline in Venezuela. The decline in Venezuela is a reflection of the continued economic and political pressures affecting the country.
Unit case volume in North America increased 4 percent, including 3 percent growth attributable to the new license agreements with DPS. The group's unit case volume growth was driven by 3 percent growth in sparkling beverages, primarily due to the sale of Dr Pepper brands under the new license agreements. Coca-Cola Zero continued its strong performance in North America with 11 percent unit case volume growth. Unit case volume for still beverages in North America increased 4 percent, including 12 percent growth in Trademark Powerade, 10 percent growth in Trademark Dasani and 48 percent growth in Gold Peak. The growth in still beverages in North America was partially offset by a decline of 2 percent in juice and juice drinks, a reflection of increased pricing to offset commodity costs. In December 2011, the Company acquired Great Plains Coca-Cola Bottling Company ("Great Plains") in the United States. As a result of this acquisition, we will report volume from cross-licensed brands, primarily Dr Pepper, that were previously distributed by Great Plains. Unit case volume for these cross-licensed brands was 12 million unit cases for full year 2011. The Company began reporting unit case volume for these cross-licensed brands in December 2011.
48
In Pacific, unit case volume increased 5 percent, which consisted of 4 percent growth in sparkling beverages and 8 percent growth in still beverages. The group's volume growth was led by 13 percent growth in China, which included 12 percent growth in sparkling beverages attributable to strong growth in Trademark Sprite, Coca-Cola and Fanta. The group also benefited from China's 16 percent growth in still beverages, including strong growth in Minute Maid Pulpy and other still beverages, including water. In Japan, unit case volume growth was even, reflecting the impact of the earthquake and tsunami that devastated the northern and eastern portions of the country on March 11, 2011. The group's unit case volume growth in the markets described above was partially offset by a 9 percent volume decline in the Philippines.
Unit case volume for Bottling Investments was even when compared to the prior year. The group had growth in key markets where we own or otherwise consolidate bottling operations, including unit case volume growth of 13 percent in China, 12 percent in India and 6 percent in Germany. The Company's consolidated bottling operations accounted for 34 percent, 66 percent and 100 percent of the unit case volume in China, India and Germany, respectively. However, growth in these markets was offset by the unfavorable impact of the Company's sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE during the fourth quarter of 2010 as well as a unit case volume decline of 9 percent in the Philippines where we own 100 percent of the country's bottling operations.
Year Ended December 31, 2010, versus Year Ended December 31, 2009
In Eurasia and Africa, unit case volume increased 12 percent, which consisted of 10 percent growth in sparkling beverages and 21 percent growth in still beverages. The group's unit case volume growth was primarily attributable to 17 percent growth in India, which included growth of 15 percent and 23 percent in sparkling and still beverages, respectively. India's growth in sparkling beverages was led by double-digit growth in Trademarks Sprite, Thums Up and Coca-Cola, which reflected the benefit of successful national marketing programs. Still beverage growth in India included the impact of 22 percent growth in our Maaza juice brand. In addition to growth in India, the group's unit case volume growth included 14 percent growth in Turkey, 8 percent growth in North and West Africa, 16 percent growth in Russia, 20 percent growth in Southern Eurasia, 12 percent growth in East and Central Africa and 5 percent growth in South Africa. The growth across the African continent was attributable to the strong performance of both sparkling and still beverages and the benefit of our FIFA World CupTM activation programs.
Unit case volume in Europe was even, which reflected the impact of continuing difficult macroeconomic conditions throughout certain regions in Europe. The group's unit case volume included unit case volume growth of 5 percent in France, 1 percent in Germany and 2 percent in our Nordic Business Unit. The growth in these regions was offset by unit case volume declines in other regions, including a 7 percent decline in South and Eastern Europe, primarily due to continuing macroeconomic pressures. The group's unit case volume also included unit case volume declines of 2 percent and 1 percent in Italy and Iberia, respectively.
In Latin America, unit case volume increased 5 percent, which consisted of 4 percent growth in sparkling beverages and 9 percent growth in still beverages. The group's unit case volume growth was led by 11 percent growth in Brazil and 3 percent growth in Mexico. Brazil's unit case volume growth was primarily due to 11 percent growth in sparkling beverages, led by 11 percent growth in Trademark Coca-Cola. Mexico's unit case volume growth was impacted by adverse weather conditions. The group's unit case volume growth also included 5 percent growth in our South Latin Business Unit. All of the aforementioned markets benefited from our strong FIFA World CupTM activation programs.
Unit case volume in North America increased 2 percent, including 1 percent attributable to the new license agreements with DPS. The group's unit case volume growth was driven by 5 percent growth in still beverages, led by 19 percent growth in Trademark Powerade, 12 percent growth in teas and 23 percent growth in Trademark Simply. Unit case volume for sparkling beverages in North America increased 1 percent, primarily due to the sale of DPS brands under the new license agreements. Coca-Cola Zero continued its strong performance in North America with 15 percent growth in 2010. The group's strong marketing initiatives, including our FIFA World CupTM activation programs, contributed to the unit case volume growth in North America.
The volume and net operating revenues attributable to the sale of DPS brands have been included as a structural change in our analysis of net operating revenues. Refer to the heading "Net Operating Revenues" below and "Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" above.
In Pacific, unit case volume increased 6 percent, which consisted of 13 percent growth in still beverages and 2 percent growth in sparkling beverages. The group's volume growth was led by 6 percent growth in China, 15 percent growth in the Philippines and 3 percent growth in Japan. China's volume growth included 21 percent growth in juices and juice drinks primarily due to the continued strong momentum of Minute Maid Pulpy, as well as strong growth in other still beverages including water. Tough weather conditions, including flooding in the higher per capita consumption regions, negatively impacted unit case volume in China. In the Philippines, unit case volume growth was led by 14 percent growth in Trademark Coca-Cola. In Japan, the unit case volume growth was driven by successful in-market activations, strong innovation and favorable weather conditions.
49
Included in Japan's unit case volume growth was 5 percent growth in Trademark Coca-Cola, primarily due to strong FIFA World CupTM activation programs and our Coca-Cola Summer Promotion. Japan's unit case volume growth also benefited from 17 percent growth in sports drinks.
Unit case volume for Bottling Investments decreased 1 percent, primarily due to the deconsolidation of certain entities as a result of the Company's adoption of new accounting guidance issued by the FASB. These entities are primarily bottling operations and have been accounted for under the equity method of accounting since they were deconsolidated on January 1, 2010. Refer to the heading "Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates — Principles of Consolidation" and "Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" above. The deconsolidation of these entities negatively impacted the unit case volume for Bottling Investments by approximately 9 percent. Unit case volume for Bottling Investments was also negatively impacted by the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE. The unfavorable impact of the aforementioned items was partially offset by growth in markets where we own or otherwise consolidate the bottling operations. Unit case volume grew 6 percent in China, 17 percent in India, 15 percent in the Philippines and 1 percent in Germany. The Company's consolidated bottling operations account for 33 percent, 66 percent, 100 percent and 100 percent of the unit case volume in China, India, the Philippines and Germany, respectively.
Concentrate Sales Volume
In 2011, concentrate sales volume and unit case volume both grew 5 percent compared to 2010. Likewise, in 2010, concentrate sales volume and unit case volume both grew 5 percent compared to 2009. The differences between concentrate sales volume and unit case volume growth rates for individual operating segments in 2011 and 2010 were primarily due to the timing of concentrate shipments and the impact of unit case volume from certain joint ventures in which the Company has an equity interest, but to which the Company does not sell concentrates, syrups, beverage bases or powders.
50
Analysis of Consolidated Statements of Income
Percent Change
|
|||||||||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
2011 vs. 2010 |
2010 vs. 2009 |
||||||||||||
(In millions except percentages and per share data) |
|||||||||||||||||
NET OPERATING REVENUES |
$ |
46,542 |
$ |
35,119 |
$ |
30,990 |
33 |
% |
13 |
% |
|||||||
Cost of goods sold |
18,216 |
12,693 |
11,088 |
44 |
14 |
||||||||||||
GROSS PROFIT |
28,326 |
22,426 |
19,902 |
26 |
13 |
||||||||||||
GROSS PROFIT MARGIN |
60.9 |
% |
63.9 |
% |
64.2 |
% |
|||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
17,440 |
13,158 |
11,358 |
33 |
16 |
||||||||||||
Other operating charges |
732 |
819 |
313 |
* |
* |
||||||||||||
OPERATING INCOME |
10,154 |
8,449 |
8,231 |
20 |
3 |
||||||||||||
OPERATING MARGIN |
21.8 |
% |
24.1 |
% |
26.6 |
% |
|||||||||||
Interest income |
483 |
317 |
249 |
52 |
27 |
||||||||||||
Interest expense |
417 |
733 |
355 |
(43 |
) |
106 |
|||||||||||
Equity income (loss) — net |
690 |
1,025 |
781 |
(33 |
) |
31 |
|||||||||||
Other income (loss) — net |
529 |
5,185 |
40 |
* |
* |
||||||||||||
INCOME BEFORE INCOME TAXES |
11,439 |
14,243 |
8,946 |
(20 |
) |
59 |
|||||||||||
Income taxes |
2,805 |
2,384 |
2,040 |
18 |
17 |
||||||||||||
Effective tax rate |
24.5 |
% |
16.7 |
% |
22.8 |
% |
|||||||||||
CONSOLIDATED NET INCOME |
8,634 |
11,859 |
6,906 |
(27 |
) |
72 |
|||||||||||
Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests |
62 |
50 |
82 |
24 |
(39 |
) |
|||||||||||
|
NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO SHAREOWNERS OF
THE COCA-COLA COMPANY
|
$ |
8,572 |
$ |
11,809 |
$ |
6,824 |
(27 |
)% |
73 |
% |
|||||||
BASIC NET INCOME PER SHARE1
|
$ |
3.75 |
$ |
5.12 |
$ |
2.95 |
(27 |
)% |
74 |
% |
|||||||
DILUTED NET INCOME PER SHARE1
|
$ |
3.69 |
$ |
5.06 |
$ |
2.93 |
(27 |
)% |
73 |
% |
|||||||
* |
Calculation is not meaningful. |
1 |
Basic net income per share and diluted net income per share are calculated based on net income attributable to shareowners of The Coca-Cola Company. |
51
Net Operating Revenues
Year Ended December 31, 2011, versus Year Ended December 31, 2010
The Company's net operating revenues increased $11,423 million, or 33 percent.
Net operating revenues for the North America operating segment increased $9,366 million, or 84 percent. This increase primarily reflects the impact of structural changes related to the acquisition of CCE's North American operations in addition to the impact of our new license agreements with DPS. Net operating revenues for the North America operating segment also included a 1 percent increase in pricing to retailers, driven by a 2 percent increase in pricing on sparkling beverages, and a 1 percent favorable impact due to foreign currency exchange fluctuations.
The following table illustrates, on a percentage basis, the estimated impact of key factors resulting in the increase (decrease) in net operating revenues for each of our international and Bottling Investments operating segments:
Percent Change 2011 vs. 2010 |
||||||||||||||
Volume2
|
Structural Changes |
Price, Product &
Geographic Mix
|
Currency
Fluctuations
|
Total |
||||||||||
International (including Bottling Investments)1
|
5 |
% |
(3 |
)% |
2 |
% |
4 |
% |
8 |
% |
||||
Eurasia & Africa |
5 |
% |
— |
% |
7 |
% |
(1 |
)% |
11 |
% |
||||
Europe |
1 |
— |
— |
3 |
4 |
|||||||||
Latin America |
5 |
(2 |
) |
7 |
4 |
14 |
||||||||
Pacific |
6 |
— |
(2 |
) |
7 |
11 |
||||||||
Bottling Investments |
4 |
(8 |
) |
3 |
4 |
3 |
||||||||
1 |
Represents the total change in net operating revenues for Bottling Investments and each of our geographic operating segments, excluding North America. |
2 |
Represents the percent change in net operating revenues attributable to the increase (decrease) in concentrate sales volume for our geographic operating segments (expressed in equivalent unit cases). For our Bottling Investments operating segment, this represents the percent change in net operating revenues attributable to the increase (decrease) in unit case volume for the Bottling Investments operating segment after considering the impact of structural changes. Our Bottling Investments operating segment data reflects unit case volume growth for consolidated bottlers only. Refer to the heading "Beverage Volume" above. |
Refer to the heading "Beverage Volume" above for additional information related to changes in our unit case and concentrate sales volume.
The structural change in the Bottling Investments operating segment was primarily related to the sale of all our ownership interests in our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE on October 2, 2010. Refer to the heading "Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" above. The structural change in the Latin America operating segment was related to the sale of 50 percent of our investment in Leão Junior, S.A. ("Leão Junior") during the third quarter of 2010.
Price, product and geographic mix had a favorable 2 percent impact on our international and Bottling Investments net operating revenues. Price, product and geographic mix for our operating segments was impacted by a variety of factors and events including, but not limited to, the following:
• |
Our international and Bottling Investments operating segments' results were unfavorably impacted by geographic mix as a result of growth in our emerging and developing markets. The revenue per unit sold in these markets is generally less than in developed markets; |
• |
Eurasia and Africa was favorably impacted by price mix as a result of pricing increases in a number of key markets; |
• |
Europe's price mix was even, including a negative 1 percent impact as a result of a change in our concentrate pricing strategy in Germany with our consolidated bottler; |
• |
Latin America was favorably impacted by price mix as a result of pricing increases in a number of key markets. Also, still beverages grew faster than sparkling beverages in Latin America, bolstered by the strong performance of Del Valle; |
• |
Pacific was unfavorably impacted by geographic mix due to the growth in emerging and developing markets. The revenue per unit sold in these markets is generally less than in developed markets; |
• |
Pacific was unfavorably impacted by channel and product mix due to the earthquake and tsunami that devastated |
52
northern and eastern Japan on March 11, 2011; and
• |
Bottling Investments was favorably impacted by price mix as a result of pricing increases in a number of key markets, including China, India and Latin America. |
The favorable impact of foreign currency fluctuations increased net operating revenues for our international and Bottling Investments operating segments by 4 percent. The favorable impact of changes in foreign currency exchange rates was primarily due to a weaker U.S. dollar compared to certain other foreign currencies, including the euro, Japanese yen, Mexican peso, Brazilian real, British pound, South African rand and Australian dollar, which had a favorable impact on the Eurasia and Africa, Europe, Latin America, Pacific and Bottling Investments operating segments. Refer to the heading "Liquidity, Capital Resources and Financial Position — Foreign Exchange."
Year Ended December 31, 2010, versus Year Ended December 31, 2009
Net operating revenues increased $4,129 million, or 13 percent. The following table illustrates, on a percentage basis, the estimated impact of key factors resulting in the increase (decrease) in net operating revenues by operating segment:
Percent Change 2010 vs. 2009 |
||||||||||||||||
Structural Changes |
||||||||||||||||
Volume 1
|
Volume2
|
Other |
Price, Product &
Geographic Mix
|
Currency
Fluctuations
|
Total |
|||||||||||
Consolidated |
5 |
% |
— |
% |
5 |
% |
1 |
% |
2 |
% |
13 |
% |
||||
Eurasia & Africa |
12 |
% |
— |
% |
— |
% |
(2 |
)% |
6 |
% |
16 |
% |
||||
Europe |
— |
— |
2 |
1 |
(2 |
) |
1 |
|||||||||
Latin America |
7 |
— |
(13 |
) |
9 |
3 |
6 |
|||||||||
North America |
1 |
1 |
32 |
— |
1 |
35 |
||||||||||
Pacific |
6 |
— |
1 |
(5 |
) |
6 |
8 |
|||||||||
Bottling Investments |
10 |
(11 |
) |
— |
(1 |
) |
2 |
— |
||||||||
Corporate |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
||||||||||
* |
Calculation is not meaningful. |
1 |
Represents the percent change in net operating revenues attributable to the increase (decrease) in concentrate sales volume for our geographic operating segments, excluding the impact of volume associated with new license agreements (expressed in equivalent unit cases). For our Bottling Investments operating segment, this represents the percent change in net operating revenues attributable to the increase (decrease) in unit case volume for the Bottling Investments operating segment after considering the impact of structural changes. Our Bottling Investments operating segment data reflects unit case volume growth for consolidated bottlers only. Refer to the heading "Beverage Volume" above. |
2 |
Represents the percent change in net operating revenues attributable to the increase (decrease) in concentrate sales volume related to new license agreements for our geographic operating segments. For our Bottling Investments operating segment, this represents the percent change in net operating revenues attributable to the increase (decrease) in unit case volume for the Bottling Investments operating segment due to structural changes. Our Bottling Investments operating segment data reflects unit case volume growth for consolidated bottlers only. Refer to the heading "Beverage Volume" above. |
Refer to the heading "Beverage Volume" above for additional information related to changes in our unit case and concentrate sales volume.
Refer to the heading "Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" above for additional information related to significant structural changes. Although we do not normally consider new license agreements to be structural changes, in the case of the DPS license agreements, given their correlation to our acquisition of CCE's North American business, we have included the impact of these license agreements as structural changes when explaining our 2010 financial results. Likewise, the total revenues attributable to CCE's North American business, including DPS, recognized by the Company during the three months following the date of acquisition in 2010 are considered a structural change.
53
Price, product and geographic mix had a favorable 1 percent impact on consolidated net operating revenues. Price, product and geographic mix for our operating segments was impacted by a variety of factors and events including, but not limited to, the following:
• |
Consolidated results were unfavorably impacted by geographic mix as a result of growth in our emerging and developing markets. The growth in our emerging and developing markets resulted in unfavorable geographic mix due to the fact that the revenue per unit sold in these markets is generally less than in developed markets; |
• |
Eurasia and Africa was unfavorably impacted by negative geographic mix due to the growth in emerging and developing markets such as India and Russia. The revenue per unit sold in these markets is generally less than in developed markets; |
• |
Latin America was favorably impacted by pricing in a number of our key markets and the impact of still beverages growing faster than sparkling beverages; and |
• |
Pacific was negatively impacted by unfavorable geographic mix due to the growth in emerging and developing markets such as China and the Philippines. The revenue per unit sold in these markets is generally less than in developed markets. |
The favorable impact of foreign currency fluctuations increased net operating revenues by 2 percent. The favorable impact of changes in foreign currency exchange rates was primarily due to a weaker U.S. dollar compared to certain other foreign currencies, including the Japanese yen, Mexican peso, Brazilian real, South African rand and Australian dollar, which had a favorable impact on the Eurasia and Africa, Latin America, Pacific and Bottling Investments operating segments. The favorable impact of a weaker U.S. dollar compared to the aforementioned currencies was partially offset by the impact of a stronger U.S. dollar compared to certain other foreign currencies, including the euro and British pound, which had an unfavorable impact on the Europe and Bottling Investments operating segments. Refer to the heading "Liquidity, Capital Resources and Financial Position — Foreign Exchange."
Net Operating Revenues by Operating Segment
Information about our net operating revenues by operating segment as a percentage of Company net operating revenues is as follows:
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
|||||
Eurasia & Africa |
5.8 |
% |
6.9 |
% |
6.4 |
% |
||
Europe |
10.3 |
12.6 |
13.9 |
|||||
Latin America |
9.4 |
11.0 |
12.0 |
|||||
North America |
44.2 |
31.7 |
26.4 |
|||||
Pacific |
11.7 |
14.1 |
14.6 |
|||||
Bottling Investments |
18.3 |
23.4 |
26.4 |
|||||
Corporate |
0.3 |
0.3 |
0.3 |
|||||
100.0 |
% |
100.0 |
% |
100.0 |
% |
|||
Net operating revenue growth rates are impacted by sales volume, structural changes, price and product/geographic mix, and foreign currency fluctuations. The percentage of the Company's net operating revenues contributed by our North America operating segment increased 12.5 percent and 5.3 percent in 2011 and 2010, respectively, as a result of our acquisition of CCE's North American business on October 2, 2010. The CCE acquisition resulted in a decrease in the proportionate share of the Company's consolidated net operating revenues contributed by our operating segments outside of North America for both 2011 and 2010. The percentage of the Company's net operating revenues contributed by our Bottling Investments operating segment decreased 5.1 percent and 3.0 percent in 2011 and 2010, respectively, primarily due to the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE and the segment's proportionate decrease in the Company's consolidated net operating revenues due to the CCE acquisition in North America. Refer to the heading "Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" above.
The size and timing of structural changes are not consistent from period to period. As a result, anticipating the impact of such events on future net operating revenues, and other financial statement line items, usually is not possible. We expect structural changes to have an impact on our consolidated financial statements in future periods.
54
Gross Profit Margin
Year Ended December 31, 2011, versus Year Ended December 31, 2010
Our gross profit margin decreased to 60.9 percent in 2011 from 63.9 percent in 2010. The decrease was primarily due to the full year impact of consolidating CCE's North American business as well as a significant increase in commodity costs. The unfavorable impact of these items was partially offset by favorable geographic and product mix, price increases in many of our key markets and foreign currency exchange fluctuations. In addition, the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations during the fourth quarter of 2010 had a favorable impact on our full year 2011 gross profit margin.
The Company's acquisition of CCE's North American business during the fourth quarter of 2010 resulted in a significant adjustment to our overall cost structure, especially in North America. Finished products operations typically have lower gross profit margins and greater exposure to fluctuations in the cost of raw materials when compared to concentrate operations. The following inputs represent a substantial portion of the Company's total cost of goods sold: (1) sweeteners, (2) metals, (3) juices and (4) PET. The bulk of these costs reside within our North America and Bottling Investments operating segments. The cost to purchase these inputs increased significantly in 2011 when compared to 2010. As a result, the Company incurred incremental costs of $800 million related to these inputs during 2011. The Company anticipates that the cost of underlying commodities will continue to face upward pressure in 2012. We currently expect the incremental impact of increased commodity costs related to these inputs, primarily juices and sweeteners, to range between $350 million and $450 million on our full year 2012 consolidated results.
Upon the close of our acquisition of CCE's North American business, the Company increased our hedging activities related to certain commodities in order to mitigate a portion of the price risk associated with forecasted purchases. Many of the derivative financial instruments used by the Company to mitigate the risk associated with these commodity exposures do not qualify for hedge accounting. As a result, the change in fair value of these derivative instruments was included as a component of net income in each reporting period. Refer to Note 5 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. Refer to the heading "Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" above for additional information regarding the impact of our acquisition of CCE's North American business.
The favorable geographic mix was primarily due to many of our emerging markets recovering from the global recession at a quicker pace than our developed markets. Although this shift in geographic mix has a negative impact on net operating revenues, it generally has a favorable impact on our gross profit margin due to the correlated impact it has on our product mix. The product mix in the majority of our emerging and developing markets is more heavily skewed toward our sparkling beverage products, which generally yield a higher gross profit margin compared to our still beverages and finished products. Refer to the heading "Net Operating Revenues" above.
Year Ended December 31, 2010, versus Year Ended December 31, 2009
Our gross profit margin decreased to 63.9 percent in 2010 from 64.2 percent in 2009. The decrease was primarily due to our acquisition of CCE's North American business, partially offset by favorable geographic mix, product mix, the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations and the deconsolidation of certain entities as a result of the Company's adoption of new accounting guidance issued by the FASB.
Refer to the heading "Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" above for additional information regarding the impact of our acquisition of CCE's North American business, the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations and the deconsolidation of certain entities as a result of the Company's adoption of new accounting guidance issued by the FASB. The favorable geographic mix was primarily due to many of our emerging markets recovering from the global recession at a quicker pace than our developed markets. Although this shift in geographic mix has a negative impact on net operating revenues, it generally has a favorable impact on our gross profit margin due to the correlated impact it has on our product mix. The product mix in the majority of our emerging and developing markets is more heavily skewed toward our sparkling beverage products, which generally yield a higher gross profit margin compared to our still beverages and finished products. Refer to the heading "Net Operating Revenues" above.
55
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
The following table sets forth the significant components of selling, general and administrative expenses (in millions):
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense |
$ |
354 |
$ |
380 |
$ |
241 |
|||||
Advertising expenses |
3,256 |
2,917 |
2,791 |
||||||||
Bottling and distribution expenses |
8,501 |
3,902 |
2,627 |
||||||||
Other operating expenses |
5,329 |
5,959 |
5,699 |
||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
$ |
17,440 |
$ |
13,158 |
$ |
11,358 |
|||||
Year Ended December 31, 2011, versus Year Ended December 31, 2010
Selling, general and administrative expenses increased $4,282 million, or 33 percent. Foreign currency fluctuations increased selling, general and administrative expenses by 3 percent. The decrease in stock-based compensation expense was primarily related to the impact of modifications made to certain replacement performance share unit awards on our prior year results, partially offset by higher estimated payouts tied to performance in conjunction with our long-term incentive compensation programs. Advertising expenses increased during the year and reflect the Company's continued investment in the health and strength of our brands and building market execution capabilities. The increase in bottling and distribution expenses was primarily due to the full year impact of consolidating CCE's North American business in addition to our continued investments in our other bottling operations around the world. This increase was partially offset by the full year impact of the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE during the fourth quarter of 2010. Other operating expenses decreased during the year, partially reflecting the impact of the Company's productivity and integration initiatives.
In 2012, our pension expense is expected to decrease by approximately $50 million compared to 2011. The anticipated decrease is primarily due to approximately $953 million of contributions the Company expects to make to various plans in 2012, of which $900 million was contributed to the Company's U.S. pension plans during the first quarter of 2012. The expected favorable impact of this item will be partially offset by the expected unfavorable impact of a decrease in the weighted-average discount rate used to calculate the Company's benefit obligation. Refer to the heading "Liquidity, Capital Resources and Financial Position" below for information related to these contributions. Refer to the heading "Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates — Pension Plan Valuations" above and Note 13 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information related to the discount rates used by the Company.
As of December 31, 2011, we had $516 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to nonvested share-based compensation arrangements granted under our plans. This cost is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.8 years as stock-based compensation expense. This expected cost does not include the impact of any future stock-based compensation awards. Refer to Note 12 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Year Ended December 31, 2010, versus Year Ended December 31, 2009
Selling, general and administrative expenses increased $1,800 million, or 16 percent. Foreign currency fluctuations increased selling, general and administrative expenses by 1 percent. The increase in stock-based compensation was primarily related to higher payouts tied to performance in conjunction with our long-term incentive compensation programs and the impact of modifications made to certain replacement performance share unit awards issued by the Company in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. The Company modified primarily all of these replacement performance share unit awards to eliminate the remaining holding period, which resulted in $74 million of accelerated expense in the fourth quarter of 2010. Refer to Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. The increase in advertising expenses reflected the Company's continued investment in our brands and building market execution capabilities.
The increase in bottling and distribution expenses was primarily related to the impact of our acquisition of CCE's North American business and our continued investments in our other bottling operations. The unfavorable impact of these items was partially offset by the deconsolidation of certain entities as a result of the Company's adoption of new accounting guidance issued by the FASB. These entities are primarily bottling operations and accounted for approximately 2 percent of the Company's consolidated selling, general and administrative expenses in 2009. Bottling and distribution expenses were also reduced due to the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE. Refer to the heading "Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" above for additional information related to significant structural changes.
56
Other Operating Charges
Other operating charges incurred by operating segment were as follows (in millions):
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
Eurasia & Africa |
$ |
12 |
$ |
7 |
$ |
4 |
|||||
Europe |
25 |
50 |
7 |
||||||||
Latin America |
4 |
— |
— |
||||||||
North America |
374 |
133 |
31 |
||||||||
Pacific |
54 |
22 |
1 |
||||||||
Bottling Investments |
89 |
122 |
141 |
||||||||
Corporate |
174 |
485 |
129 |
||||||||
Total |
$ |
732 |
$ |
819 |
$ |
313 |
|||||
In 2011, the Company incurred other operating charges of $732 million, which primarily consisted of $633 million associated with the Company's productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives; $50 million due to charges associated with the earthquake and tsunami that devastated northern and eastern Japan on March 11, 2011; $35 million of costs associated with the merger of Embotelladoras Arca, S.A.B. de C.V. ("Arca") and Grupo Continental S.A.B. ("Contal"); and $10 million associated with the floods in Thailand that impacted the Company's supply chain operations in the region. The Company's integration activities include costs associated with the integration of CCE's North American business, as well as the integration of 18 German bottling and distribution operations acquired in 2007.
In 2010, the Company began an integration initiative related to our acquisition of CCE's North American business on October 2, 2010. Upon completion of the CCE transaction, we combined the management of the acquired North American business with the management of our existing foodservice business; Minute Maid and Odwalla juice businesses; North America supply chain operations; and Company-owned bottling operations in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, into a unified bottling and customer service organization called CCR. In addition, we reshaped our remaining CCNA operations into an organization that primarily provides franchise leadership and consumer marketing and innovation for the North American market. As a result of the transaction and related reorganization, our North American businesses operate as aligned and agile organizations with distinct capabilities, responsibilities and strengths. Refer to Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
We incurred expenses of $358 million in 2011 related to this initiative which impacted the North America and Corporate operating segments. These expenses were primarily related to both internal and external costs associated with the development, design and initial implementation of our future operating framework as well as contract termination fees and relocation costs. We believe this acquisition will result in an evolved franchise system that will enable us to better serve the unique needs of the North American market. The creation of a unified operating system will strategically position us to better market and distribute our nonalcoholic beverage brands in North America. The Company initially estimated that the total cost of these integration initiatives would be approximately $425 million, and the initiatives were expected to generate annualized savings of at least $350 million per year. The Company realized nearly all of the $350 million in annualized savings by the end of 2011, and the total cost we incurred since the inception of this integration initiative was $493 million. As such, this initiative was successfully completed at the end of 2011. Refer to Note 18 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information related to this integration initiative.
The Company's integration initiatives include costs related to the integration of 18 German bottling and distribution operations acquired in 2007. We incurred expenses of $67 million in 2011 related to this initiative. The expenses recorded in connection with these integration activities have been primarily due to involuntary terminations. The Company began these integration initiatives in 2008 and has incurred total pretax expenses of $292 million since they commenced. The Company is currently reviewing other integration and restructuring opportunities within the German bottling and distribution operations, which if implemented will result in additional charges in future periods. However, as of December 31, 2011, the Company had not finalized any additional plans. Refer to Note 18 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information related to this integration initiative.
During 2011, the Company successfully completed our four-year global productivity program and exceeded our target of providing $500 million in annualized savings from these initiatives by the end of 2011. These savings have provided the Company additional flexibility to invest for growth. The Company generated these savings in a number of areas, which include aggressively managing operating expenses supported by lean techniques, redesigning key processes to drive standardization and effectiveness, better leveraging our size and scale, and driving savings in indirect costs through the implementation of a "procure-to-pay" program. In realizing these savings, the Company incurred total costs of $508 million related to these
57
productivity initiatives since they commenced during the first quarter of 2008. Refer to Note 18 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information related to the Company's ongoing productivity initiatives.
In February 2012, the Company announced a new four-year productivity and reinvestment program. This program will further enable our efforts to strengthen our brands and reinvest our resources to drive long-term profitable growth. The first component of this program is a new global productivity initiative that will target annualized savings of $350 million to $400 million. This initiative will be focused around four primary areas: global supply chain optimization; global marketing and innovation effectiveness; operating expense leverage and operational excellence; and data and IT systems standardization. The Company is in the initial stages of defining the costs associated with this initiative.
The second component of our new productivity and reinvestment program involves beginning a new integration initiative in North America related to our acquisition of CCE's North American business. The Company has identified incremental synergies in North America, primarily in the area of our North American product supply, which will better enable us to service our customers and consumers. We believe these efforts will create annualized savings of $200 million to $250 million and will result in costs of approximately $300 million.
As a combined productivity and reinvestment program, the Company anticipates generating annualized savings of $550 million to $650 million which will be phased in over the next four years starting in 2012. We expect to begin fully realizing the annual benefit of these savings in 2015, the final year of the program. The savings generated by this program will be reinvested in brand-building initiatives, and in the short term will also mitigate potential incremental commodity costs.
In 2010, the Company incurred other operating charges of $819 million, which consisted of $478 million associated with the Company's productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives; $250 million related to charitable contributions; $81 million due to transaction costs incurred in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business and the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE; and $10 million of charges related to bottling activities in Eurasia. The Company's integration activities include costs associated with the integration of CCE's North American business, as well as the integration of 18 German bottling and distribution operations acquired in 2007. The charitable contributions were primarily attributable to a cash donation to The Coca-Cola Foundation. Refer to Note 18 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information on our productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives. Refer to Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information related to the transaction costs.
In 2009, the Company incurred other operating charges of $313 million, which consisted of $273 million related to the Company's productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives and $40 million due to asset impairments. Refer to Note 18 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information on our productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives. The impairment charges were related to a $23 million impairment of an intangible asset and a $17 million impairment of a building. The impairment of the intangible asset was due to a change in the expected useful life of the asset, which was previously determined to have an indefinite life. The $17 million impairment was due to a change in disposal strategy related to a building that is no longer occupied. The Company had originally intended to sell the building along with the related land. However, we determined that the maximum potential sales proceeds would likely be realized through the sale of vacant land. As a result, the building was removed. The land was not considered held-for-sale, primarily due to the fact that it was not probable a sale would be completed within one year.
58
Operating Income and Operating Margin
Information about our operating income contribution by operating segment on a percentage basis is as follows:
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
|||||
Eurasia & Africa |
10.8 |
% |
11.6 |
% |
9.8 |
% |
||
Europe |
30.4 |
35.2 |
35.8 |
|||||
Latin America |
27.7 |
28.5 |
24.8 |
|||||
North America |
22.8 |
18.0 |
20.7 |
|||||
Pacific |
21.2 |
24.2 |
22.9 |
|||||
Bottling Investments |
2.2 |
2.7 |
2.2 |
|||||
Corporate |
(15.1 |
) |
(20.2 |
) |
(16.2 |
) |
||
Total |
100.0 |
% |
100.0 |
% |
100.0 |
% |
||
Information about our operating margin on a consolidated basis and by operating segment is as follows:
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
|||||
Consolidated |
21.8 |
% |
24.1 |
% |
26.6 |
% |
||
Eurasia & Africa |
40.6 |
% |
40.4 |
% |
41.0 |
% |
||
Europe |
64.7 |
67.3 |
68.4 |
|||||
Latin America |
63.9 |
62.0 |
55.2 |
|||||
North America |
11.3 |
13.6 |
20.7 |
|||||
Pacific |
39.4 |
41.4 |
41.6 |
|||||
Bottling Investments |
2.6 |
2.8 |
2.2 |
|||||
Corporate |
* |
* |
* |
|||||
* |
Calculation is not meaningful. |
As demonstrated by the tables above, the percentage contribution to operating income and operating margin by operating segment fluctuated from year to year. Operating income and operating margin by operating segment were influenced by a variety of factors and events, including the following:
• |
In 2011, foreign currency exchange rates favorably impacted consolidated operating income by 4 percent. The favorable impact of changes in foreign currency exchange rates was primarily due to a weaker U.S. dollar compared to most foreign currencies, including the euro, Japanese yen, Mexican peso, Brazilian real, British pound, South African rand and Australian dollar, which had a favorable impact on the Eurasia and Africa, Europe, Latin America, Pacific and Bottling Investments operating segments. Refer to the heading "Liquidity, Capital Resources and Financial Position — Foreign Exchange." |
• |
In 2011, operating income was favorably impacted by fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates by 2 percent for Europe, 4 percent for Latin America, 1 percent for North America, 7 percent for Pacific, 7 percent for Bottling Investments and 1 percent for Corporate. Operating income was unfavorably impacted by fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates by 1 percent for Eurasia and Africa. |
• |
In 2011, our consolidated operating margin was favorably impacted by geographic mix. The favorable geographic mix was primarily due to many of our emerging markets recovering from the global recession at a quicker pace than our developed markets. Although this shift in geographic mix has a negative impact on net operating revenues, it generally has a favorable impact on our gross profit margin and operating margin due to the correlated impact it has on our product mix. The product mix in the majority of our emerging and developing markets is more heavily skewed toward products in our sparkling beverage portfolio, which generally yield a higher gross profit margin compared to our still beverages and finished products. Consequently, the shift in our geographic mix is driving favorable product mix from a global perspective. |
• |
In 2011, operating income and operating margin for Europe were unfavorably impacted by a change in our concentrate pricing strategy in Germany with our consolidated bottler. |
59
• |
In 2011, operating income and operating margin for Latin America were favorably impacted by volume growth across all of the group's business units and pricing increases in key markets, partially offset by continued investments in the business. |
• |
In 2011, the operating margin for North America was unfavorably impacted by the full year impact of the Company's acquisition of CCE's North American business. Generally, bottling and finished products operations have higher net operating revenues but lower operating margins when compared to concentrate and syrup operations. The impact of this transaction was also reflected in the Company's operating margin. Refer to the heading "Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" above. |
• |
In 2011, operating income and operating margin for North America were unfavorably impacted by higher commodity costs in the segment's finished products businesses. |
• |
In 2011, operating income was reduced by $19 million for North America due to the amortization of favorable supply contracts acquired in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. |
• |
In 2011, operating income and operating margin for Pacific and North America were unfavorably impacted as a result of the earthquake and tsunami that devastated northern and eastern Japan on March 11, 2011. Operating income was reduced by $82 million and $2 million for Pacific and North America, respectively. The charges were primarily related to the Company's charitable donations in support of relief and rebuilding efforts in Japan as well as funds we provided certain bottling partners in the affected regions. |
• |
In 2011, operating income was reduced by $10 million for Corporate due to charges associated with the floods in Thailand that impacted the Company's supply chain operations in the region. |
• |
In 2011, operating income was reduced by $12 million for Eurasia and Africa, $25 million for Europe, $4 million for Latin America, $374 million for North America, $4 million for Pacific, $89 million for Bottling Investments and $164 million for Corporate, primarily due to the Company’s ongoing productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives as well as costs associated with the merger of Arca and Contal. |
• |
In 2010, foreign currency exchange rates favorably impacted consolidated operating income by 3 percent. The favorable impact of changes in foreign currency exchange rates was primarily due to a weaker U.S. dollar compared to most foreign currencies, including the Japanese yen, Mexican peso, Brazilian real, South African rand and Australian dollar, which had a favorable impact on the Eurasia and Africa, Latin America, Pacific and Bottling Investments operating segments. The favorable impact of a weaker U.S. dollar compared to the aforementioned currencies was partially offset by the impact of a stronger U.S. dollar compared to certain other foreign currencies, including the euro and British pound, which had an unfavorable impact on the Europe and Bottling Investments operating segments. Refer to the heading "Liquidity, Capital Resources and Financial Position — Foreign Exchange" below. |
• |
In 2010, operating income was favorably impacted by fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates by 7 percent for Eurasia and Africa, 3 percent for Latin America, 8 percent for Pacific and 9 percent for Bottling Investments. Operating income was unfavorably impacted by fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates by 1 percent for Europe. Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates had a nominal impact on operating income for North America and Corporate. |
• |
In 2010, our consolidated operating margin was favorably impacted by geographic mix. The favorable geographic mix was primarily due to many of our emerging markets recovering from the global recession at a quicker pace than our developed markets. Although this shift in geographic mix has a negative impact on net operating revenues, it generally has a favorable impact on our gross profit margin and operating margin due to the correlated impact it has on our product mix. The product mix in the majority of our emerging and developing markets is more heavily skewed toward products in our sparkling beverage portfolio, which generally yield a higher gross profit margin compared to our still beverages and finished products. |
• |
In 2010, our consolidated operating margin was favorably impacted by the deconsolidation of certain entities as a result of the Company's adoption of new accounting guidance issued by the FASB. These entities are primarily bottling operations and have been accounted for under the equity method of accounting since they were deconsolidated on January 1, 2010. Generally, bottling and finished products operations produce higher net revenues but lower operating margins compared to concentrate and syrup operations. The majority of the deconsolidated entities had previously been included in our Bottling Investments operating segment. |
60
• |
In 2010, the operating margin for the Latin America operating segment was favorably impacted by the sale of 50 percent of our ownership interest in Leão Junior, resulting in its deconsolidation, as well as the deconsolidation of certain entities as a result of the Company's adoption of new accounting guidance issued by the FASB. Price and product mix also favorably impacted Latin America's operating income and operating margin during the year. |
• |
In 2010, the operating margin for the North America operating segment was unfavorably impacted by the Company's acquisition of CCE's North American business. Generally, bottling and finished products operations have higher net operating revenues but lower operating margins when compared to concentrate and syrup operations. Refer to the heading "Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" above. |
• |
In 2010, operating income for the North America operating segment was reduced by $74 million due to the acceleration of expense associated with certain share-based replacement awards issued in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
• |
In 2010, operating income for the North America operating segment was negatively impacted by $235 million, primarily due to the elimination of gross profit in inventory on intercompany sales and an inventory fair value adjustment as a result of our acquisition of CCE's North American business. Prior to the acquisition, we recognized the profit associated with concentrate sales when the concentrate was sold to CCE, excluding the portion that was deemed to be intercompany due to our previous ownership interest in CCE. However, subsequent to the acquisition, the Company does not recognize the profit associated with concentrate sold to CCE's legacy North American business until the finished beverage products made from those concentrates are sold. |
• |
In 2010, operating income for the North America operating segment was reduced by $20 million due to the amortization of favorable supply contracts acquired in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. |
• |
In 2010, operating income was reduced by $7 million for Eurasia and Africa, $50 million for Europe, $133 million for North America, $22 million for Pacific, $122 million for Bottling Investments and $485 million for Corporate, primarily due to the Company's productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives; charitable donations; transaction costs incurred in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business and the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE; and other charges related to bottling activities in Eurasia. Refer to the heading "Other Operating Charges" above. |
• |
In 2009, operating income was reduced by $4 million for Eurasia and Africa, $7 million for Europe, $31 million for North America, $1 million for Pacific, $141 million for Bottling Investments and $129 million for Corporate, primarily as a result of restructuring costs, the Company's ongoing productivity initiatives and asset impairments. Refer to the heading "Other Operating Charges" above. |
Interest Income
Year Ended December 31, 2011, versus Year Ended December 31, 2010
Interest income was $483 million in 2011, compared to $317 million in 2010, an increase of $166 million, or 52 percent. The increase was primarily due to the impact of higher average cash, cash equivalents and short-term investment balances in addition to higher average interest rates, particularly in international locations. The majority of our cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments are held by our international locations.
Year Ended December 31, 2010, versus Year Ended December 31, 2009
Interest income was $317 million in 2010, compared to $249 million in 2009, an increase of $68 million, or 27 percent. The increase was primarily due to the impact of higher average cash and short-term investment balances, partially offset by lower average interest rates.
Interest Expense
Year Ended December 31, 2011, versus Year Ended December 31, 2010
Interest expense was $417 million in 2011, compared to $733 million in 2010, a decrease of $316 million, or 43 percent. The decrease was primarily due to a $342 million charge recorded in 2010 related to debt assumed in connection with the Company's acquisition of CCE's North American business. See prior year's discussion below for further information related to the charge recorded during 2010. This decrease was partially offset by the full year impact of increased interest expense on long-term debt assumed in connection with the CCE acquisition as well as additional long-term debt issued by the Company in 2011. The Company's interest expense also includes the impact of interest rate swap agreements. Refer to Note 5 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information related to our interest rate swaps.
61
During 2011, the Company issued $2,979 million of long-term debt. We used $979 million of this newly issued debt and paid a premium of $208 million to exchange $1,022 million of existing long-term debt that was assumed in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business in the fourth quarter of 2010. The remaining cash from the issuance was used to reduce the Company's outstanding commercial paper balance and exchange a certain amount of short-term debt.
The general terms of the notes issued during 2011 are as follows:
• |
$1,655 million total principal amount of notes due September 1, 2016, at a fixed interest rate of 1.8 percent; and
|
• |
$1,324 million total principal amount of notes due September 1, 2021, at a fixed interest rate of 3.3 percent.
|
During the fourth quarter of 2011, the Company extinguished long-term debt that had a carrying value of $20 million and was not scheduled to mature until 2012. This debt was outstanding prior to the Company's acquisition of CCE's North American business. In addition, the Company repurchased long-term debt during 2011 that was assumed in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. The repurchased debt included $99 million in unamortized fair value adjustments recorded as part of our purchase accounting for the CCE transaction and was settled throughout the year as follows:
• |
During the first quarter of 2011, the Company repurchased all of our outstanding U.K. pound sterling notes that had a carrying value of $674 million;
|
• |
During the second quarter of 2011, the Company repurchased long-term debt that had a carrying value of $42 million; and
|
• |
During the third quarter of 2011, the Company repurchased long-term debt that had a carrying value of $19 million.
|
The Company recorded a net charge of $9 million in the line item interest expense in our consolidated statement of income during the year ended December 31, 2011. This net charge was due to the exchange, repurchase and/or extinguishment of long-term debt described above.
As of December 31, 2011, the carrying value of the Company's long-term debt included $733 million of fair value adjustments related to the debt assumed from CCE. These fair value adjustments will be amortized over a weighted-average period of approximately 16 years, which is equal to the weighted-average maturity of the assumed debt to which these fair value adjustments relate. The amortization of these fair value adjustments will be a reduction of interest expense in future periods, which will typically result in our interest expense being less than the actual interest paid to service the debt. Total interest paid was $573 million in 2011.
Year Ended December 31, 2010, versus Year Ended December 31, 2009
Interest expense was $733 million in 2010, compared to $355 million in 2009, an increase of $378 million, or 106 percent. The increase was primarily due to a $342 million charge related to the premiums paid to repurchase long-term debt and the costs associated with the settlement of treasury rate locks issued in connection with the debt tender offer. The increase also reflects the impact of interest expense on debt assumed from CCE. In connection with the Company's acquisition of CCE's North American business, we assumed $266 million of short-term borrowings and $7,602 million of long-term debt. The estimated fair value of the long-term debt was $9,345 million as of the acquisition date. In accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, we recorded the assumed debt at its fair value as of the acquisition date. On November 15, 2010, the Company issued $4,500 million of long-term notes and used some of the proceeds to repurchase $2,910 million of long-term debt. The remaining cash from the issuance was used to reduce our outstanding commercial paper balance.
Equity Income (Loss) — Net
Year Ended December 31, 2011, versus Year Ended December 31, 2010
Equity income (loss) — net represents our Company's proportionate share of net income or loss from each of our equity method investees. In 2011, equity income was $690 million, compared to equity income of $1,025 million in 2010, a decrease of $335 million, or 33 percent. The decrease was primarily due to the Company's acquisition and consolidation of CCE's North American business during the fourth quarter of 2010. As a result of this transaction, the Company stopped recording equity income related to CCE beginning October 2, 2010, and our 2011 consolidated statement of income reflects the full year impact of not having an equity interest in New CCE. Refer to the heading "Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" above. In addition, the decrease in equity income (loss) — net was partially due to the Company's sale of its investment in Coca-Cola Embonor, S.A. ("Embonor") during the first quarter of 2011. The unfavorable impact of these items was partially offset by the Company's proportionate share of increased net income from certain of our equity method investees and the favorable impact of foreign currency exchange fluctuations.
62
Year Ended December 31, 2010, versus Year Ended December 31, 2009
In 2010, equity income was $1,025 million, compared to equity income of $781 million in 2009, an increase of $244 million, or 31 percent. The increase was primarily due to our proportionate share of increased net income from certain of our equity method investees; the favorable impact of foreign currency exchange fluctuations; a decrease in the Company's proportionate share of asset impairments and restructuring charges recorded by equity method investees; and the impact of the Company's adoption of new accounting guidance issued by the FASB. The impact of these items was partially offset by the impact of our acquisition and consolidation of CCE's North American business. As a result of this transaction, the Company stopped recording equity income related to CCE beginning October 2, 2010. Refer to the heading "Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" above.
The Company's adoption of new accounting guidance issued by the FASB resulted in the deconsolidation of certain entities. On January 1, 2010, the Company began to account for these entities under the equity method of accounting. Refer to the heading "Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" above. The entities that have been deconsolidated accounted for approximately 4 percent of the Company's equity income in 2010.
Other Income (Loss) — Net
Other income (loss) — net includes, among other things, the impact of foreign currency exchange gains and losses; dividend income; rental income; gains and losses related to the disposal of property, plant and equipment; realized and unrealized gains and losses on trading securities; realized gains and losses on available-for-sale securities; other-than-temporary impairments of available-for-sale securities; and the accretion of expense related to certain acquisitions. The foreign currency exchange gains and losses are primarily the result of the remeasurement of monetary assets and liabilities from certain currencies into functional currencies. The effects of the remeasurement of these assets and liabilities are partially offset by the impact of our economic hedging program for certain exposures on our consolidated balance sheets. Refer to Note 5 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
In 2011, other income (loss) — net was income of $529 million, primarily related to a net gain of $417 million the Company recognized as a result of the merger of Arca and Contal; a net gain of $122 million the Company recognized as a result of an equity method investee issuing additional shares of its own stock at per share amounts greater than the carrying value of the Company's per share investment, partially offset by charges associated with certain of the Company's equity method investments in Japan; and a gain of $102 million related to the sale of our investment in Embonor. Other income (loss) — net also included $10 million of realized and unrealized gains on trading securities. The net favorable impact of the previous items was partially offset by foreign currency exchange losses of $73 million; charges of $41 million due to the impairment of an investment in an entity accounted for under the equity method of accounting; $17 million due to other-than-temporary declines in the fair value of certain of the Company's available-for-sale securities; and $5 million related to the finalization of working capital adjustments associated with the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish Bottling operations to New CCE during the fourth quarter of 2010. Refer to Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
In 2010, other income (loss) — net was income of $5,185 million, primarily related to a $4,978 million gain due to the remeasurement of our equity investment in CCE to fair value upon the close of our acquisition of CCE's North American business and a $597 million gain related to the sale of all our ownership interests in our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE. Refer to the heading "Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" above and Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. These gains were partially offset by a $265 million charge related to preexisting relationships with CCE and foreign currency exchange losses of $148 million. The charge related to preexisting relationships was primarily due to the write-off of our investment in infrastructure programs with CCE. The foreign currency exchange losses were primarily due to a charge of $103 million related to the remeasurement of our Venezuelan subsidiary's net assets. Refer to the heading "Liquidity, Capital Resources and Financial Position — Foreign Exchange" below. In addition to the items mentioned above, other income (loss) — net also included a $23 million gain on the sale of 50 percent of our investment in Leão Junior and $48 million of charges related to other-than-temporary impairments and a donation of preferred shares in one of our equity investees. Refer to Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
In 2009, other income (loss) — net was income of $40 million, primarily related to a realized gain of $44 million on the sale of equity securities classified as available-for-sale, $40 million from the sale of other investments and $18 million of dividend income from cost method investments. Refer to Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information related to the gain on the sale of available-for-sale securities. These gains were partially offset by $34 million in net foreign currency exchange losses and an other-than-temporary impairment charge of $27 million on a cost method investment. Refer to the heading "Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates — Investments in Equity and Debt Securities" above and Note 16 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
63
Income Taxes
Our effective tax rate reflects the tax benefits of having significant operations outside the United States, which are generally taxed at rates lower than the U.S. statutory rate of 35 percent. As a result of employment actions and capital investments made by the Company, certain tax jurisdictions provide income tax incentive grants, including Brazil, Costa Rica, Singapore and Swaziland. The terms of these grants range from 2015 to 2020. We expect each of the grants to be renewed indefinitely. Tax incentive grants favorably impacted our income tax expense by $193 million, $145 million and $191 million for the years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. In addition, our effective tax rate reflects the benefits of having significant earnings generated in investments accounted for under the equity method of accounting, which are generally taxed at rates lower than the U.S. statutory rate.
A reconciliation of the statutory U.S. federal tax rate and our effective tax rate is as follows:
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||
Statutory U.S. federal tax rate |
35.0 |
% |
35.0 |
% |
35.0 |
% |
|||
State and local income taxes — net of federal benefit |
0.9 |
0.6 |
0.7 |
||||||
Earnings in jurisdictions taxed at rates different from the statutory U.S. federal rate |
(9.5 |
) |
1,2.3 |
(5.6 |
) |
11 |
(11.6 |
) |
19 |
Equity income or loss |
(1.4 |
) |
4 |
(1.9 |
) |
12 |
(2.3 |
) |
20 |
CCE transaction |
— |
(12.5 |
) |
13,14 |
— |
||||
Sale of Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations |
— |
5 |
0.4 |
15 |
— |
||||
Other operating charges |
0.3 |
6 |
0.4 |
16 |
0.6 |
21 |
|||
Other — net |
(0.8 |
) |
7,8,9,10 |
0.3 |
17,18 |
0.4 |
22,23 |
||
Effective tax rate |
24.5 |
% |
16.7 |
% |
22.8 |
% |
|||
1 |
Includes a tax benefit of $6 million related to amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties, in various international jurisdictions. |
2 |
Includes a zero percent effective tax rate on charges due to the impairment of available-for-sale securities. Refer to Note 3 and Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
3 |
Includes a tax expense of $299 million (or a 0.7 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to the net gain recognized as a result of the merger of Arca and Contal, the gain recognized on the sale of our investment in Embonor and gains the Company recognized as a result of an equity method investee issuing additional shares of its own stock during the year at per share amounts greater than the carrying value of the Company's per share investment. These gains were partially offset by charges associated with certain of the Company's equity method investments in Japan. Refer to Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
4 |
Includes a tax benefit of $7 million (or a 0.1 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to our proportionate share of asset impairments and restructuring charges recorded by certain of our equity method investees. Refer to Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
5 |
Includes a tax benefit of $2 million related to the finalization of working capital adjustments on the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations. Refer to Note 2 and Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
6 |
Includes a tax benefit of $224 million (or a 0.3 percent impact on our effective tax rate) primarily related to the Company's productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives, transaction costs incurred in connection with the merger of Arca and Contal, costs associated with the earthquake and tsunami that devastated northern and eastern Japan and costs associated with the flooding in Thailand. Refer to Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
7 |
Includes a tax benefit of $8 million related to the amortization of favorable supply contracts acquired in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. |
8 |
Includes a tax benefit of $3 million related to net charges we recognized on the repurchase and/or exchange of certain long-term debt assumed in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business as well as the early extinguishment of certain other long-term debt. Refer to Note 10 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
9 |
Includes a tax benefit of $14 million on charges due to the impairment of an investment in an entity accounted for under the equity method of accounting. Refer to Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
10 |
Includes a tax benefit of $2 million related to amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties, in certain domestic jurisdictions. |
11 |
Includes tax expense of $265 million (or a 1.9 percent impact on our effective tax rate), primarily related to deferred tax expense on certain current year undistributed foreign earnings that are not considered indefinitely reinvested and amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties. |
12 |
Includes a tax benefit of $9 million (or a 0.1 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to charges recorded by our equity method investees. Refer to Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
64
13 |
Includes a tax benefit of $34 million (or a reduction of 12.5 percent on our effective tax rate) related to the remeasurement of our equity investment in CCE to fair value upon our acquisition of CCE's North American business. The tax benefit reflects the impact of reversing deferred tax liabilities associated with our equity investment in CCE prior to the acquisition. Refer to Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
14 |
Includes a tax benefit of $99 million related to charges associated with the write-off of preexisting relationships with CCE. Refer to Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
15 |
Includes a tax expense of $261 million (or a 0.4 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations. Refer to Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
16 |
Includes a tax benefit of $223 million (or a 0.4 percent impact on our effective tax rate), primarily related to the Company's productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives, transaction costs and charitable contributions. Refer to Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
17 |
Includes a tax benefit of $114 million (or a 0.5 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to charges associated with the repurchase of certain long-term debt and costs associated with the settlement of treasury rate locks issued in connection with the debt tender offer, the loss related to the remeasurement of our Venezuelan subsidiary's net assets, other-than-temporary impairment charges and a donation of preferred shares in one of our equity method investees. Refer to Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
18 |
Includes a tax expense of $31 million (or a 0.2 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties, and other tax matters in certain domestic jurisdictions. |
19 |
Includes a tax benefit of $16 million (or a reduction of 0.2 percent on our effective tax rate) related to amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties, in various international jurisdictions. |
20 |
Includes a tax benefit of $17 million (or a 0.1 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to charges recorded by our equity method investees. Refer to Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
21 |
Includes a tax benefit of $16 million (or a 0.6 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to restructuring charges and asset impairments. Refer to Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
22 |
Includes a zero percent effective rate (or a reduction of 0.2 percent on our effective tax rate) related to the sale of all or a portion of certain investments. Refer to Note 3 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
23 |
Includes a zero percent effective rate (or a 0.1 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to an other-than-temporary impairment of a cost method investment. Refer to Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
In 2010, the Company recorded a $4,978 million pre-tax remeasurement gain associated with the acquisition of CCE's North American business. This remeasurement gain was not recognized for tax purposes and therefore no tax expense was recorded on this gain. Also, as a result of this acquisition, the Company was required to reverse $34 million of deferred tax liabilities which were associated with our equity investment in CCE prior to the acquisition. In addition, the Company recognized a $265 million charge related to the settlement of preexisting relationships with CCE, and we recorded a tax benefit of 37 percent related to this charge. The tax impact of the remeasurement gain, reversal of the net deferred tax liabilities on our equity investment and the settlement of preexisting relationships with CCE will not impact our future effective tax rate.
As of December 31, 2011, the gross amount of unrecognized tax benefits was $320 million. If the Company were to prevail on all uncertain tax positions, the net effect would be a benefit to the Company's effective tax rate of $149 million, exclusive of any benefits related to interest and penalties. The remaining $171 million, which was recorded as a deferred tax asset, primarily represents tax benefits that would be received in different tax jurisdictions in the event the Company did not prevail on all uncertain tax positions. Refer to Note 14 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
A reconciliation of the changes in the gross balance of unrecognized tax benefit amounts is as follows (in millions):
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
Beginning balance of unrecognized tax benefits |
$ |
387 |
$ |
354 |
$ |
369 |
|||||
Increases related to prior period tax positions |
9 |
26 |
49 |
||||||||
Decreases related to prior period tax positions |
(19 |
) |
(10 |
) |
(28 |
) |
|||||
Increases related to current period tax positions |
6 |
33 |
16 |
||||||||
Decreases related to current period tax positions |
(1 |
) |
— |
— |
|||||||
Decreases related to settlements with taxing authorities |
(5 |
) |
— |
(27 |
) |
||||||
Reductions as a result of a lapse of the applicable statute of limitations |
(46 |
) |
(1 |
) |
(73 |
) |
|||||
Increase related to acquisition of CCE's North American business |
— |
6 |
— |
||||||||
Increases (decreases) from effects of foreign currency exchange rates |
(11 |
) |
(21 |
) |
48 |
||||||
Ending balance of unrecognized tax benefits |
$ |
320 |
$ |
387 |
$ |
354 |
|||||
65
The Company recognizes accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense. The Company had $110 million, $112 million and $94 million in interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits accrued as of December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. Of these amounts, $2 million of benefit, $17 million of expense and $16 million of benefit was recognized through income tax expense in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. If the Company were to prevail on all uncertain tax positions, the reversal of this accrual would also be a benefit to the Company's effective tax rate.
Based on current tax laws, the Company's effective tax rate in 2012 is expected to be approximately 24.0 percent to 25.0 percent before considering the effect of any unusual or special items that may affect our tax rate in future years.
Liquidity, Capital Resources and Financial Position
We believe our ability to generate cash from operating activities is one of our fundamental financial strengths. Refer to the heading "Cash Flows from Operating Activities" below. The near-term outlook for our business remains strong, and we expect to generate substantial cash flows from operations in 2012. As a result of our expected cash flows from operations, we have significant flexibility to meet our financial commitments. The Company does not typically raise capital through the issuance of stock. Instead, we use debt financing to lower our overall cost of capital and increase our return on shareowners' equity. Refer to the heading "Cash Flows from Financing Activities" below. We have a history of borrowing funds domestically and continue to have the ability to borrow funds domestically at reasonable interest rates. Our debt financing includes the use of an extensive commercial paper program as part of our overall cash management strategy. The Company reviews its optimal mix of short-term and long-term debt regularly and may replace certain amounts of commercial paper, short-term debt and current maturities of long-term debt with new issuances of long-term debt in the future. In addition to the Company's cash balances, commercial paper program, and our ability to issue long-term debt, we also had $4,625 million in lines of credit for general corporate purposes, including commercial paper backup, as of December 31, 2011. These backup lines of credit expire at various times from 2012 through 2016.
We have significant operations outside the United States. Unit case volume outside the United States represented approximately 80 percent of the Company's worldwide unit case volume in 2011. We earn a substantial amount of our consolidated operating income and income before income taxes in foreign subsidiaries that either sell concentrate to our local bottling partners or, in certain instances, sell finished products directly to our customers to fulfill the demand for Company beverage products outside the United States. A significant portion of these foreign earnings is deemed to be indefinitely reinvested in foreign jurisdictions. As a result, the majority of our cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments are held by our foreign subsidiaries. We do not intend, nor foresee a need, to repatriate these funds. Additionally, the government in Venezuela has enacted certain monetary policies that restrict the ability of companies to pay dividends from retained earnings. As of December 31, 2011, cash held by our Venezuelan subsidiary accounted for approximately 2 percent of our consolidated cash and cash equivalents balance.
Net operating revenues in the United States were $18.7 billion in 2011, or approximately 40 percent of the Company's consolidated net operating revenues. We expect existing domestic cash, cash equivalents, short-term investments, cash flows from operations and the issuance of debt to continue to be sufficient to fund our domestic operating activities and cash commitments for investing and financing activities. In addition, we expect existing foreign cash, cash equivalents, short-term investments, and cash flows from operations to continue to be sufficient to fund our foreign operating activities and cash commitments for investing activities.
In the future, should we require more capital to fund significant discretionary activities in the United States than is generated by our domestic operations, or is available through the issuance of debt, we could elect to repatriate future periods' earnings from foreign jurisdictions. This alternative could result in a higher effective tax rate.
Based on all the aforementioned factors, the Company believes its current liquidity position is strong, and we will continue to meet all our financial commitments for the foreseeable future. These commitments include, but are not limited to, regular quarterly dividends, debt maturities, capital expenditures, share repurchases and other obligations included under the heading “Off-Balance Sheet Agreements and Aggregate Contractual Obligations” below.
Cash Flows from Operating Activities
Net cash provided by operating activities for the years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009 was $9,474 million, $9,532 million and $8,186 million, respectively.
Cash flows from operating activities decreased $58 million, or 1 percent, in 2011 compared to 2010. This decrease was primarily attributable to an increase in contributions to our pension plans of $924 million during 2011; the temporary extension of the Company's credit terms in Japan as a result of the natural disasters that devastated the northern and eastern portions of the country during the first quarter of 2011; an increase in interest payments related to long-term debt; and an increase in cash payments related to our productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives. The unfavorable impact of these items was
66
partially offset by an increase in cash receipts from customers, a decrease in tax payments, and the favorable impact of foreign currency exchange rates on operations. Refer to the heading "Net Operating Revenues" above.
Cash flows from operating activities increased $1,346 million, or 16 percent, in 2010 compared to 2009. This increase was primarily attributable to increased receipts from customers, the impact of our acquisition of CCE's North American business, the favorable impact of exchange rates on operations and a decrease in contributions to our pension plans. The impact of these items was partially offset by higher tax payments in 2010. The increase in cash receipts from customers was primarily due to an increase in net operating revenues. Refer to the heading "Net Operating Revenues" above. Also, in 2009, cash flows from operating activities included the receipt of a $183 million special dividend from Coca-Cola Hellenic. The Company contributed approximately $77 million to our pension plans during the year ended December 31, 2010, compared to $269 million during the year ended December 31, 2009.
Cash Flows from Investing Activities
Our cash flows provided by (used in) investing activities are summarized as follows (in millions):
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
Purchases of short-term investments |
$ |
(4,057 |
) |
$ |
(4,579 |
) |
$ |
(2,130 |
) |
||
Proceeds from disposals of short-term investments |
5,647 |
4,032 |
— |
||||||||
Acquisitions and investments |
(977 |
) |
(2,511 |
) |
(300 |
) |
|||||
Purchases of other investments |
(787 |
) |
(132 |
) |
(22 |
) |
|||||
Proceeds from disposals of bottling companies and other investments |
562 |
972 |
240 |
||||||||
Purchases of property, plant and equipment |
(2,920 |
) |
(2,215 |
) |
(1,993 |
) |
|||||
Proceeds from disposals of property, plant and equipment |
101 |
134 |
104 |
||||||||
Other investing activities |
(93 |
) |
(106 |
) |
(48 |
) |
|||||
Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities |
$ |
(2,524 |
) |
$ |
(4,405 |
) |
$ |
(4,149 |
) |
||
Short-Term Investments
In 2011, purchases of short-term investments were $4,057 million, and proceeds from disposals of short-term investments were $5,647 million. This activity resulted in a net cash inflow of $1,590 million during 2011. In 2010, purchases of short-term investments were $4,579 million, and proceeds from disposals of short-term investments were $4,032 million. This activity resulted in a net cash outflow of $547 million during 2010. In 2009, purchases of short-term investments were $2,130 million. These short-term investments are time deposits that have maturities of greater than three months but less than one year, and are classified in the line item short-term investments in our consolidated balance sheets. The Company began investing in longer-term time deposits during the fourth quarter of 2009 to match the maturities of short-term debt issued as part of our commercial paper program. Refer to the heading "Cash Flows from Financing Activities" below. These time deposits are classified in the line item short-term investments in our consolidated balance sheets.
Acquisitions and Investments
In 2011, the Company's acquisition and investment activities totaled $977 million. These activities were primarily related to the acquisitions of Great Plains and Honest Tea, Inc. ("Honest Tea"), and an additional investment in Coca-Cola Central Japan Company ("Central Japan"). In addition, the Company's acquisition and investment activities during 2011 included immaterial cash payments for the finalization of working capital adjustments related to our acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to our discussion of this transaction below. None of the Company's other acquisitions or investments was individually significant.
In 2010, the Company's acquisition and investment activities totaled $2,511 million, which was primarily related to our acquisition of CCE's North American business; DPS license agreements; our acquisition of OAO Nidan Juices ("Nidan"), a Russian juice company; and our additional investment in Fresh Trading Ltd. ("innocent"). The Company and the existing shareowners of innocent have a series of outstanding put and call options for the Company to potentially acquire the remaining shares not already owned by the Company. The put and call options are exercisable in stages between 2013 and 2014. Refer to the heading "Operations Review — Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" above and Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information related to our acquisitions during the year.
In 2009, our Company's acquisition and investment activities totaled $300 million. None of the acquisitions or investments was individually significant. Included in these investment activities was the acquisition of a minority interest in innocent. Refer to Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information related to our acquisitions during the year.
67
Purchases of Other Investments
In 2011, purchases of other investments were $787 million, primarily related to long-term investments made by the Company for nonoperating activities. These investments are primarily classified as available-for-sale securities.
Proceeds from Disposals of Bottling Companies and Other Investments
In 2011, proceeds from disposals of bottling companies and other investments were $562 million. These proceeds were primarily related to the sale of our investment in Embonor for $394 million. Refer to Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information.
In 2010, proceeds from disposals of bottling companies and other investments were $972 million. These proceeds were primarily related to the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE for $0.9 billion and the sale of 50 percent of our investment in Leão Junior for $83 million. Refer to the heading "Operations Review — Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" above and Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information.
In 2009, proceeds from the disposal of bottling companies and other investments totaled $240 million, none of which was individually significant.
Purchases of Property, Plant and Equipment — Net
Purchases of property, plant and equipment net of disposals for the years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009 were $2,819 million, $2,081 million and $1,889 million, respectively. The increase in 2011 compared to 2010 and 2009 was primarily attributable to the full year impact of our acquisition of CCE's North American business during the fourth quarter of 2010. Refer to the heading "Operations Review — Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements." Generally, bottling and finished products operations are more capital intensive compared to concentrate and syrup operations. Total capital expenditures for property, plant and equipment (including our investments in information technology) and the percentage of such totals by operating segment were as follows (in millions):
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
Capital expenditures |
$ |
2,920 |
$ |
2,215 |
$ |
1,993 |
|||||
Eurasia & Africa |
2.9 |
% |
2.7 |
% |
3.5 |
% |
|||||
Europe |
1.3 |
1.5 |
3.4 |
||||||||
Latin America |
3.6 |
4.2 |
6.2 |
||||||||
North America |
46.7 |
32.1 |
23.0 |
||||||||
Pacific |
3.2 |
4.6 |
4.6 |
||||||||
Bottling Investments |
35.6 |
42.5 |
41.4 |
||||||||
Corporate |
6.7 |
12.4 |
17.9 |
||||||||
We expect our annual 2012 capital expenditures to range between $3.0 billion and $3.2 billion as we continue to integrate CCE's North American business and make investments to further enhance our operational effectiveness.
Other Investing Activities
In 2011, other investing activities primarily related to the Company's investments in joint ventures. None of these investments were individually significant.
In 2010, other investing activities were primarily related to the deconsolidation of certain entities due to the Company's adoption of new accounting guidance issued by the FASB. Refer to the heading "Operations Review — Structural Changes, Acquired Brands and New License Agreements" above and Note 1 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information. The cash flow impact in other investing activities primarily represents the balance of cash and cash equivalents on the deconsolidated entities' balance sheets as of December 31, 2009.
68
Cash Flows from Financing Activities
Our cash flows provided by (used in) financing activities were as follows (in millions):
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
Issuances of debt |
$ |
27,495 |
$ |
15,251 |
$ |
14,689 |
|||||
Payments of debt |
(22,530 |
) |
(13,403 |
) |
(12,326 |
) |
|||||
Issuances of stock |
1,569 |
1,666 |
664 |
||||||||
Purchases of stock for treasury |
(4,513 |
) |
(2,961 |
) |
(1,518 |
) |
|||||
Dividends |
(4,300 |
) |
(4,068 |
) |
(3,800 |
) |
|||||
Other financing activities |
45 |
50 |
(2 |
) |
|||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities |
$ |
(2,234 |
) |
$ |
(3,465 |
) |
$ |
(2,293 |
) |
||
Debt Financing
Our Company maintains debt levels we consider prudent based on our cash flows, interest coverage ratio and percentage of debt to capital. We use debt financing to lower our overall cost of capital, which increases our return on shareowners' equity. This exposes us to adverse changes in interest rates. Our interest expense may also be affected by our credit ratings.
As of December 31, 2011, our long-term debt was rated "A+" by Standard & Poor's, "Aa3" by Moody's and "A+" by Fitch. Our commercial paper program was rated "A-1" by Standard & Poor's, "P-1" by Moody's and "F-1" by Fitch. In assessing our credit strength, all three agencies consider our capital structure (including the amount and maturity dates of our debt) and financial policies as well as the aggregated balance sheet and other financial information for the Company. In addition, some rating agencies also consider financial information for certain bottlers, including New CCE, Coca-Cola Amatil, Coca-Cola Bottling Co. Consolidated, Coca-Cola FEMSA and Coca-Cola Hellenic. While the Company has no legal obligation for the debt of these bottlers, the rating agencies believe the strategic importance of the bottlers to the Company's business model provides the Company with an incentive to keep these bottlers viable. It is our expectation that the credit rating agencies will continue using this methodology. If our credit ratings were to be downgraded as a result of changes in our capital structure, our major bottlers' financial performance, changes in the credit rating agencies' methodology in assessing our credit strength, or for any other reason, our cost of borrowing could increase. Additionally, if certain bottlers' credit ratings were to decline, the Company's share of equity income could be reduced as a result of the potential increase in interest expense for these bottlers.
We monitor our financial ratios and, as indicated above, the rating agencies consider these ratios in assessing our credit ratings. Each rating agency employs a different aggregation methodology and has different thresholds for the various financial ratios. These thresholds are not necessarily permanent, nor are they always fully disclosed to our Company.
Our global presence and strong capital position give us access to key financial markets around the world, enabling us to raise funds at a low effective cost. This posture, coupled with active management of our mix of short-term and long-term debt and our mix of fixed-rate and variable-rate debt, results in a lower overall cost of borrowing. Our debt management policies, in conjunction with our share repurchase programs and investment activity, can result in current liabilities exceeding current assets.
Issuances and payments of debt included both short-term and long-term financing activities. On December 31, 2011, we had $4,625 million in lines of credit available for general corporate purposes, including commercial paper backup. These backup lines of credit expire at various times from 2012 through 2016. There were no borrowings under these backup lines of credit during 2011. These credit facilities are subject to normal banking terms and conditions. Some of the financial arrangements require compensating balances, none of which is presently significant to our Company.
In 2011, the Company had issuances of debt of $27,495 million, which included $25,219 million of issuances of commercial paper and short-term debt with maturities greater than 90 days. The Company's total issuances of debt also included long-term debt issuances of $2,276 million, net of the debt issued to exchange a certain amount of our existing long-term debt. The Company issued $2,979 million of long-term debt during 2011. We used $979 million of this newly issued debt and paid a premium of $208 million to exchange $1,022 million of existing long-term debt that was assumed in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business in the fourth quarter of 2010. The remaining cash from the issuance was used to reduce the Company's outstanding commercial paper balance and exchange a certain amount of short-term debt.
69
The general terms of the notes issued during 2011 are as follows:
• |
$1,655 million total principal amount of notes due September 1, 2016, at a fixed interest rate of 1.8 percent; and
|
• |
$1,324 million total principal amount of notes due September 1, 2021, at a fixed interest rate of 3.3 percent.
|
During the fourth quarter of 2011, the Company extinguished long-term debt that had a carrying value of $20 million and was not scheduled to mature until 2012. This debt was outstanding prior to the Company's acquisition of CCE's North American business. In addition, the Company repurchased long-term debt during 2011 that was assumed in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. The repurchased debt included $99 million in unamortized fair value adjustments recorded as part of our purchase accounting for the CCE transaction and was settled throughout the year as follows:
• |
During the first quarter of 2011, the Company repurchased all of our outstanding U.K. pound sterling notes that had a carrying value of $674 million;
|
• |
During the second quarter of 2011, the Company repurchased long-term debt that had a carrying value of $42 million; and
|
• |
During the third quarter of 2011, the Company repurchased long-term debt that had a carrying value of $19 million.
|
In 2011, the Company had payments of debt of $22,530 million, including the repurchased debt discussed above. Total payments of debt included $91 million of net payments of commercial paper and short-term debt with maturities of 90 days or less and $20,334 million of payments of commercial paper and short-term debt with maturities greater than 90 days. The Company's total payments of debt also included long-term debt payments of $2,105 million. The Company recorded a net charge of $9 million in the line item interest expense in our consolidated statement of income during the year ended December 31, 2011. This net charge was due to the exchange, repurchase and/or extinguishment of long-term debt described above.
In 2010, the Company had issuances of debt of $15,251 million, which included $1,171 million of net issuances of commercial paper and short-term debt with maturities of 90 days or less and $9,503 million of issuances of commercial paper and short-term debt with maturities greater than 90 days. We also assumed $7.9 billion of debt as a result of our acquisition of CCE's North American business. In addition, on November 15, 2010, the Company issued $4,500 million of long-term notes. The proceeds from the debt issuance were used to repurchase $2,910 million of long-term debt, and the remainder was used to reduce our commercial paper balance. The long-term notes issued on November 15, 2010, had the following general terms:
• |
$1,250 million total principal notes due May 15, 2012, at a variable interest rate of 3 month LIBOR plus 0.05 percent; |
• |
$1,250 million total principal notes due November 15, 2013, at a fixed interest rate of 0.75 percent; |
• |
$1,000 million total principal notes due November 15, 2015, at a fixed interest rate of 1.5 percent; and |
• |
$1,000 million total principal notes due November 15, 2020, at a fixed interest rate of 3.15 percent. |
In 2010, the Company had payments of debt of $13,403 million, including the repurchased long-term debt discussed above. Total payments of debt also included $9,667 million related to commercial paper and short-term debt with maturities greater than 90 days. The Company recorded a charge of $342 million related to the premiums paid to repurchase the long-term debt and the costs associated with the settlement of treasury rate locks issued in connection with the debt tender offer. Refer to Note 10 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information related to the Company's long-term debt.
In 2009, the Company had issuances of debt of $14,689 million and payments of debt of $12,326 million. The issuances of debt included $12,397 million of issuances of commercial paper and short-term debt with maturities greater than 90 days, as well as $900 million and $1,350 million of long-term debt due March 15, 2014, and March 15, 2019, respectively. The payments of debt included $1,861 million of net payments of commercial paper and short-term debt with maturities of 90 days or less; $10,017 million related to commercial paper and short-term debt with maturities greater than 90 days; and $448 million related to long-term debt. The increase in issuances and payments of commercial paper with maturities of greater than 90 days was primarily due to a favorable interest rate environment on longer-term commercial paper. As a result, the Company also began investing in longer-term time deposits that have maturities of greater than three months. Refer to the heading "Cash Flows from Investing Activities" above.
70
Issuances of Stock
The issuances of stock in 2011, 2010 and 2009 were primarily related to the exercise of stock options by Company employees.
Share Repurchases
On July 20, 2006, the Board of Directors of the Company authorized a share repurchase program of up to 300 million shares of the Company's common stock. The program took effect on October 31, 2006. The table below presents annual shares repurchased and average price per share:
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
Number of shares repurchased (in millions) |
63 |
49 |
26 |
||||||||
Average price per share |
$ |
67.46 |
$ |
63.85 |
$ |
57.09 |
|||||
Since the inception of our initial share repurchase program in 1984 through our current program as of December 31, 2011, we have purchased approximately 1.4 billion shares of our Company's common stock at an average price per share of $23.43. In addition to shares repurchased under the stock repurchase plans authorized by our Board of Directors, the Company's treasury stock activity also includes shares surrendered to the Company to pay the exercise price and/or to satisfy tax withholding obligations in connection with so-called stock swap exercises of employee stock options and/or the vesting of restricted stock issued to employees. In 2011, we repurchased $4.3 billion of our stock. However, due to the timing of settlements, the total amount of treasury stock purchases that settled during 2011 was $4.5 billion, which includes treasury stock that was purchased and settled during 2011 as well as treasury stock purchased in December 2010 that settled in early 2011. The net impact of the Company's treasury stock issuance and purchase activities in 2011 resulted in a net cash outflow of $2.9 billion. We currently expect to repurchase an additional $2.5 billion to $3.0 billion of our stock during 2012, net of proceeds from the issuance of stock due to the exercise of employee stock options.
Dividends
At its February 2012 meeting, our Board of Directors increased our quarterly dividend by 8.5 percent, raising it to $0.51 per share, equivalent to a full year dividend of $2.04 per share in 2012. This is our 50th consecutive annual increase. Our annual common stock dividend was $1.88 per share, $1.76 per share and $1.64 per share in 2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively. The 2011 dividend represented a 7 percent increase from 2010, and the 2010 dividend represented a 7 percent increase from 2009.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements and Aggregate Contractual Obligations
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
In accordance with the definition under SEC rules, the following qualify as off-balance sheet arrangements:
• |
any obligation under certain guarantee contracts; |
• |
a retained or contingent interest in assets transferred to an unconsolidated entity or similar arrangement that serves as credit, liquidity or market risk support to that entity for such assets; |
• |
any obligation under certain derivative instruments; and |
• |
any obligation arising out of a material variable interest held by the registrant in an unconsolidated entity that provides financing, liquidity, market risk or credit risk support to the registrant, or engages in leasing, hedging or research and development services with the registrant. |
As of December 31, 2011, we were contingently liable for guarantees of indebtedness owed by third parties of $654 million, of which $321 million was related to VIEs. These guarantees are primarily related to third-party customers, bottlers, vendors and container manufacturing operations and have arisen through the normal course of business. These guarantees have various terms, and none of these guarantees was individually significant. The amount represents the maximum potential future payments that we could be required to make under the guarantees; however, we do not consider it probable that we will be required to satisfy these guarantees. Management concluded that the likelihood of any significant amounts being paid by our Company under these guarantees is not probable. As of December 31, 2011, we were not directly liable for the debt of any unconsolidated entity, and we did not have any retained or contingent interest in assets as defined above.
Our Company recognizes all derivatives as either assets or liabilities at fair value in our consolidated balance sheets. Refer to Note 5 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
As of December 31, 2011, the Company had $4,625 million in lines of credit for general corporate purposes, including commercial paper backup. These backup lines of credit expire at various times from 2012 through 2016. There were no
71
borrowings under these backup lines of credit during 2011. These credit facilities are subject to normal banking terms and conditions. Some of the financial arrangements require compensating balances, none of which is presently significant to our Company.
Aggregate Contractual Obligations
As of December 31, 2011, the Company's contractual obligations, including payments due by period, were as follows (in millions):
Payments Due by Period
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Total |
2012 |
2013-2014 |
2015-2016 |
2017 and
Thereafter
|
|||||||||||||||
Short-term loans and notes payable:1
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Commercial paper borrowings |
$ |
12,135 |
$ |
12,135 |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
|||||||||
Lines of credit and other short-term borrowings |
736 |
736 |
— |
— |
— |
||||||||||||||
Current maturities of long-term debt2
|
2,038 |
2,038 |
— |
— |
— |
||||||||||||||
Long-term debt, net of current maturities2
|
12,941 |
— |
3,107 |
3,076 |
6,758 |
||||||||||||||
Estimated interest payments3
|
5,007 |
431 |
784 |
633 |
3,159 |
||||||||||||||
Accrued income taxes4
|
362 |
362 |
— |
— |
— |
||||||||||||||
Purchase obligations5
|
13,357 |
9,741 |
1,611 |
1,035 |
970 |
||||||||||||||
Marketing obligations6
|
4,389 |
2,600 |
736 |
421 |
632 |
||||||||||||||
Lease obligations |
1,213 |
282 |
387 |
226 |
318 |
||||||||||||||
Total contractual obligations4
|
$ |
52,178 |
$ |
28,325 |
$ |
6,625 |
$ |
5,391 |
$ |
11,837 |
|||||||||
1 |
Refer to Note 10 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for information regarding short-term loans and notes payable. Upon payment of outstanding commercial paper, we typically issue new commercial paper. Lines of credit and other short-term borrowings are expected to fluctuate depending upon current liquidity needs, especially at international subsidiaries. |
2 |
Refer to Note 10 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for information regarding long-term debt. We will consider several alternatives to settle this long-term debt, including the use of cash flows from operating activities, issuance of commercial paper or issuance of other long-term debt. |
3 |
We calculated estimated interest payments for our long-term fixed-rate debt based on the applicable rates and payment dates. We typically expect to settle such interest payments with cash flows from operating activities and/or short-term borrowings. |
4 |
Refer to Note 14 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for information regarding income taxes. As of December 31, 2011, the noncurrent portion of our income tax liability, including accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits, was $418 million, which was not included in the total above. At this time, the settlement period for the noncurrent portion of our income tax liability cannot be determined. In addition, any payments related to unrecognized tax benefits would be partially offset by reductions in payments in other jurisdictions.
|
5 |
Purchase obligations include agreements to purchase goods or services that are enforceable and legally binding and that specify all significant terms, including long-term contractual obligations, open purchase orders, accounts payable and certain accrued liabilities. We expect to fund these obligations with cash flows from operating activities. |
6 |
We expect to fund these marketing obligations with cash flows from operating activities. |
The total accrued benefit liability for pension and other postretirement benefit plans recognized as of December 31, 2011, was $3,320 million. Refer to Note 13 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. This amount is impacted by, among other items, pension expense, funding levels, plan amendments, changes in plan demographics and assumptions, and the investment return on plan assets. Because the accrued liability does not represent expected liquidity needs, we did not include this amount in the contractual obligations table.
The Pension Protection Act of 2006 ("PPA") was enacted in August 2006 and established, among other things, new standards for funding of U.S. defined benefit pension plans. We generally expect to fund all future contributions with cash flows from operating activities. Our international pension plans are generally funded in accordance with local laws and income tax regulations.
72
As of December 31, 2011, the projected benefit obligation of the U.S. qualified pension plans was $5,571 million, and the fair value of plan assets was $4,274 million. The majority of this underfunding was due to the negative impact that the recent credit crisis and financial system instability had on the value of our pension plan assets and the decrease in the weighted-average discount rate used to calculate the Company's benefit obligation.
As of December 31, 2011, the projected benefit obligation of all pension plans other than the U.S. qualified pension plans was $2,684 million, and the fair value of all other pension plan assets was $1,897 million. The majority of this underfunding is attributable to an international pension plan for certain non-U.S. employees that is unfunded due to tax law restrictions, as well as our unfunded U.S. nonqualified pension plans. These U.S. nonqualified pension plans provide, for certain associates, benefits that are not permitted to be funded through a qualified plan because of limits imposed by the Internal Revenue Code of 1986. The expected benefit payments for these unfunded pension plans are not included in the table above. However, we anticipate annual benefit payments for these unfunded pension plans to be approximately $60 million in 2012 and remain near that level through 2030, decreasing annually thereafter. Refer to Note 13 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
In 2012, we expect to contribute an additional $953 million to various plans, of which approximately $900 million was contributed in the first quarter of 2012 to the Company's U.S. pension plans. Refer to Note 13 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. We did not include our estimated contributions to our various plans in the table above.
On December 14, 2011, the Company entered into a definitive agreement with Aujan Industries (“Aujan”), one of the largest independent beverage companies in the Middle East, to acquire approximately half of the equity in Aujan's existing beverage business, excluding Aujan's Iranian manufacturing and distribution business. Under the terms of the agreement, we will acquire 50 percent of the Aujan entity that holds the rights to Aujan-owned brands, and 49 percent of Aujan's bottling and distribution company, which will continue to hold the licensed brand Vimto. Total consideration for this investment, which will be accounted for under the equity method, is approximately $980 million, which we expect to fund from our existing cash reserves. Closing of the transaction is subject to certain conditions and is expected to occur in the first half of 2012. We did not include our anticipated investment in Aujan in the table above.
In general, we are self-insured for large portions of many different types of claims; however, we do use commercial insurance above our self-insured retentions to reduce the Company's risk of catastrophic loss. Our reserves for the Company's self-insured losses are estimated through actuarial procedures of the insurance industry and by using industry assumptions, adjusted for our specific expectations based on our claim history. As of December 31, 2011, our self-insurance reserves totaled approximately $527 million. Refer to Note 11 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. We did not include estimated payments related to our self-insurance reserves in the table above.
Deferred income tax liabilities as of December 31, 2011, were $4,713 million. Refer to Note 14 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. This amount is not included in the total contractual obligations table because we believe this presentation would not be meaningful. Deferred income tax liabilities are calculated based on temporary differences between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their respective book bases, which will result in taxable amounts in future years when the liabilities are settled at their reported financial statement amounts. The results of these calculations do not have a direct connection with the amount of cash taxes to be paid in any future periods. As a result, scheduling deferred income tax liabilities as payments due by period could be misleading, because this scheduling would not relate to liquidity needs.
73
Foreign Exchange
Our international operations are subject to certain opportunities and risks, including currency fluctuations and governmental actions. We closely monitor our operations in each country and seek to adopt appropriate strategies that are responsive to changing economic and political environments, and to fluctuations in foreign currencies.
We use 73 functional currencies. Due to our global operations, weakness in some of these currencies might be offset by strength in others. In 2011, 2010 and 2009, the weighted-average exchange rates for foreign currencies in which the Company conducted operations (all operating currencies), and for certain individual currencies, strengthened (weakened) against the U.S. dollar as follows:
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
|||||
All operating currencies |
6 |
% |
3 |
% |
(9 |
)% |
||
Brazilian real |
5 |
% |
11 |
% |
(8 |
)% |
||
Mexican peso |
4 |
6 |
(24 |
) |
||||
Australian dollar |
14 |
13 |
(8 |
) |
||||
South African rand |
1 |
11 |
(1 |
) |
||||
British pound |
4 |
(2 |
) |
(18 |
) |
|||
Euro |
7 |
(5 |
) |
(8 |
) |
|||
Japanese yen |
10 |
6 |
9 |
|||||
These percentages do not include the effects of our hedging activities and, therefore, do not reflect the actual impact of fluctuations in exchange rates on our operating results. Our foreign currency management program is designed to mitigate, over time, a portion of the impact of exchange rate changes on our net income and earnings per share. The total currency impact on operating income, including the effect of our hedging activities, was an increase of approximately 4 percent and 3 percent in 2011 and 2010, respectively. Based on the anticipated impact of hedging coverage in place, the Company expects currencies to have a low single-digit negative impact on operating income for the first quarter of 2012 and a mid single-digit negative impact on operating income for the full year of 2012.
Foreign currency exchange gains and losses are primarily the result of the remeasurement of monetary assets and liabilities from certain currencies into functional currencies. The effects of the remeasurement of these assets and liabilities are partially offset by the impact of our economic hedging program for certain exposures on our consolidated balance sheets. Refer to Note 5 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. Foreign currency exchange gains and losses are included as a component of other income (loss) — net in our consolidated financial statements. Refer to the heading "Operations Review — Other Income (Loss) — Net" above. The Company recorded foreign currency exchange losses of $73 million, $148 million and $34 million in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
The remeasurement loss recorded in 2010 was primarily related to our Venezuelan subsidiary. Subsequent to December 31, 2009, the Venezuelan government announced a currency devaluation, and Venezuela was determined to be a hyperinflationary economy. As a result, our local subsidiary was required to use the U.S. dollar as its functional currency and we recorded a net remeasurement loss of $103 million during the first quarter of 2010, in the line item other income (loss) — net in our consolidated statement of income. As of December 31, 2011, our Venezuelan subsidiary held monetary assets of $300 million.
In addition to the foreign currency exchange exposure related to our Venezuelan subsidiary's net assets, we also sell concentrate to our bottling partner in Venezuela from outside the country. These sales are denominated in U.S. dollars. Some of our concentrate sales were approved by the CADIVI to receive the official rate for essential goods of 2.6 bolivars per U.S. dollar prior to the elimination of the official rate for essential goods in December 2010. Prior to the elimination of the official rate for essential goods, our bottling partner in Venezuela was able to convert bolivars to U.S. dollars to settle our receivables related to sales approved by the CADIVI. However, if we are unable to utilize a government-approved exchange rate mechanism to settle future concentrate sales to our bottling partner in Venezuela, the Company's outstanding receivables balance related to these sales will continue to increase.
The Company will continue to manage its foreign currency exposure to mitigate, over time, a portion of the impact of exchange rate changes on net income and earnings per share.
Impact of Inflation and Changing Prices
Inflation affects the way we operate in many markets around the world. In general, we believe that, over time, we are able to increase prices to counteract the majority of the inflationary effects of increasing costs and to generate sufficient cash flows to maintain our productive capability.
74
Overview of Financial Position
The following table illustrates the change in the individual line items of the Company's consolidated balance sheet (in millions):
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
Increase (Decrease) |
Percent Change |
||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ |
12,803 |
$ |
8,517 |
$ |
4,286 |
50 |
% |
||||||
Short-term investments |
1,088 |
2,682 |
(1,594 |
) |
(59 |
) |
||||||||
Marketable securities |
144 |
138 |
6 |
4 |
||||||||||
Trade accounts receivable — net |
4,920 |
4,430 |
490 |
11 |
||||||||||
Inventories |
3,092 |
2,650 |
442 |
17 |
||||||||||
Prepaid expenses and other assets |
3,450 |
3,162 |
288 |
9 |
||||||||||
Equity method investments |
7,233 |
6,954 |
279 |
4 |
||||||||||
Other investments, principally bottling companies |
1,141 |
631 |
510 |
81 |
||||||||||
Other assets |
3,495 |
2,121 |
1,374 |
65 |
||||||||||
Property, plant and equipment — net |
14,939 |
14,727 |
212 |
1 |
||||||||||
Trademarks with indefinite lives |
6,430 |
6,356 |
74 |
1 |
||||||||||
Bottlers' franchise rights with indefinite lives |
7,770 |
7,511 |
259 |
3 |
||||||||||
Goodwill |
12,219 |
11,665 |
554 |
5 |
||||||||||
Other intangible assets |
1,250 |
1,377 |
(127 |
) |
(9 |
) |
||||||||
Total assets |
$ |
79,974 |
$ |
72,921 |
$ |
7,053 |
10 |
% |
||||||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
$ |
9,009 |
$ |
8,859 |
$ |
150 |
2 |
% |
||||||
Loans and notes payable |
12,871 |
8,100 |
4,771 |
59 |
||||||||||
Current maturities of long-term debt |
2,041 |
1,276 |
765 |
60 |
||||||||||
Accrued income taxes |
362 |
273 |
89 |
33 |
||||||||||
Long-term debt |
13,656 |
14,041 |
(385 |
) |
(3 |
) |
||||||||
Other liabilities |
5,420 |
4,794 |
626 |
13 |
||||||||||
Deferred income taxes |
4,694 |
4,261 |
433 |
10 |
||||||||||
Total liabilities |
$ |
48,053 |
$ |
41,604 |
$ |
6,449 |
16 |
% |
||||||
Net assets |
$ |
31,921 |
$ |
31,317 |
$ |
604 |
1 |
2 |
% |
|||||
1 |
Includes a decrease in net assets of $692 million resulting from translation adjustments in various balance sheet accounts. |
The table above includes the impact of the following transactions and events:
• |
Cash and cash equivalents increased $4,286 million, or 50 percent, primarily due to increased receipts from customers and proceeds from the net issuances of commercial paper. A majority of the Company's consolidated cash and cash equivalents balance is held by our foreign subsidiaries. |
• |
Short-term investments decreased $1,594 million, or 59 percent, primarily due to the maturity of time deposits. |
• |
Other investments, principally bottling companies increased $510 million, or 81 percent, primarily due to the merger of Arca and Contal. Refer to Note 17 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information related to the merger. |
• |
Other assets increased $1,374 million, or 65 percent, primarily due to long-term investments made by our captive insurance company, the fair value of interest rate swap agreements, and the impact of certain pension contributions. These pension contributions resulted in certain plans being in a net asset position. |
• |
Goodwill increased $554 million, or 5 percent, primarily due to our acquisitions of Great Plains and Honest Tea in addition to purchase accounting adjustments related to our acquisition of CCE's North American business. |
• |
Loans and notes payable increased $4,771 million, or 59 percent, primarily due to an increase in our commercial paper balance. |
• |
Other liabilities increased $626 million, or 13 percent, primarily due to the decrease in the weighted-average discount rate used to calculate the Company's pension benefit obligation. |
75
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Our Company uses derivative financial instruments primarily to reduce our exposure to adverse fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates, interest rates, commodity prices and other market risks. We do not enter into derivative financial instruments for trading purposes. As a matter of policy, all of our derivative positions are used to reduce risk by hedging an underlying economic exposure. Because of the high correlation between the hedging instrument and the underlying exposure, fluctuations in the value of the instruments are generally offset by reciprocal changes in the value of the underlying exposure. The Company generally hedges anticipated exposures up to 36 months in advance; however, the majority of our derivative instruments expire within 24 months or less. Virtually all of our derivatives are straightforward over-the-counter instruments with liquid markets.
We monitor our exposure to financial market risks using several objective measurement systems. In prior years, the Company primarily used the value at risk methodology for its quantitative and qualitative disclosures about market risk. However, with the Company's acquisition of CCE's North American business in 2010, and the related changes to our consolidated balance sheet, the Company has provided a sensitivity analysis to measure our exposure to fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates, interest rates and commodity prices. Refer to Note 5 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information about our hedging transactions and derivative financial instruments.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rates
We manage most of our foreign currency exposures on a consolidated basis, which allows us to net certain exposures and take advantage of any natural offsets. In 2011, we generated $27.8 billion of our net operating revenues from operations outside the United States; therefore, weakness in one particular currency might be offset by strengths in other currencies over time. We use derivative financial instruments to further reduce our net exposure to currency fluctuations.
Our Company enters into forward exchange contracts and purchases currency options (principally euro and Japanese yen) and collars to hedge certain portions of forecasted cash flows denominated in foreign currencies. Additionally, we enter into forward exchange contracts to offset the earnings impact related to exchange rate fluctuations on certain monetary assets and liabilities. We also enter into forward exchange contracts as hedges of net investments in international operations.
The total notional value of our foreign currency derivatives was $10.5 billion and $6.3 billion as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively. This total includes derivative instruments that are designated and qualify for hedge accounting as well as economic hedges. The fair value of the contracts that qualify for hedge accounting resulted in an asset of $129 million as of December 31, 2011. At the end of 2011, we estimate that an unfavorable 10 percent change in the exchange rates would have eliminated the net unrealized gain and created an unrealized loss of $490 million. The fair value of the contracts that do not qualify for hedge accounting resulted in a liability of $87 million, and we estimate that an unfavorable 10 percent change in rates would have increased our net losses by $336 million. All losses were offset by changes in the underlying hedged item, resulting in no net material impact on earnings.
Interest Rates
We monitor our mix of fixed-rate and variable-rate debt, as well as our mix of short-term debt versus long-term debt. From time to time, we enter into interest rate swap agreements to manage our mix of fixed-rate and variable-rate debt.
Based on the Company's variable-rate debt and derivative instruments outstanding as of December 31, 2011, a 1 percentage point increase in interest rates would have increased interest expense by $191 million in 2011. However, this increase in interest expense would have been partially offset by the increase in interest income related to higher interest rates.
Commodity Prices
The Company is subject to market risk with respect to commodity price fluctuations, principally related to our purchases of aluminum and plastic, sweeteners, and energy. Whenever possible, we manage our exposure to commodity risks primarily through the use of supplier pricing agreements that enable us to establish the purchase prices for certain inputs that are used in our manufacturing and distribution business. We also use derivative financial instruments to manage our exposure to commodity risks at times. Certain of these derivatives do not qualify for hedge accounting, but they are effective economic hedges that help the Company mitigate the price risk associated with the purchases of materials used in our manufacturing processes and the fuel used to operate our extensive vehicle fleet.
Open commodity derivatives that qualify for hedge accounting had a notional value of $26 million as of December 31, 2011. These contracts had a fair value of $1 million. The potential change in fair value of these commodity derivative instruments, assuming a 10 percent decrease in underlying commodity prices, would have eliminated the net unrealized gain and created an unrealized loss of $1 million.
Open commodity derivatives that do not qualify for hedge accounting had a notional value of $1,165 million as of December 31, 2011. These contracts had a fair value of $7 million. The potential change in fair value of these commodity derivative instruments, assuming a 10 percent decrease in underlying commodity prices, would have eliminated our net unrealized gain and created an unrealized loss of $78 million.
76
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
|
||
77
THE COCA-COLA COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
(In millions except per share data) |
|||||||||||
NET OPERATING REVENUES |
$ |
46,542 |
$ |
35,119 |
$ |
30,990 |
|||||
Cost of goods sold |
18,216 |
12,693 |
11,088 |
||||||||
GROSS PROFIT |
28,326 |
22,426 |
19,902 |
||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
17,440 |
13,158 |
11,358 |
||||||||
Other operating charges |
732 |
819 |
313 |
||||||||
OPERATING INCOME |
10,154 |
8,449 |
8,231 |
||||||||
Interest income |
483 |
317 |
249 |
||||||||
Interest expense |
417 |
733 |
355 |
||||||||
Equity income (loss) — net |
690 |
1,025 |
781 |
||||||||
Other income (loss) — net |
529 |
5,185 |
40 |
||||||||
INCOME BEFORE INCOME TAXES |
11,439 |
14,243 |
8,946 |
||||||||
Income taxes |
2,805 |
2,384 |
2,040 |
||||||||
CONSOLIDATED NET INCOME |
8,634 |
11,859 |
6,906 |
||||||||
Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests |
62 |
50 |
82 |
||||||||
|
NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO SHAREOWNERS OF
THE COCA-COLA COMPANY
|
$ |
8,572 |
$ |
11,809 |
$ |
6,824 |
|||||
BASIC NET INCOME PER SHARE1
|
$ |
3.75 |
$ |
5.12 |
$ |
2.95 |
|||||
DILUTED NET INCOME PER SHARE1
|
$ |
3.69 |
$ |
5.06 |
$ |
2.93 |
|||||
AVERAGE SHARES OUTSTANDING |
2,284 |
2,308 |
2,314 |
||||||||
Effect of dilutive securities |
39 |
25 |
15 |
||||||||
AVERAGE SHARES OUTSTANDING ASSUMING DILUTION |
2,323 |
2,333 |
2,329 |
||||||||
1 |
Basic net income per share and diluted net income per share are calculated based on net income attributable to shareowners of |
The Coca-Cola Company.
Refer to Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
78
THE COCA-COLA COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
|||||
(In millions except par value) |
|||||||
ASSETS |
|||||||
CURRENT ASSETS |
|||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ |
12,803 |
$ |
8,517 |
|||
Short-term investments |
1,088 |
2,682 |
|||||
TOTAL CASH, CASH EQUIVALENTS AND SHORT-TERM INVESTMENTS |
13,891 |
11,199 |
|||||
Marketable securities |
144 |
138 |
|||||
Trade accounts receivable, less allowances of $83 and $48, respectively |
4,920 |
4,430 |
|||||
Inventories |
3,092 |
2,650 |
|||||
Prepaid expenses and other assets |
3,450 |
3,162 |
|||||
TOTAL CURRENT ASSETS |
25,497 |
21,579 |
|||||
EQUITY METHOD INVESTMENTS |
7,233 |
6,954 |
|||||
OTHER INVESTMENTS, PRINCIPALLY BOTTLING COMPANIES |
1,141 |
631 |
|||||
OTHER ASSETS |
3,495 |
2,121 |
|||||
PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT — net |
14,939 |
14,727 |
|||||
TRADEMARKS WITH INDEFINITE LIVES |
6,430 |
6,356 |
|||||
BOTTLERS' FRANCHISE RIGHTS WITH INDEFINITE LIVES |
7,770 |
7,511 |
|||||
GOODWILL |
12,219 |
11,665 |
|||||
OTHER INTANGIBLE ASSETS |
1,250 |
1,377 |
|||||
TOTAL ASSETS |
$ |
79,974 |
$ |
72,921 |
|||
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY |
|||||||
CURRENT LIABILITIES |
|||||||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
$ |
9,009 |
$ |
8,859 |
|||
Loans and notes payable |
12,871 |
8,100 |
|||||
Current maturities of long-term debt |
2,041 |
1,276 |
|||||
Accrued income taxes |
362 |
273 |
|||||
TOTAL CURRENT LIABILITIES |
24,283 |
18,508 |
|||||
LONG-TERM DEBT |
13,656 |
14,041 |
|||||
OTHER LIABILITIES |
5,420 |
4,794 |
|||||
DEFERRED INCOME TAXES |
4,694 |
4,261 |
|||||
THE COCA-COLA COMPANY SHAREOWNERS' EQUITY |
|||||||
|
Common stock, $0.25 par value; Authorized — 5,600 shares;
Issued — 3,520 and 3,520 shares, respectively
|
880 |
880 |
|||||
Capital surplus |
11,212 |
10,057 |
|||||
Reinvested earnings |
53,550 |
49,278 |
|||||
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) |
(2,703 |
) |
(1,450 |
) |
|||
Treasury stock, at cost — 1,257 and 1,228 shares, respectively |
(31,304 |
) |
(27,762 |
) |
|||
EQUITY ATTRIBUTABLE TO SHAREOWNERS OF THE COCA-COLA COMPANY |
31,635 |
31,003 |
|||||
EQUITY ATTRIBUTABLE TO NONCONTROLLING INTERESTS |
286 |
314 |
|||||
TOTAL EQUITY |
31,921 |
31,317 |
|||||
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND EQUITY |
$ |
79,974 |
$ |
72,921 |
|||
Refer to Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
79
THE COCA-COLA COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
(In millions) |
|||||||||||
OPERATING ACTIVITIES |
|||||||||||
Consolidated net income |
$ |
8,634 |
$ |
11,859 |
$ |
6,906 |
|||||
Depreciation and amortization |
1,954 |
1,443 |
1,236 |
||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense |
354 |
380 |
241 |
||||||||
Deferred income taxes |
1,028 |
617 |
353 |
||||||||
Equity (income) loss — net of dividends |
(269 |
) |
(671 |
) |
(359 |
) |
|||||
Foreign currency adjustments |
7 |
151 |
61 |
||||||||
Significant (gains) losses on sales of assets — net |
(220 |
) |
(645 |
) |
(43 |
) |
|||||
Other significant (gains) losses — net |
— |
(4,713 |
) |
— |
|||||||
Other operating charges |
214 |
264 |
134 |
||||||||
Other items |
(335 |
) |
477 |
221 |
|||||||
Net change in operating assets and liabilities |
(1,893 |
) |
370 |
(564 |
) |
||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities |
9,474 |
9,532 |
8,186 |
||||||||
INVESTING ACTIVITIES |
|||||||||||
Purchases of short-term investments |
(4,057 |
) |
(4,579 |
) |
(2,130 |
) |
|||||
Proceeds from disposals of short-term investments |
5,647 |
4,032 |
— |
||||||||
Acquisitions and investments |
(977 |
) |
(2,511 |
) |
(300 |
) |
|||||
Purchases of other investments |
(787 |
) |
(132 |
) |
(22 |
) |
|||||
Proceeds from disposals of bottling companies and other investments |
562 |
972 |
240 |
||||||||
Purchases of property, plant and equipment |
(2,920 |
) |
(2,215 |
) |
(1,993 |
) |
|||||
Proceeds from disposals of property, plant and equipment |
101 |
134 |
104 |
||||||||
Other investing activities |
(93 |
) |
(106 |
) |
(48 |
) |
|||||
Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities |
(2,524 |
) |
(4,405 |
) |
(4,149 |
) |
|||||
FINANCING ACTIVITIES |
|||||||||||
Issuances of debt |
27,495 |
15,251 |
14,689 |
||||||||
Payments of debt |
(22,530 |
) |
(13,403 |
) |
(12,326 |
) |
|||||
Issuances of stock |
1,569 |
1,666 |
664 |
||||||||
Purchases of stock for treasury |
(4,513 |
) |
(2,961 |
) |
(1,518 |
) |
|||||
Dividends |
(4,300 |
) |
(4,068 |
) |
(3,800 |
) |
|||||
Other financing activities |
45 |
50 |
(2 |
) |
|||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities |
(2,234 |
) |
(3,465 |
) |
(2,293 |
) |
|||||
|
EFFECT OF EXCHANGE RATE CHANGES ON CASH AND
CASH EQUIVALENTS
|
(430 |
) |
(166 |
) |
576 |
||||||
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS |
|||||||||||
Net increase (decrease) during the year |
4,286 |
1,496 |
2,320 |
||||||||
Balance at beginning of year |
8,517 |
7,021 |
4,701 |
||||||||
Balance at end of year |
$ |
12,803 |
$ |
8,517 |
$ |
7,021 |
|||||
Refer to Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
80
THE COCA-COLA COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREOWNERS' EQUITY
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
(In millions except per share data) |
|||||||||||
EQUITY ATTRIBUTABLE TO SHAREOWNERS OF THE COCA-COLA COMPANY |
|||||||||||
NUMBER OF COMMON SHARES OUTSTANDING
|
|||||||||||
Balance at beginning of year |
2,292 |
2,303 |
2,312 |
||||||||
Purchases of treasury stock |
(63 |
) |
(49 |
) |
(26 |
) |
|||||
Treasury stock issued to employees related to stock compensation plans |
34 |
38 |
17 |
||||||||
Balance at end of year |
2,263 |
2,292 |
2,303 |
||||||||
COMMON STOCK
|
$ |
880 |
$ |
880 |
$ |
880 |
|||||
CAPITAL SURPLUS
|
|||||||||||
Balance at beginning of year |
10,057 |
8,537 |
7,966 |
||||||||
Stock issued to employees related to stock compensation plans |
724 |
855 |
339 |
||||||||
Replacement share-based awards issued in connection with an acquisition |
— |
237 |
— |
||||||||
Tax benefit (charge) from employees' stock option and restricted stock plans |
79 |
48 |
(6 |
) |
|||||||
Stock-based compensation |
354 |
380 |
238 |
||||||||
Other activities |
(2 |
) |
— |
— |
|||||||
Balance at end of year |
11,212 |
10,057 |
8,537 |
||||||||
REINVESTED EARNINGS
|
|||||||||||
Balance at beginning of year |
49,278 |
41,537 |
38,513 |
||||||||
Net income attributable to shareowners of The Coca-Cola Company |
8,572 |
11,809 |
6,824 |
||||||||
Dividends (per share — $1.88, $1.76 and $1.64 in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively) |
(4,300 |
) |
(4,068 |
) |
(3,800 |
) |
|||||
Balance at end of year |
53,550 |
49,278 |
41,537 |
||||||||
ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
|
|||||||||||
Balance at beginning of year |
(1,450 |
) |
(757 |
) |
(2,674 |
) |
|||||
Net foreign currency translation adjustment |
(640 |
) |
(935 |
) |
1,824 |
||||||
Net gain (loss) on derivatives |
145 |
(120 |
) |
34 |
|||||||
Net change in unrealized gain on available-for-sale securities |
(7 |
) |
102 |
(52 |
) |
||||||
Net change in pension and other benefit liabilities |
(751 |
) |
260 |
111 |
|||||||
Net other comprehensive income (loss) |
(1,253 |
) |
(693 |
) |
1,917 |
||||||
Balance at end of year |
(2,703 |
) |
(1,450 |
) |
(757 |
) |
|||||
TREASURY STOCK
|
|||||||||||
Balance at beginning of year |
(27,762 |
) |
(25,398 |
) |
(24,213 |
) |
|||||
Stock issued to employees related to stock compensation plans |
830 |
824 |
333 |
||||||||
Purchases of treasury stock |
(4,372 |
) |
(3,188 |
) |
(1,518 |
) |
|||||
Balance at end of year |
(31,304 |
) |
(27,762 |
) |
(25,398 |
) |
|||||
TOTAL EQUITY ATTRIBUTABLE TO SHAREOWNERS OF THE COCA-COLA COMPANY |
$ |
31,635 |
$ |
31,003 |
$ |
24,799 |
|||||
EQUITY ATTRIBUTABLE TO NONCONTROLLING INTERESTS |
|||||||||||
Balance at beginning of year |
$ |
314 |
$ |
547 |
$ |
390 |
|||||
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests |
62 |
50 |
82 |
||||||||
Net foreign currency translation adjustment |
(52 |
) |
(12 |
) |
49 |
||||||
Dividends paid to noncontrolling interests |
(38 |
) |
(32 |
) |
(14 |
) |
|||||
Contributions by noncontrolling interests |
— |
1 |
40 |
||||||||
Increase due to business combinations |
— |
13 |
— |
||||||||
Deconsolidation of certain variable interest entities |
— |
(253 |
) |
— |
|||||||
TOTAL EQUITY ATTRIBUTABLE TO NONCONTROLLING INTERESTS |
$ |
286 |
$ |
314 |
$ |
547 |
|||||
COMPREHENSIVE INCOME |
|||||||||||
Consolidated net income |
$ |
8,634 |
$ |
11,859 |
$ |
6,906 |
|||||
Consolidated net other comprehensive income (loss) |
(1,305 |
) |
(705 |
) |
1,966 |
||||||
CONSOLIDATED COMPREHENSIVE INCOME |
$ |
7,329 |
$ |
11,154 |
$ |
8,872 |
|||||
Refer to Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
81
THE COCA-COLA COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1: BUSINESS AND SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Description of Business
The Coca-Cola Company is the world's largest beverage company. We own or license and market more than 500 nonalcoholic beverage brands, primarily sparkling beverages but also a variety of still beverages such as waters, enhanced waters, juices and juice drinks, ready-to-drink teas and coffees, and energy and sports drinks. We own and market four of the world's top five nonalcoholic sparkling beverage brands: Coca-Cola, Diet Coke, Fanta and Sprite. Finished beverage products bearing our trademarks, sold in the United States since 1886, are now sold in more than 200 countries.
We make our branded beverage products available to consumers throughout the world through our network of Company-owned or controlled bottling and distribution operations, bottling partners, distributors, wholesalers and retailers — the world's largest beverage distribution system. Of the approximately 56 billion beverage servings of all types consumed worldwide every day, beverages bearing trademarks owned by or licensed to us account for more than 1.7 billion.
On October 2, 2010, we acquired the North American business of Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. ("CCE"), one of our major bottlers, consisting of CCE's production, sales and distribution operations in the United States, Canada, the British Virgin Islands, the United States Virgin Islands and the Cayman Islands, and a substantial majority of CCE's corporate segment. Upon completion of the CCE transaction, we combined the management of the acquired North American business with the management of our existing foodservice business; Minute Maid and Odwalla juice businesses; North America supply chain operations; and Company-owned bottling operations in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, into a unified bottling and customer service organization called Coca-Cola Refreshments ("CCR"). In addition, we reshaped our remaining Coca-Cola North America ("CCNA") operations into an organization that primarily provides franchise leadership and consumer marketing and innovation for the North American market.
Our Company markets, manufactures and sells:
•
|
beverage concentrates, sometimes referred to as "beverage bases," and syrups, including fountain syrups (we refer to this part of our business as our "concentrate business" or "concentrate operations"); and
|
•
|
finished sparkling and still beverages (we refer to this part of our business as our "finished products business" or "finished products operations").
|
Generally, finished products operations generate higher net operating revenues but lower gross profit margins than concentrate operations.
In our concentrate operations, we typically generate net operating revenues by selling concentrates and syrups to authorized bottling and canning operations (to which we typically refer as our "bottlers" or our "bottling partners"). Our bottling partners either combine the concentrates with sweeteners (depending on the product), still water and/or sparkling water, or combine the syrups with sparkling water to produce finished beverages. The finished beverages are packaged in authorized containers bearing our trademarks or trademarks licensed to us — such as cans and refillable and nonrefillable glass and plastic bottles — and are then sold to retailers directly or, in some cases, through wholesalers or other bottlers. Outside the United States, we also sell concentrates for fountain beverages to our bottling partners who are typically authorized to manufacture fountain syrups, which they sell to fountain retailers such as restaurants and convenience stores which use the fountain syrups to produce beverages for immediate consumption, or to fountain wholesalers who in turn sell and distribute the fountain syrups to fountain retailers.
Our finished products operations consist primarily of the production, sales and distribution operations managed by CCR and our Company-owned or controlled bottling and distribution operations. CCR is included in our North America operating segment, and our Company-owned or controlled bottling and distribution operations are included in our Bottling Investments operating segment. Our finished products operations generate net operating revenues by selling sparkling beverages and a variety of still beverages, such as juices and juice drinks, energy and sports drinks, ready-to-drink teas and coffees, and certain water products, to retailers or to distributors, wholesalers and bottling partners who distribute them to retailers. In addition, in the United States, we manufacture fountain syrups and sell them to fountain retailers, such as restaurants and convenience stores who use the fountain syrups to produce beverages for immediate consumption, or to authorized fountain wholesalers or bottling partners who resell the fountain syrups to fountain retailers. In the United States, we authorize wholesalers to resell our fountain syrups through nonexclusive appointments that neither restrict us in setting the prices at which we sell fountain syrups to the wholesalers nor restrict the territories in which the wholesalers may resell in the United States.
82
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation
Our consolidated financial statements are prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States. The preparation of our consolidated financial statements requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities in our consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. Although these estimates are based on our knowledge of current events and actions we may undertake in the future, actual results may ultimately differ from these estimates and assumptions. Furthermore, when testing assets for impairment in future periods, if management uses different assumptions or if different conditions occur, impairment charges may result.
We use the equity method to account for investments in companies, if our investment provides us with the ability to exercise significant influence over operating and financial policies of the investee. Our consolidated net income includes our Company's proportionate share of the net income or loss of these companies. Our judgment regarding the level of influence over each equity method investment includes considering key factors such as our ownership interest, representation on the board of directors, participation in policy-making decisions and material intercompany transactions.
We eliminate from our financial results all significant intercompany transactions, including the intercompany transactions with consolidated variable interest entities ("VIEs") and the intercompany portion of transactions with equity method investees.
Certain amounts in the prior years' consolidated financial statements and notes have been revised to conform to the current year presentation.
Principles of Consolidation
Our Company consolidates all entities that we control by ownership of a majority voting interest as well as VIEs for which our Company is the primary beneficiary. Generally, we consolidate only business enterprises that we control by ownership of a majority voting interest. However, there are situations in which consolidation is required even though the usual condition of consolidation (ownership of a majority voting interest) does not apply. Generally, this occurs when an entity holds an interest in another business enterprise that was achieved through arrangements that do not involve voting interests, which results in a disproportionate relationship between such entity's voting interests in, and its exposure to the economic risks and potential rewards of, the other business enterprise. This disproportionate relationship results in what is known as a variable interest, and the entity in which we have the variable interest is referred to as a "VIE". An enterprise must consolidate a VIE if it is determined to be the primary beneficiary of the VIE. The primary beneficiary has both (a) the power to direct the activities of the VIE that most significantly impact the entity's economic performance, and (b) the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive benefits from the VIE that could potentially be significant to the VIE.
Our Company holds interests in certain VIEs, primarily bottling and container manufacturing operations, for which we were not determined to be the primary beneficiary. Our variable interests in these VIEs primarily relate to profit guarantees or subordinated financial support. Refer to Note 11. Although these financial arrangements resulted in us holding variable interests in these entities, the majority of these arrangements did not empower us to direct the activities of the VIEs that most significantly impact the VIEs' economic performance. Our Company's investments, plus any loans and guarantees, related to these VIEs totaled $1,183 million and $1,274 million as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively, representing our maximum exposures to loss. The Company's investments, plus any loans and guarantees, related to these VIEs were not significant to the Company's consolidated financial statements.
In addition, our Company holds interests in certain VIEs, primarily bottling and container manufacturing operations, for which we were determined to be the primary beneficiary. As a result, we have consolidated these entities. Our Company's investments, plus any loans and guarantees, related to these VIEs totaled $199 million and $191 million as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively, representing our maximum exposures to loss. The assets and liabilities of VIEs for which we are the primary beneficiary were not significant to the Company's consolidated financial statements.
Creditors of our VIEs do not have recourse against the general credit of the Company, regardless of whether they are accounted for as consolidated entities.
The information presented above reflects the impact of the Company's adoption of accounting guidance issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") related to VIEs in June 2009. This accounting guidance resulted in a change in our accounting policy effective January 1, 2010. Among other things, the guidance requires more qualitative than quantitative analyses to determine the primary beneficiary of a VIE, requires continuous assessments of whether an enterprise is the primary beneficiary of a VIE, enhances disclosures about an enterprise's involvement with a VIE, and amends certain guidance for determining whether an entity is a VIE.
83
Beginning January 1, 2010, we deconsolidated certain entities as a result of this change in accounting policy. These entities are primarily bottling operations and had previously been consolidated due to certain loan guarantees and/or other financial support given by the Company. These financial arrangements, although not significant to our consolidated financial statements, resulted in a disproportionate relationship between our voting interests in these entities and our exposure to the economic risks and potential rewards of the entities. As a result, we determined that we held a majority of the variable interests in these entities and, therefore, were deemed to be the primary beneficiary in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States as of December 31, 2009. Although these financial arrangements resulted in us holding a majority of the variable interests in these VIEs, the majority of these arrangements did not empower us to direct the activities of the VIEs that most significantly impact the VIEs' economic performance. Consequently, subsequent to the change in accounting policy, the Company deconsolidated the majority of these VIEs.
The entities that have been deconsolidated accounted for less than 1 percent of net income attributable to shareowners of The Coca-Cola Company in 2009. On January 1, 2010, the Company began to account for these entities under the equity method of accounting. Although the deconsolidation of these entities impacted individual line items in our consolidated financial statements, the impact on net income attributable to shareowners of The Coca-Cola Company in future periods will be nominal. The equity method of accounting is intended to be a single line consolidation and, therefore, generally should result in the same net income attributable to the investor as would be the case if the investee had been consolidated. The main impact on our consolidated financial statements in 2010 was that instead of these entities' results of operations and balance sheets affecting our consolidated line items, our proportionate share of net income or loss from these entities was reported in equity income (loss) — net in our consolidated statements of income, and our investment in these entities was reported as equity method investments in our consolidated balance sheets. Refer to Note 6.
Risks and Uncertainties
Factors that could adversely impact the Company's operations or financial results include, but are not limited to, the following: obesity and other health concerns; water scarcity and poor quality; changes in the nonalcoholic beverage business environment and retail trends; risks related to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed, as well as the integration of CCE's North American business; the continuing uncertainty in the credit and equity markets; increased competition; an inability to expand operations in developing and emerging markets; fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates; interest rate increases; an inability to maintain good relationships with our bottling partners; a deterioration in our bottling partners' financial condition; increases in income tax rates or changes in income tax laws; increased or new indirect taxes in the United States or in other major markets; an inability to renew collective bargaining agreements on satisfactory terms or strikes, work stoppages or labor unrest (including at bottling partners' manufacturing locations); increased cost, disruption of supply or shortage of energy; increased cost, disruption of supply or shortage of ingredients, other raw materials or packaging materials; changes in laws and regulations relating to beverage containers and packaging; significant additional labeling or warning requirements; unfavorable general economic conditions in the United States or in other major markets; unfavorable economic and political conditions in international markets; litigation or legal proceedings; adverse weather conditions; damage to our brand image and corporate reputation from product safety or quality issues, or negative publicity, even if unwarranted; changes in, or failure to comply with, the laws and regulations applicable to our products or our business operations; changes in accounting standards; an inability to achieve our overall long-term goals; an inability to realize the significant benefits from our productivity and reinvestment program; an inability to protect our information systems against service interruption, misappropriation of data or breaches of security; future impairment charges, including charges by equity method investees; an inability to successfully integrate and manage our Company-owned or controlled bottling operations; climate change; and global or regional catastrophic events.
Our Company monitors our operations with a view to minimizing the impact to our overall business that could arise as a result of the risks and uncertainties inherent in our business.
Revenue Recognition
Our Company recognizes revenue when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, delivery of products has occurred, the sales price charged is fixed or determinable, and collectibility is reasonably assured. For our Company, this generally means that we recognize revenue when title to our products is transferred to our bottling partners, resellers or other customers. In particular, title usually transfers upon shipment to or receipt at our customers' locations, as determined by the specific sales terms of the transactions. Our sales terms do not allow for a right of return except for matters related to any manufacturing defects on our part.
84
Deductions from Revenue
Our customers can earn certain incentives including, but not limited to, cash discounts, funds for promotional and marketing activities, volume-based incentive programs and support for infrastructure programs. The costs associated with these incentives are included in deductions from revenue, a component of net operating revenues in our consolidated statements of income. For customer incentives that must be earned, management must make estimates related to the contractual terms, customer performance and sales volume to determine the total amounts earned and to be recorded in deductions from revenue. In making these estimates, management considers past results. The actual amounts ultimately paid may be different from our estimates.
In some situations, the Company may determine it to be advantageous to make advance payments to specific customers to fund certain marketing activities intended to generate profitable volume and/or invest in infrastructure programs with our bottlers that are directed at strengthening our bottling system and increasing unit case volume. The Company also makes advance payments to certain customers for distribution rights. The advance payments made to customers are initially capitalized and included in our consolidated balance sheets in prepaid expenses and other assets and noncurrent other assets, depending on the duration of the agreements. The assets are amortized over the applicable periods and included in deductions from revenue. The duration of these agreements typically ranges from 4 to 10 years.
Amortization expense for infrastructure programs was $90 million, $137 million and $150 million in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. The aggregate deductions from revenue recorded by the Company in relation to these programs, including amortization expense on infrastructure programs, were $5.8 billion, $5.0 billion and $4.5 billion in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
Advertising Costs
Our Company expenses production costs of print, radio, television and other advertisements as of the first date the advertisements take place. All other marketing expenditures are expensed in the annual period in which the expenditure is incurred. Advertising costs included in the line item selling, general and administrative expenses in our consolidated statements of income were $3.3 billion, $2.9 billion and $2.8 billion in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. As of December 31, 2011 and 2010, advertising and production costs of $349 million and $305 million, respectively, were primarily recorded in the line item prepaid expenses and other assets in our consolidated balance sheets.
For interim reporting purposes, we allocate our estimated full year marketing expenditures that benefit multiple interim periods to each of our interim reporting periods. We use the proportion of each interim period's actual unit case volume to the estimated full year unit case volume as the basis for the allocation. This methodology results in our marketing expenditures being recognized at a standard rate per unit case. At the end of each interim reporting period, we review our estimated full year unit case volume and our estimated full year marketing expenditures in order to evaluate if a change in estimate is necessary. The impact of any changes in these full year estimates is recognized in the interim period in which the change in estimate occurs. Our full year marketing expenditures are not impacted by this interim accounting policy.
Shipping and Handling Costs
Shipping and handling costs related to the movement of finished goods from manufacturing locations to our sales distribution centers are included in the line item cost of goods sold in our consolidated statements of income. Shipping and handling costs incurred to move finished goods from our sales distribution centers to customer locations are included in the line item selling, general and administrative expenses in our consolidated statements of income. As a result of our acquisition of CCE's North American business, the amount of shipping and handling costs recorded in the line item selling, general and administrative expenses increased significantly and totaled $2.4 billion during the year ended December 31, 2011. Our customers do not pay us separately for shipping and handling costs related to finished goods.
Net Income Per Share
Basic net income per share is computed by dividing net income by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding during the reporting period. Diluted net income per share is computed similarly to basic net income per share, except that it includes the potential dilution that could occur if dilutive securities were exercised. Approximately 16 million, 38 million and 103 million stock option awards were excluded from the computations of diluted net income per share in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively, because the awards would have been antidilutive for the years presented.
Cash Equivalents
We classify time deposits and other investments that are highly liquid and have maturities of three months or less at the date of purchase as cash equivalents. We manage our exposure to counterparty credit risk through specific minimum credit standards, diversification of counterparties and procedures to monitor our credit risk concentrations.
85
Short-Term Investments
We classify time deposits and other investments that have maturities of greater than three months but less than one year as short-term investments.
Investments in Equity and Debt Securities
We use the equity method to account for our investments in equity securities if our investment gives us the ability to exercise significant influence over operating and financial policies of the investee. We include our proportionate share of earnings and/or losses of our equity method investees in equity income (loss) — net in our consolidated statements of income. The carrying value of our equity investments is reported in equity method investments in our consolidated balance sheets. Refer to Note 6.
We account for investments in companies that we do not control or account for under the equity method either at fair value or under the cost method, as applicable. Investments in equity securities are carried at fair value if the fair value of the security is readily determinable. Equity investments carried at fair value are classified as either trading or available-for-sale securities with their cost basis determined by the specific identification method. Realized and unrealized gains and losses on trading securities and realized gains and losses on available-for-sale securities are included in other income (loss) — net in our consolidated statements of income. Unrealized gains and losses, net of deferred taxes, on available-for-sale securities are included in our consolidated balance sheets as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) ("AOCI"). Trading securities are reported as either marketable securities or other assets in our consolidated balance sheets. Securities classified as available-for-sale are reported as either marketable securities, other investments or other assets in our consolidated balance sheets, depending on the length of time we intend to hold the investment. Refer to Note 3.
Investments in equity securities that we do not control or account for under the equity method and do not have readily determinable fair values are accounted for under the cost method. Cost method investments are originally recorded at cost, and we record dividend income when applicable dividends are declared. Cost method investments are reported as other investments in our consolidated balance sheets, and dividend income from cost method investments is reported in the line item other income (loss) — net in our consolidated statements of income.
Our investments in debt securities are carried at either amortized cost or fair value. Investments in debt securities that the Company has the positive intent and ability to hold to maturity are carried at amortized cost and classified as held-to-maturity. Investments in debt securities that are not classified as held-to-maturity are carried at fair value and classified as either trading or available-for-sale.
Each reporting period we review all of our investments in equity and debt securities, except for those classified as trading, to determine whether a significant event or change in circumstances has occurred that may have an adverse effect on the fair value of each investment. When such events or changes occur, we evaluate the fair value compared to our cost basis in the investment. We also perform this evaluation every reporting period for each investment for which our cost basis exceeded the fair value in the prior period. The fair values of most of our investments in publicly traded companies are often readily available based on quoted market prices. For investments in nonpublicly traded companies, management's assessment of fair value is based on valuation methodologies including discounted cash flows, estimates of sales proceeds and appraisals, as appropriate. We consider the assumptions that we believe hypothetical marketplace participants would use in evaluating estimated future cash flows when employing the discounted cash flow or estimates of sales proceeds valuation methodologies.
In the event the fair value of an investment declines below our cost basis, management determines if the decline in fair value is other than temporary. If management determines the decline is other than temporary, an impairment charge is recorded. Management's assessment as to the nature of a decline in fair value is based on, among other things, the length of time and the extent to which the market value has been less than our cost basis, the financial condition and near-term prospects of the issuer, and our intent and ability to retain the investment for a period of time sufficient to allow for any anticipated recovery in market value.
86
Trade Accounts Receivable
We record trade accounts receivable at net realizable value. This value includes an appropriate allowance for estimated uncollectible accounts to reflect any loss anticipated on the trade accounts receivable balances and charged to the provision for doubtful accounts. We calculate this allowance based on our history of write-offs, the level of past-due accounts based on the contractual terms of the receivables, and our relationships with, and the economic status of, our bottling partners and customers. We believe our exposure to concentrations of credit risk is limited due to the diverse geographic areas covered by our operations. Activity in the allowance for doubtful accounts was as follows (in millions):
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
Balance at beginning of year |
$ |
48 |
$ |
55 |
$ |
51 |
|||||
Net charges to costs and expenses |
56 |
21 |
24 |
||||||||
Write-offs |
(12 |
) |
(18 |
) |
(22 |
) |
|||||
Other1
|
(9 |
) |
(10 |
) |
2 |
||||||
Balance at end of year |
$ |
83 |
$ |
48 |
$ |
55 |
|||||
1 |
Other includes acquisitions, divestitures and currency translation. |
A significant portion of our net operating revenues and corresponding accounts receivable is derived from sales of our products in international markets. Refer to Note 19. We also generate a significant portion of our net operating revenues by selling concentrates and syrups to bottlers in which we have a noncontrolling interest, including Coca-Cola Hellenic Bottling Company S.A. ("Coca-Cola Hellenic"), Coca-Cola FEMSA, S.A.B. de C.V. ("Coca-Cola FEMSA") and Coca-Cola Amatil Limited ("Coca-Cola Amatil"). Refer to Note 6.
Inventories
Inventories consist primarily of raw materials and packaging (which includes ingredients and supplies) and finished goods (which include concentrates and syrups in our concentrate operations, and finished beverages in our finished products operations). Inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market. We determine cost on the basis of the average cost or first-in, first-out methods. Refer to Note 4.
Derivative Instruments
Our Company, when deemed appropriate, uses derivatives as a risk management tool to mitigate the potential impact of certain market risks. The primary market risks managed by the Company through the use of derivative instruments are foreign currency exchange rate risk, commodity price risk and interest rate risk. All derivatives are carried at fair value in our consolidated balance sheets in the line items prepaid expenses and other assets or accounts payable and accrued expenses, as applicable. Refer to Note 5.
Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost. Repair and maintenance costs that do not improve service potential or extend economic life are expensed as incurred. Depreciation is recorded principally by the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of our assets, which are reviewed periodically and generally have the following ranges: buildings and improvements: 40 years or less; machinery, equipment and vehicle fleet: 20 years or less; cold-drink equipment: 13 years or less; and containers: 12 years or less. Land is not depreciated, and construction in progress is not depreciated until ready for service. Leasehold improvements are amortized using the straight-line method over the shorter of the remaining lease term, including renewals that are deemed to be reasonably assured, or the estimated useful life of the improvement. Depreciation expense, including the depreciation expense of assets under capital lease, totaled $1,654 million, $1,188 million and $1,005 million in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. Amortization expense for leasehold improvements totaled $18 million, $16 million and $18 million in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
Certain events or changes in circumstances may indicate that the recoverability of the carrying amount of property, plant and equipment should be assessed, including, among others, a significant decrease in market value, a significant change in the business climate in a particular market, or a current period operating or cash flow loss combined with historical losses or projected future losses. When such events or changes in circumstances are present, we estimate the future cash flows expected to result from the use of the asset (or asset group) and its eventual disposition. These estimated future cash flows are consistent with those we use in our internal planning. If the sum of the expected future cash flows (undiscounted and without interest charges) is less than the carrying amount, we recognize an impairment loss. The impairment loss recognized is the amount by which the carrying amount exceeds the fair value. We use a variety of methodologies to determine the fair value of property,
87
plant and equipment, including appraisals and discounted cash flow models, which are consistent with the assumptions we believe hypothetical marketplace participants would use. Refer to Note 7.
Goodwill, Trademarks and Other Intangible Assets
We classify intangible assets into three categories: (1) intangible assets with definite lives subject to amortization, (2) intangible assets with indefinite lives not subject to amortization and (3) goodwill. We determine the useful lives of our identifiable intangible assets after considering the specific facts and circumstances related to each intangible asset. Factors we consider when determining useful lives include the contractual term of any agreement related to the asset, the historical performance of the asset, the Company's long-term strategy for using the asset, any laws or other local regulations which could impact the useful life of the asset, and other economic factors, including competition and specific market conditions. Intangible assets that are deemed to have definite lives are amortized, primarily on a straight-line basis, over their useful lives, generally ranging from 1 to 20 years. Refer to Note 8.
When facts and circumstances indicate that the carrying value of definite-lived intangible assets may not be recoverable, management assesses the recoverability of the carrying value by preparing estimates of sales volume and the resulting gross profit and cash flows. These estimated future cash flows are consistent with those we use in our internal planning. If the sum of the expected future cash flows (undiscounted and without interest charges) is less than the carrying amount, we recognize an impairment loss. The impairment loss recognized is the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset (or asset group) exceeds the fair value. We use a variety of methodologies to determine the fair value of these assets, including discounted cash flow models, which are consistent with the assumptions we believe hypothetical marketplace participants would use.
We test intangible assets determined to have indefinite useful lives, including trademarks, franchise rights and goodwill, for impairment annually, or more frequently if events or circumstances indicate that assets might be impaired. Our Company performs these annual impairment reviews as of the first day of our third fiscal quarter. We use a variety of methodologies in conducting impairment assessments of indefinite-lived intangible assets, including, but not limited to, discounted cash flow models, which are based on the assumptions we believe hypothetical marketplace participants would use. For indefinite-lived intangible assets, other than goodwill, if the carrying amount exceeds the fair value, an impairment charge is recognized in an amount equal to that excess.
We perform impairment tests of goodwill at our reporting unit level, which is one level below our operating segments. Our operating segments are primarily based on geographic responsibility, which is consistent with the way management runs our business. Our operating segments are subdivided into smaller geographic regions or territories that we sometimes refer to as "business units." These business units are also our reporting units. The Bottling Investments operating segment includes all Company-owned or consolidated bottling operations, regardless of geographic location, except for bottling operations managed by CCR, which are included in our North America operating segment. Generally, each Company-owned or consolidated bottling operation within our Bottling Investments operating segment is its own reporting unit. Goodwill is assigned to the reporting unit or units that benefit from the synergies arising from each business combination.
The goodwill impairment test consists of a two-step process, if necessary. The first step is to compare the fair value of a reporting unit to its carrying value, including goodwill. We typically use discounted cash flow models to determine the fair value of a reporting unit. The assumptions used in these models are consistent with those we believe hypothetical marketplace participants would use. If the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying value, the second step of the impairment test must be performed in order to determine the amount of impairment loss, if any. The second step compares the implied fair value of the reporting unit's goodwill with the carrying amount of that goodwill. If the carrying amount of the reporting unit's goodwill exceeds its implied fair value, an impairment charge is recognized in an amount equal to that excess. The loss recognized cannot exceed the carrying amount of goodwill.
Impairment charges related to intangible assets are generally recorded in the line item other operating charges or, to the extent they relate to equity method investees, in the line item equity income (loss) — net in our consolidated statements of income.
Contingencies
Our Company is involved in various legal proceedings and tax matters. Due to their nature, such legal proceedings and tax matters involve inherent uncertainties including, but not limited to, court rulings, negotiations between affected parties and governmental actions. Management assesses the probability of loss for such contingencies and accrues a liability and/or discloses the relevant circumstances, as appropriate. Refer to Note 11.
Stock-Based Compensation
Our Company currently sponsors stock option plans and restricted stock award plans. The fair values of the stock awards are determined using an estimated expected life. The Company recognizes compensation expense on a straight-line basis over the period the award is earned by the employee. Refer to Note 12.
88
Pension and Other Postretirement Benefit Plans
Our Company sponsors and/or contributes to pension and postretirement health care and life insurance benefit plans covering substantially all U.S. employees. We also sponsor nonqualified, unfunded defined benefit pension plans for certain associates and participate in multi-employer pension plans in the United States. In addition, our Company and its subsidiaries have various pension plans and other forms of postretirement arrangements outside the United States. Refer to Note 13.
Income Taxes
Income tax expense includes United States, state, local and international income taxes, plus a provision for U.S. taxes on undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries not deemed to be indefinitely reinvested. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the tax consequences of temporary differences between the financial reporting basis and the tax basis of existing assets and liabilities. The tax rate used to determine the deferred tax assets and liabilities is the enacted tax rate for the year and manner in which the differences are expected to reverse. Valuation allowances are recorded to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount that will more likely than not be realized. The Company records taxes that are collected from customers and remitted to governmental authorities on a net basis in our consolidated statements of income.
The Company is involved in various tax matters, with respect to some of which the outcome is uncertain. We establish reserves to remove some or all of the tax benefit of any of our tax positions at the time we determine that it becomes uncertain based upon one of the following conditions: (1) the tax position is not "more likely than not" to be sustained, (2) the tax position is "more likely than not" to be sustained, but for a lesser amount, or (3) the tax position is "more likely than not" to be sustained, but not in the financial period in which the tax position was originally taken. For purposes of evaluating whether or not a tax position is uncertain, (1) we presume the tax position will be examined by the relevant taxing authority that has full knowledge of all relevant information; (2) the technical merits of a tax position are derived from authorities such as legislation and statutes, legislative intent, regulations, rulings and case law and their applicability to the facts and circumstances of the tax position; and (3) each tax position is evaluated without consideration of the possibility of offset or aggregation with other tax positions taken. A number of years may elapse before a particular uncertain tax position is audited and finally resolved or when a tax assessment is raised. The number of years subject to tax assessments varies depending on the tax jurisdiction. The tax benefit that has been previously reserved because of a failure to meet the "more likely than not" recognition threshold would be recognized in our income tax expense in the first interim period when the uncertainty disappears under any one of the following conditions: (1) the tax position is "more likely than not" to be sustained, (2) the tax position, amount, and/or timing is ultimately settled through negotiation or litigation, or (3) the statute of limitations for the tax position has expired. Refer to Note 14.
Translation and Remeasurement
We translate the assets and liabilities of our foreign subsidiaries from their respective functional currencies to U.S. dollars at the appropriate spot rates as of the balance sheet date. Generally, our foreign subsidiaries use the local currency as their functional currency. Changes in the carrying value of these assets and liabilities attributable to fluctuations in spot rates are recognized in foreign currency translation adjustment, a component of AOCI. Refer to Note 15. Income statement accounts are translated using the monthly average exchange rates during the year.
Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in a currency that is different from a reporting entity's functional currency must first be remeasured from the applicable currency to the legal entity's functional currency. The effect of this remeasurement process is recognized in the line item other income (loss) — net in our consolidated statements of income and is partially offset by the impact of our economic hedging program for certain exposures on our consolidated balance sheets. Refer to Note 5.
Hyperinflationary Economies
A hyperinflationary economy is one that has cumulative inflation of approximately 100 percent or more over a three-year period. Effective January 1, 2010, Venezuela was determined to be a hyperinflationary economy, and the Venezuelan government devalued the bolivar by resetting the official rate of exchange ("official rate") from 2.15 bolivars per U.S. dollar to 2.6 bolivars per U.S. dollar for essential goods and 4.3 bolivars per U.S. dollar for nonessential goods. In accordance with hyperinflationary accounting under accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, our local subsidiary was required to use the U.S. dollar as its functional currency. As a result, we remeasured the net assets of our Venezuelan subsidiary using the official rate for nonessential goods of 4.3 bolivars per U.S. dollar. During the first quarter of 2010, we recorded a loss of $103 million related to the remeasurement of our Venezuelan subsidiary's net assets. The loss was recorded in the line item other income (loss) — net in our consolidated statement of income. We classified the impact of the remeasurement loss in the line item effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents in our consolidated statement of cash flows.
89
In early June 2010, the Venezuelan government introduced a newly regulated foreign currency exchange system known as the Transaction System for Foreign Currency Denominated Securities ("SITME"). This new system, which is subject to annual limits, replaced the parallel market whereby entities domiciled in Venezuela are able to exchange their bolivars to U.S. dollars through authorized financial institutions (commercial banks, savings and lending institutions, etc.).
In December 2010, the Venezuelan government announced that it was eliminating the official rate of 2.6 bolivars per U.S. dollar for essential goods. As a result, there are only two exchange rates available for remeasuring bolivar-denominated transactions as of December 31, 2011, the official rate of 4.3 bolivars per U.S. dollar for nonessential goods and the SITME rate. As discussed above, the Company has remeasured the net assets of our Venezuelan subsidiary using the official rate for nonessential goods of 4.3 bolivars per U.S. dollar since January 1, 2010. Therefore, the elimination of the official rate for essential goods had no impact on the remeasurement of the net assets of our Venezuelan subsidiary. We continue to use the official exchange rate for nonessential goods to remeasure the financial statements of our Venezuelan subsidiary. If the official exchange rate devalues further, it would result in our Company recognizing additional foreign currency exchange losses in our consolidated financial statements. As of December 31, 2011, our Venezuelan subsidiary held monetary assets of $300 million, including cash, which accounted for approximately 2 percent of our consolidated cash and cash equivalents balance.
In addition to the foreign currency exchange exposure related to our Venezuelan subsidiary's net assets, we also sell concentrate to our bottling partner in Venezuela from outside the country. These sales are denominated in U.S. dollars. Some of our concentrate sales were approved by the government-operated Foreign Exchange Administration Board ("CADIVI") to receive the official rate for essential goods of 2.6 bolivars per U.S. dollar prior to the elimination of the official rate for essential goods in December 2010. Prior to the elimination of the official rate for essential goods, our bottling partner in Venezuela was able to convert bolivars to U.S. dollars to settle our receivables related to sales approved by the CADIVI. Therefore, as of December 31, 2011, our receivable balance related to concentrate sales that had been approved by the CADIVI was not significant. If we are unable to utilize a government-approved exchange rate mechanism for future concentrate sales to our bottling partner in Venezuela, the amount of receivables related to these sales will increase. In addition, we have certain intangible assets associated with products sold in Venezuela. If we are unable to utilize a government-approved exchange rate mechanism for concentrate sales, or if the bolivar further devalues, it could result in the impairment of these intangible assets. As of December 31, 2011, the carrying value of our accounts receivable from our bottling partner in Venezuela and intangible assets associated with products sold in Venezuela was $147 million. The revenues and cash flows associated with concentrate sales to our bottling partner in Venezuela in 2012 are not anticipated to be significant to the Company's consolidated financial statements.
Recently Issued Accounting Guidance
In June 2011, the FASB issued an amendment to an existing accounting standard which requires companies to present net income and other comprehensive income in one continuous statement or in two separate, but consecutive, statements. In addition, in December 2011, the FASB issued an amendment to an existing accounting standard which defers the requirement to present components of reclassifications of other comprehensive income on the face of the income statement. This new accounting pronouncement is effective for our first quarter of 2012 and we do not expect any material impact on our financial statements from its adoption.
As previously discussed, in June 2009, the FASB amended its guidance on accounting for VIEs. Please refer to the heading "Principles of Consolidation" above.
NOTE 2: ACQUISITIONS AND DIVESTITURES
Acquisitions
During 2011, cash payments related to the Company's acquisition and investment activities totaled $977 million. These payments were primarily related to the acquisitions of Great Plains Coca-Cola Bottling Company ("Great Plains") and Honest Tea, Inc. ("Honest Tea"), and an additional investment in Coca-Cola Central Japan Company ("Central Japan"). In addition, the Company's acquisition and investment activities during 2011 included immaterial cash payments for the finalization of working capital adjustments related to our acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to our discussion of this transaction below.
The Company acquired Great Plains on December 30, 2011. The total purchase price for the Great Plains acquisition was approximately $360 million, of which $321 million was paid at closing. The purchase price was primarily allocated to property, plant and equipment, identifiable intangible assets and goodwill. The Company anticipates finalizing our purchase accounting for the Great Plains acquisition no later than the end of 2012, upon the finalization of appraisals primarily related to fixed assets and intangible assets.
90
During 2011, the Company also acquired the remaining ownership interest of Honest Tea not already owned by the Company. Prior to the Company acquiring the remaining ownership interest of Honest Tea, we accounted for our investment under the equity method of accounting. We remeasured our equity interest in Honest Tea to fair value upon the close of the transaction. The resulting gain on the remeasurement was not significant to our consolidated financial statements. The Company finalized our purchase accounting for Honest Tea during the fourth quarter of 2011.
In December 2011, the Company acquired an additional minority interest in Central Japan. As a result, the Company began to account for our investment in Central Japan under the equity method of accounting beginning in December 2011.
During 2010, cash payments related to the Company's acquisition and investment activities totaled $2,511 million. These payments were primarily related to the Company's acquisition of CCE's North American business and the acquisition of certain distribution rights from Dr Pepper Snapple Group, Inc. ("DPS"). See the relevant sections below for further discussion of these transactions.
In addition to the transactions listed in the preceding paragraph, our acquisition and investment activities during 2010 also included the acquisition of OAO Nidan Juices ("Nidan"), a Russian juice company, and an additional investment in Fresh Trading Ltd. ("innocent"). Total consideration for the Nidan acquisition was approximately $276 million, which was primarily allocated to property, plant and equipment, identifiable intangible assets and goodwill. The Company finalized our purchase accounting for Nidan in the third quarter of 2011. Under the terms of the agreement for our additional investment in innocent, innocent's founders retain operational control of the business, and we will continue to account for our investment under the equity method of accounting. Additionally, we have a series of outstanding put and call options with the existing shareowners of innocent for the Company to potentially acquire the remaining shares not already owned by the Company. The put and call options are exercisable in stages between 2013 and 2014.
During 2009, cash payments related to the Company's acquisition and investment activities totaled $300 million. None of the acquisitions or investments was individually significant. Included in these investment activities was the acquisition of a minority interest in innocent.
Acquisition of Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc.'s North American Business
Pursuant to the terms of the business separation and merger agreement entered into on February 25, 2010, as amended (the "merger agreement"), on October 2, 2010 (the "acquisition date"), we acquired CCE's North American business. We believe this acquisition will result in an evolved franchise system that will enable us to better serve the unique needs of the North American market. The creation of a unified operating system will strategically position us to better market and distribute our nonalcoholic beverage brands in North America. Refer to Note 18 for information related to the Company's integration initiative associated with this acquisition.
Under the terms of the merger agreement, the Company acquired the 67 percent of CCE's North American business that was not already owned by the Company for consideration that included: (1) the Company's 33 percent indirect ownership interest in CCE's European operations; (2) cash consideration; and (3) replacement awards issued to certain current and former employees of CCE's North American and corporate operations. At closing, CCE shareowners other than the Company exchanged their CCE common stock for common stock in a new entity, which was renamed Coca-Cola Enterprises, Inc. (which is referred to herein as "New CCE") and which continues to hold the European operations held by CCE prior to the acquisition. At closing, New CCE became 100 percent owned by shareowners that held shares of common stock of CCE immediately prior to the closing, other than the Company. As a result of this transaction, the Company does not own any interest in New CCE.
As of October 1, 2010, our Company owned 33 percent of the outstanding common stock of CCE. Based on the closing price of CCE's common stock on the last day of trading prior to the acquisition date, the fair value of our investment in CCE was $5,373 million, which reflected the fair value of our ownership in both CCE's North American business and European operations. We remeasured our equity interest in CCE to fair value upon the close of the transaction. As a result, we recognized a gain of $4,978 million, which was classified in the line item other income (loss) — net in our consolidated statement of income. The gain included a $137 million reclassification adjustment related to foreign currency translation gains recognized upon the disposal of our indirect investment in CCE's European operations. The Company relinquished its indirect ownership interest in CCE's European operations to New CCE as part of the consideration to acquire the 67 percent of CCE's North American business that was not already owned by the Company.
Although the CCE transaction was structured to be primarily cashless, under the terms of the merger agreement, we agreed to assume $8.9 billion of CCE debt. In the event the actual CCE debt on the acquisition date was less than the agreed amount, we agreed to make a cash payment to New CCE for the difference. As of the acquisition date, the debt assumed by the Company was $7.9 billion. The total cash consideration paid to New CCE as part of the transaction was $1.4 billion, which included $1.0 billion related to the debt shortfall. In addition, the cash consideration paid to New CCE included amounts related to working capital adjustments which were finalized in 2011.
91
Under the terms of the merger agreement, the Company replaced share-based payment awards for certain current and former employees of CCE's North American and corporate operations. The following table provides a list of all replacement awards and the estimated fair value of those awards issued in conjunction with our acquisition of CCE's North American business (in millions):
|
Number of
Shares, Options
and Units Issued
|
Fair Value |
|||||
Performance share units |
1.6 |
$ |
192 |
|||
Stock options |
4.8 |
109 |
||||
Restricted share units |
0.8 |
50 |
||||
Restricted stock |
0.2 |
12 |
||||
Total |
7.4 |
$ |
363 |
|||
The portion of the fair value of the replacement awards related to services provided prior to the business combination was included in the total purchase price. The portion of the fair value associated with future service is recognized as expense over the future service period, which varies by award. The Company determined that $237 million ($154 million net of tax) of the replacement awards was related to services rendered prior to the business combination.
Each CCE performance share unit ("PSU") replaced by the Company was converted at 100 percent of target into an adjusted PSU of The Coca-Cola Company, determined by multiplying the number of shares of each PSU by an exchange ratio (the "closing exchange ratio") equal to the closing price of a share of CCE common stock on the last day of trading prior to the acquisition date divided by the closing price of the Company's common stock on the same day. At the time we issued these replacement PSUs, they were subject to the same vesting conditions and other terms applicable to the CCE PSUs immediately prior to the closing date. However, in the fourth quarter of 2010, the Company modified primarily all of these PSUs to eliminate the remaining holding period, which resulted in $74 million of accelerated expense. Refer to Note 12 for additional information.
Each CCE stock option replaced by the Company was converted into an adjusted stock option of The Coca-Cola Company to acquire a number of shares of Coca-Cola common stock, determined by multiplying the number of shares of CCE common stock subject to the CCE stock option by the closing exchange ratio. The exercise price per share of the replacement awards was equal to the per share exercise price of the CCE stock option divided by the closing exchange ratio. All of the replacement stock options are subject to the same vesting conditions and other terms applicable to the CCE stock options immediately prior to the closing date. Refer to Note 12 for additional information.
Each CCE restricted share unit ("RSU") replaced by the Company was converted into an adjusted RSU of The Coca-Cola Company, determined by multiplying the number of shares of each RSU by the closing exchange ratio. All of the replacement RSUs are subject to the same vesting conditions and other terms applicable to the CCE RSUs immediately prior to the closing date. Refer to Note 12 for additional information.
Each share of CCE restricted stock replaced by the Company was converted into an adjusted share of restricted stock of The Coca-Cola Company, determined by multiplying the number of shares of CCE restricted stock by the closing exchange ratio. All of the replacement shares of restricted stock are subject to the same vesting conditions and other terms applicable to the CCE shares of restricted stock immediately prior to the closing date. Refer to Note 12 for additional information.
The following table reconciles the total purchase price of the Company's acquisition of CCE's North American business, including adjustments recorded as part of the Company's purchase accounting (in millions):
October 2, 2010 |
|||
Fair value of our equity investment in CCE1
|
$ |
5,373 |
|
Cash consideration2
|
1,368 |
||
Fair value of share-based payment awards3
|
154 |
||
Total purchase price |
$ |
6,895 |
|
1 |
Represents the fair value of our 33 percent ownership interest in the outstanding common stock of CCE based on the closing price of CCE's common stock on the last day the New York Stock Exchange was open prior to the acquisition date. The fair value reflects our indirect ownership interest in both CCE's North American business and European operations.
|
2 |
Primarily related to the debt shortfall and working capital adjustments. |
3 |
Represents the portion of the total fair value of the replacement awards associated with services rendered prior to the business combination, net of tax. |
92
The following table presents the final allocation of the purchase price by major class of assets and liabilities (in millions) as of the acquisition date, as well as adjustments made during 2011 (referred to as "measurement period adjustments"):
|
Amounts
Recognized as of
Acquisition Date1
|
Measurement
Period
Adjustments2
|
Amounts
Recognized as of
Acquisition Date
(as Adjusted)
|
|||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ |
49 |
$ |
— |
$ |
49 |
|||||
Marketable securities |
7 |
— |
7 |
||||||||
Trade accounts receivable3
|
1,194 |
— |
1,194 |
||||||||
Inventories |
696 |
— |
696 |
||||||||
Other current assets4
|
744 |
(5 |
) |
739 |
|||||||
Property, plant and equipment4
|
5,385 |
(682 |
) |
4,703 |
|||||||
Bottlers' franchise rights with indefinite lives4,5
|
5,100 |
100 |
5,200 |
||||||||
Other intangible assets4,6
|
1,032 |
45 |
1,077 |
||||||||
Other noncurrent assets |
261 |
— |
261 |
||||||||
Total identifiable assets acquired |
$ |
14,468 |
$ |
(542 |
) |
$ |
13,926 |
||||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses4
|
1,826 |
8 |
1,834 |
||||||||
Loans and notes payable7
|
266 |
— |
266 |
||||||||
Long-term debt7
|
9,345 |
— |
9,345 |
||||||||
Pension and other postretirement liabilities8
|
1,313 |
— |
1,313 |
||||||||
Other noncurrent liabilities4,9
|
2,603 |
(293 |
) |
2,310 |
|||||||
Total liabilities assumed |
$ |
15,353 |
$ |
(285 |
) |
$ |
15,068 |
||||
Net liabilities assumed |
(885 |
) |
(257 |
) |
(1,142 |
) |
|||||
Goodwill4,10
|
7,746 |
304 |
8,050 |
||||||||
$ |
6,861 |
$ |
47 |
$ |
6,908 |
||||||
Less: Noncontrolling interests |
13 |
— |
13 |
||||||||
Net assets acquired |
$ |
6,848 |
$ |
47 |
$ |
6,895 |
|||||
1 |
As previously reported in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010.
|
2 |
The measurement period adjustments did not have a significant impact on our consolidated statements of income for the years ended December 31, 2011, and December 31, 2010. In addition, these adjustments did not have a significant impact on our consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2010. Therefore, we have not retrospectively adjusted the comparative 2010 financial information. |
3 |
The gross amount due under receivables we acquired was $1,226 million, of which $32 million was expected to be uncollectible.
|
4 |
The measurement period adjustments were due to the finalization of appraisals related to intangible assets and certain fixed assets and resulted in the following: a decrease to property, plant and equipment; an increase to franchise rights; and a decrease to noncurrent deferred tax liabilities. The net impact of the measurement period adjustments and the payments made to New CCE that related to the finalization of working capital adjustments resulted in a net increase to goodwill. |
5 |
Represents reacquired franchise rights that had previously provided CCE with exclusive and perpetual rights to manufacture and/or distribute certain beverages in specified territories. These rights have been determined to have indefinite lives and are not amortized. |
6 |
Other intangible assets primarily relate to franchise rights that had previously provided CCE with exclusive rights to manufacture and/or distribute certain beverages in specified territories for a finite period of time, and therefore have been classified as definite-lived intangible assets. The estimated fair value of franchise rights with definite lives was $650 million as of the acquisition date. These franchise rights will be amortized over a weighted-average life of approximately eight years, which is equal to the weighted-average remaining contractual term of the franchise rights. Other intangible assets also include $380 million of customer relationships, which will be amortized over approximately 20 years.
|
7 |
Refer to Note 10 for additional information.
|
8 |
The assumed pension and other postretirement liabilities consisted of benefit obligations of $3,544 million and plan assets of $2,231 million. Refer to Note 13 for additional information related to pension and other postretirement plans assumed from CCE.
|
9 |
Primarily relates to deferred tax liabilities recorded on franchise rights. Refer to Note 14.
|
10 |
The goodwill recognized as part of this acquisition has been assigned to the North America operating segment. $170 million of this goodwill is tax deductible. The goodwill recognized in conjunction with our acquisition of CCE's North American business is primarily related to synergistic value created from having a unified operating system that will strategically position us to better market and distribute our nonalcoholic beverage brands in North America. It also includes certain other intangible assets that do not qualify for separate recognition, such as an assembled workforce.
|
93
In a concurrent transaction, we agreed to sell all of our ownership interests in Coca-Cola Drikker AS (the "Norwegian bottling operation") and Coca-Cola Drycker Sverige AB (the "Swedish bottling operation") to New CCE at fair value. The divestiture of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations also closed on October 2, 2010. See further discussion of this divestiture below. In addition, we granted New CCE the right to negotiate the acquisition of our majority interest in our German bottling operation, Coca-Cola Erfrischungsgetraenke AG ("CCEAG"), 18 to 39 months after the date of the merger agreement, at the then current fair value and subject to terms and conditions as mutually agreed.
The Company incurred $84 million of transaction costs in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business and the sale of our ownership interests in our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE since the transaction commenced. These costs were included in the line item other operating charges in our consolidated statements of income. Refer to Note 17 for additional information. In addition, the Company recorded charges of $265 million related to preexisting relationships during 2010. These charges were primarily related to the write-off of our investment in infrastructure programs with CCE. Our investment in these infrastructure programs with CCE did not meet the criteria to be recognized as an asset subsequent to the acquisition. In 2011, the Company recorded an additional charge of $1 million associated with these preexisting relationships. These charges were included in the line item other income (loss) — net in our consolidated statements of income. Refer to Note 6 for additional information.
The CCE North American business contributed net revenues of approximately $3,637 million and net losses of approximately $122 million from October 2, 2010 through December 31, 2010. The following table presents unaudited consolidated pro forma information as if our acquisition of CCE's North American business and the divestiture of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations had occurred on January 1, 2009 (in millions):
Unaudited
|
||||||||
Year Ended December 31, |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||
Net operating revenues1
|
$ |
43,106 |
$ |
41,635 |
||||
Net income attributable to shareowners of The Coca-Cola Company2
|
6,839 |
11,767 |
3 |
|||||
1 |
The deconsolidation of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations resulted in a decrease to net operating revenues of approximately $433 million and $542 million in 2010 and 2009, respectively.
|
2 |
The deconsolidation of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations resulted in a decrease to net income attributable to shareowners of The Coca-Cola Company of approximately $387 million in 2010 and an increase of $294 million in 2009.
|
3 |
Includes the gain related to the remeasurement of our equity interest in CCE to fair value upon the close of the transaction, the gain on the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations, transaction costs and charges related to preexisting relationships. The 2010 pro forma information has been adjusted to exclude the impact of these items in order to present the pro forma information as if the transactions had occurred on January 1, 2009. |
The unaudited pro forma financial information presented above does not purport to represent what the actual results of our operations would have been if our acquisition of CCE's North American business and the divestiture of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations had occurred on January 1, 2009, nor is it indicative of the future operating results of The Coca-Cola Company. The unaudited pro forma financial information does not reflect the impact of future events that may occur after the acquisition, including, but not limited to, anticipated cost savings from operating synergies.
The unaudited pro forma financial information presented in the table above has been adjusted to give effect to adjustments that are (1) directly related to the business combination; (2) factually supportable; and (3) expected to have a continuing impact. These adjustments include, but are not limited to, the application of our accounting policies; elimination of related party transactions and equity income; and depreciation and amortization related to fair value adjustments to property, plant and equipment and intangible assets.
Dr Pepper Snapple Group, Inc. Agreements
In contemplation of the closing of our acquisition of CCE's North American business, we reached an agreement with DPS to distribute certain DPS brands in territories where DPS brands had been distributed by CCE prior to the CCE transaction. Under the terms of our agreement with DPS, and concurrently with the closing of the CCE transaction, we entered into license agreements with DPS to distribute Dr Pepper trademark brands in the U.S., Canada Dry in the Northeast U.S., and Canada Dry and C' Plus in Canada, and we made a net one-time cash payment of $715 million to DPS. Under the license agreements, the Company agreed to meet certain performance obligations in order to distribute DPS products in retail and foodservice accounts and vending machines. The license agreements have initial terms of 20 years, with automatic 20-year renewal periods unless otherwise terminated under the terms of the agreements. The license agreements replaced agreements between DPS and CCE existing immediately prior to the completion of the CCE transaction. In addition, we entered into an agreement with DPS to
94
include Dr Pepper and Diet Dr Pepper in our Coca-Cola Freestyle fountain dispensers in certain outlets throughout the United States. The Coca-Cola Freestyle agreement has a term of 20 years.
Although these transactions were negotiated concurrently, they are legally separable and have distinct termination provisions and penalties, if applicable. As a result, the Company recorded an asset of $865 million related to the DPS license agreements and recorded deferred revenue of $150 million related to the Freestyle agreement. The DPS license agreements were determined to be indefinite-lived intangible assets and classified in the line item bottlers' franchise rights with indefinite lives in our consolidated balance sheet. The Company reached the conclusion that these distribution rights had an indefinite life based on several key factors, including, but not limited to, (1) our license agreements with DPS shall remain in effect for 20 years and shall automatically renew for additional 20-year successive periods thereafter unless terminated pursuant to the provisions of the agreements; (2) no additional payments shall be due for the renewal periods; (3) we anticipate using the assets indefinitely; (4) there are no known legal, regulatory or contractual provisions that are likely to limit the useful life of these assets; and (5) the classification of these assets as indefinite-lived assets is consistent with similar market transactions. The Company will amortize the deferred revenue related to the Freestyle agreement on a straight-line basis over 20 years, which is the length of the agreement. The amortization will be included as a component of the Company's net operating revenues.
Definitive Agreement to Acquire an Investment in Aujan Industries
On December 14, 2011, the Company entered into a definitive agreement with Aujan Industries (“Aujan”), one of the largest independent beverage companies in the Middle East, to acquire approximately half of the equity in Aujan's existing beverage business, excluding Aujan's Iranian manufacturing and distribution business. Under the terms of the agreement, we will acquire 50 percent of the Aujan entity that holds the rights to Aujan-owned brands, and 49 percent of Aujan's bottling and distribution company, which will continue to hold the licensed brand Vimto. Total consideration for this investment, which will be accounted for under the equity method, is approximately $980 million, which we expect to fund from our existing cash reserves. Closing of the transaction is subject to certain conditions and is expected to occur in the first half of 2012.
Divestitures
During 2011, proceeds from the disposal of bottling companies and other investments totaled $562 million, primarily related to the sale of our investment in Coca-Cola Embonor, S.A. ("Embonor"), a bottling partner with operations primarily in Chile, for $394 million. Prior to this transaction, the Company accounted for our investment in Embonor under the equity method of accounting. Refer to Note 17. None of the Company's other divestitures was individually significant.
In 2010, proceeds from the disposal of bottling companies and other investments totaled $972 million, primarily related to the sale of all our ownership interests in our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE for $0.9 billion in cash on October 2, 2010. In addition to the proceeds related to the disposal of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations, our Company sold 50 percent of our investment in Leão Junior, S.A. ("Leão Junior"), a Brazilian tea company, for $83 million. Refer to Note 17 for information related to the gain on these divestitures.
Our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations (the disposal group) met the criteria to be classified as held for sale prior to their disposal. The following table presents information related to the major classes of assets and liabilities of the disposal group as of October 1, 2010 (in millions):
Trade receivables, less allowances for doubtful accounts |
$ |
67 |
|
Inventories |
42 |
||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
17 |
||
Property, plant and equipment — net |
315 |
||
Intangible assets |
172 |
||
Total assets1
|
$ |
613 |
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
$ |
159 |
|
Accrued income taxes |
10 |
||
Deferred income taxes |
45 |
||
Total liabilities1
|
$ |
214 |
|
1 |
Prior to the divestiture of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations, the assets and liabilities of these entities were included in our Bottling Investments operating segment. Refer to Note 19.
|
We determined that our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations did not meet the criteria to be classified as discontinued operations, primarily due to our continuing significant involvement with these entities. Although we do not have an ownership
95
interest in New CCE, we have concluded that our ongoing contractual relationship, governed by the Bottler's Agreements, constitutes a continuing significant involvement.
In 2009, proceeds from the disposal of bottling companies and other investments totaled $240 million, none of which was individually significant.
NOTE 3: INVESTMENTS
Investments in debt and marketable securities, other than investments accounted for under the equity method, are classified as trading, available-for-sale or held-to-maturity. Our marketable equity investments are classified as either trading or available-for-sale with their cost basis determined by the specific identification method. Realized and unrealized gains and losses on trading securities and realized gains and losses on available-for-sale securities are included in net income. Unrealized gains and losses, net of deferred taxes, on available-for-sale securities are included in our consolidated balance sheets as a component of AOCI.
Our investments in debt securities are carried at either amortized cost or fair value. Investments in debt securities that the Company has the positive intent and ability to hold to maturity are carried at amortized cost and classified as held-to-maturity. Investments in debt securities that are not classified as held-to-maturity are carried at fair value and classified as either trading or available-for-sale.
Trading Securities
As of December 31, 2011 and 2010, our trading securities had a fair value of $211 million and $209 million, respectively. The Company had net unrealized losses on trading securities of $5 million, $3 million and $16 million as of December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. The Company's trading securities were included in the following captions in our consolidated balance sheets (in millions):
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
|||||
Marketable securities |
$ |
138 |
$ |
132 |
|||
Other assets |
73 |
77 |
|||||
Total trading securities |
$ |
211 |
$ |
209 |
|||
Available-for-Sale and Held-to-Maturity Securities
As of December 31, 2011 and 2010, available-for-sale and held-to-maturity securities consisted of the following (in millions):
|
Gross
Unrealized
|
Estimated |
||||||||||||||
Cost |
Gains |
Losses |
Fair Value |
||||||||||||
2011 |
|||||||||||||||
Available-for-sale securities:1,2
|
|||||||||||||||
Equity securities |
$ |
834 |
$ |
237 |
$ |
— |
$ |
1,071 |
|||||||
Debt securities |
332 |
1 |
(3 |
) |
330 |
||||||||||
$ |
1,166 |
$ |
238 |
$ |
(3 |
) |
$ |
1,401 |
|||||||
Held-to-maturity securities: |
|||||||||||||||
Bank and corporate debt |
$ |
113 |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
$ |
113 |
|||||||
2010 |
|||||||||||||||
Available-for-sale securities:1
|
|||||||||||||||
Equity securities |
$ |
209 |
$ |
267 |
$ |
(5 |
) |
$ |
471 |
||||||
Debt securities |
14 |
— |
— |
14 |
|||||||||||
$ |
223 |
$ |
267 |
$ |
(5 |
) |
$ |
485 |
|||||||
Held-to-maturity securities: |
|||||||||||||||
Bank and corporate debt |
$ |
111 |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
$ |
111 |
|||||||
1 |
Refer to Note 16 for additional information related to the estimated fair value.
|
2 |
During 2011, the balance of available-for-sale securities increased significantly, primarily due to long-term investments made by our captive insurance company and an investment in Arca Continental, S.A.B. de C.V. ("Arca Contal"). Refer to Note 17 for a discussion of the Arca Contal transaction.
|
96
In 2011, the Company divested certain available-for-sale securities. These divestitures resulted in cash proceeds of $37 million, gross realized gains of $5 million and gross realized losses of $1 million. In addition to the sale of available-for-sale securities, the Company also had investments classified as available-for-sale securities in which our cost basis exceeded the fair value of our investment. Management assessed each of these investments on an individual basis to determine if the decline in fair value was other than temporary. Management's assessment as to the nature of a decline in fair value is based on, among other things, the length of time and the extent to which the market value has been less than our cost basis; the financial condition and near-term prospects of the issuer; and our intent and ability to retain the investment for a period of time sufficient to allow for any anticipated recovery in market value. Based on these assessments, management determined that the decline in fair value of certain investments was other than temporary. As a result, the Company recognized other-than-temporary impairment charges of $17 million. These impairment charges were recorded in other income (loss) — net. Refer to Note 16 and Note 17.
In 2010, the Company had several investments classified as available-for-sale securities in which our cost basis exceeded the fair value of the investment. Management assessed each of these investments on an individual basis to determine if the decline in fair value was other than temporary. Based on these assessments, management determined that the decline in fair value of certain investments was other than temporary. As a result, the Company recognized other-than-temporary impairment charges of $26 million. These impairment charges were recorded in other income (loss) — net. Refer to Note 16 and Note 17. The Company did not sell any available-for-sale securities during 2010.
In 2009, the Company divested certain available-for-sale securities. These divestitures were the result of both sales and a charitable donation. The sales of available-for-sale securities resulted in cash proceeds of $157 million, gross realized gains of $44 million and gross realized losses of $2 million. In addition to the sale of available-for-sale securities, the Company donated certain available-for-sale securities to The Coca-Cola Foundation. The donated investments had a cost basis of $7 million and a fair value of $106 million at the date of donation. The net impact of this donation was an expense equal to our cost basis in the securities, which was recorded in other income (loss) — net.
The Company's available-for-sale and held-to-maturity securities were included in the following captions in our consolidated balance sheets (in millions):
December 31, 2011 |
December 31, 2010 |
||||||||||||||
|
Available-
for-Sale
Securities
|
Held-to-
Maturity
Securities
|
Available-
for-Sale
Securities
|
Held-to-
Maturity
Securities
|
||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ |
— |
$ |
112 |
$ |
— |
$ |
110 |
|||||||
Marketable securities |
5 |
1 |
5 |
1 |
|||||||||||
Other investments, principally bottling companies |
986 |
— |
471 |
— |
|||||||||||
Other assets |
410 |
— |
9 |
— |
|||||||||||
$ |
1,401 |
$ |
113 |
$ |
485 |
$ |
111 |
||||||||
The contractual maturities of these investments as of December 31, 2011, were as follows (in millions):
Available-for-Sale Securities
|
Held-to-Maturity Securities
|
||||||||||||||
Cost |
Fair Value |
Amortized Cost |
Fair Value |
||||||||||||
Within 1 year |
$ |
5 |
$ |
5 |
$ |
113 |
$ |
113 |
|||||||
After 1 year through 5 years |
32 |
32 |
— |
— |
|||||||||||
After 5 years through 10 years |
191 |
191 |
— |
— |
|||||||||||
After 10 years |
104 |
102 |
— |
— |
|||||||||||
Equity securities |
834 |
1,071 |
— |
— |
|||||||||||
$ |
1,166 |
$ |
1,401 |
$ |
113 |
$ |
113 |
||||||||
The Company expects that actual maturities may differ from the contractual maturities above because borrowers have the right to call or prepay certain obligations.
Cost Method Investments
Cost method investments are originally recorded at cost, and we record dividend income when applicable dividends are declared. Cost method investments are reported as other investments in our consolidated balance sheets, and dividend income from cost method investments is reported in other income (loss) — net in our consolidated statements of income. We review all of our cost method investments quarterly to determine if impairment indicators are present; however, we are not required to determine the fair value of these investments unless impairment indicators exist. When impairment indicators exist, we
97
generally use discounted cash flow analyses to determine the fair value. We estimate that the fair values of our cost method investments approximated or exceeded their carrying values as of December 31, 2011 and 2010. Our cost method investments had a carrying value of $155 million and $160 million as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
In 2009, the Company recorded a charge of $27 million in other income (loss) — net as a result of an other-than-temporary decline in the fair value of a cost method investment. Refer to Note 16 and Note 17 for additional information related to this impairment.
NOTE 4: INVENTORIES
Inventories consist primarily of raw materials and packaging (which includes ingredients and supplies) and finished goods (which include concentrates and syrups in our concentrate operations, and finished beverages in our finished products operations). Inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market. We determine cost on the basis of the average cost or first-in, first-out methods. Inventories consisted of the following (in millions):
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
|||||
Raw materials and packaging |
$ |
1,680 |
$ |
1,425 |
|||
Finished goods |
1,198 |
1,029 |
|||||
Other |
214 |
196 |
|||||
Total inventories |
$ |
3,092 |
$ |
2,650 |
|||
NOTE 5: HEDGING TRANSACTIONS AND DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
The Company is directly and indirectly affected by changes in certain market conditions. These changes in market conditions may adversely impact the Company's financial performance and are referred to as "market risks." Our Company, when deemed appropriate, uses derivatives as a risk management tool to mitigate the potential impact of certain market risks. The primary market risks managed by the Company through the use of derivative instruments are foreign currency exchange rate risk, commodity price risk and interest rate risk.
The Company uses various types of derivative instruments including, but not limited to, forward contracts, commodity futures contracts, option contracts, collars and swaps. Forward contracts and commodity futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell a quantity of a currency or commodity at a predetermined future date, and at a predetermined rate or price. An option contract is an agreement that conveys the purchaser the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a quantity of a currency or commodity at a predetermined rate or price during a period or at a time in the future. A collar is a strategy that uses a combination of options to limit the range of possible positive or negative returns on an underlying asset or liability to a specific range, or to protect expected future cash flows. To do this, an investor simultaneously buys a put option and sells (writes) a call option, or alternatively buys a call option and sells (writes) a put option. A swap agreement is a contract between two parties to exchange cash flows based on specified underlying notional amounts, assets and/or indices. We do not enter into derivative financial instruments for trading purposes.
All derivatives are carried at fair value in our consolidated balance sheets in the following line items, as applicable: prepaid expenses and other assets; other assets; accounts payable and accrued expenses; and other liabilities. The carrying values of the derivatives reflect the impact of legally enforceable master netting agreements and cash collateral held or placed with the same counterparties, as applicable. These master netting agreements allow the Company to net settle positive and negative positions (assets and liabilities) arising from different transactions with the same counterparty.
The accounting for gains and losses that result from changes in the fair values of derivative instruments depends on whether the derivatives have been designated and qualify as hedging instruments and the type of hedging relationships. Derivatives can be designated as fair value hedges, cash flow hedges or hedges of net investments in foreign operations. The changes in the fair values of derivatives that have been designated and qualify for fair value hedge accounting are recorded in the same line item in our consolidated statements of income as the changes in the fair values of the hedged items attributable to the risk being hedged. The changes in fair values of derivatives that have been designated and qualify as cash flow hedges or hedges of net investments in foreign operations are recorded in AOCI and are reclassified into the line item in our consolidated statement of income in which the hedged items are recorded in the same period the hedged items affect earnings. Due to the high degree of effectiveness between the hedging instruments and the underlying exposures being hedged, fluctuations in the value of the derivative instruments are generally offset by changes in the fair values or cash flows of the underlying exposures being hedged. The changes in fair values of derivatives that were not designated and/or did not qualify as hedging instruments are immediately recognized into earnings.
For derivatives that will be accounted for as hedging instruments, the Company formally designates and documents, at inception, the financial instrument as a hedge of a specific underlying exposure, the risk management objective and the strategy for undertaking the hedge transaction. In addition, the Company formally assesses, both at the inception and at least quarterly
98
thereafter, whether the financial instruments used in hedging transactions are effective at offsetting changes in either the fair values or cash flows of the related underlying exposures. Any ineffective portion of a financial instrument's change in fair value is immediately recognized into earnings.
The Company determines the fair values of its derivatives based on quoted market prices or using standard valuation models. Refer to Note 16. The notional amounts of the derivative financial instruments do not necessarily represent amounts exchanged by the parties and, therefore, are not a direct measure of our exposure to the financial risks described above. The amounts exchanged are calculated by reference to the notional amounts and by other terms of the derivatives, such as interest rates, foreign currency exchange rates, commodity rates or other financial indices. The Company does not view the fair values of its derivatives in isolation, but rather in relation to the fair values or cash flows of the underlying hedged transactions or other exposures. Virtually all of our derivatives are straightforward over-the-counter instruments with liquid markets.
The following table presents the fair values of the Company's derivative instruments that were designated and qualified as part of a hedging relationship (in millions):
Fair Value1,2
|
|||||||||
Derivatives Designated as Hedging Instruments |
Balance Sheet Location1
|
December 31, 2011 |
December 31, 2010 |
||||||
Assets: |
|||||||||
Foreign currency contracts |
Prepaid expenses and other assets |
$ |
170 |
$ |
32 |
||||
Commodity contracts |
Prepaid expenses and other assets |
2 |
4 |
||||||
Interest rate swaps |
Other assets |
246 |
— |
||||||
Total assets |
$ |
418 |
$ |
36 |
|||||
Liabilities: |
|||||||||
Foreign currency contracts |
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
$ |
41 |
$ |
141 |
||||
Commodity contracts |
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
1 |
2 |
||||||
Interest rate swaps |
Other liabilities |
— |
97 |
||||||
Total liabilities |
$ |
42 |
$ |
240 |
|||||
1 |
All of the Company's derivative instruments are carried at fair value in our consolidated balance sheets after considering the impact of legally enforceable master netting agreements and cash collateral held or placed with the same counterparties, as applicable. Current disclosure requirements mandate that derivatives must also be disclosed without reflecting the impact of master netting agreements and cash collateral. Refer to Note 16 for the net presentation of the Company's derivative instruments. |
2 |
Refer to Note 16 for additional information related to the estimated fair value. |
The following table presents the fair values of the Company's derivative instruments that were not designated as hedging instruments (in millions):
Fair Value1,2
|
|||||||||
Derivatives Not Designated as Hedging Instruments |
Balance Sheet Location1
|
December 31, 2011 |
December 31, 2010 |
||||||
Assets: |
|||||||||
Foreign currency contracts |
Prepaid expenses and other assets |
$ |
29 |
$ |
65 |
||||
Commodity contracts |
Prepaid expenses and other assets |
54 |
56 |
||||||
Other derivative instruments |
Prepaid expenses and other assets |
5 |
17 |
||||||
Total assets |
$ |
88 |
$ |
138 |
|||||
Liabilities: |
|||||||||
Foreign currency contracts |
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
$ |
116 |
$ |
144 |
||||
Commodity contracts |
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
47 |
— |
||||||
Other derivative instruments |
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
1 |
— |
||||||
Total liabilities |
$ |
164 |
$ |
144 |
|||||
1 |
All of the Company's derivative instruments are carried at fair value in our consolidated balance sheets after considering the impact of legally enforceable master netting agreements and cash collateral held or placed with the same counterparties, as applicable. Current disclosure requirements mandate that derivatives must also be disclosed without reflecting the impact of master netting agreements and cash collateral. Refer to Note 16 for the net presentation of the Company's derivative instruments. |
2 |
Refer to Note 16 for additional information related to the estimated fair value. |
99
Credit Risk Associated with Derivatives
We have established strict counterparty credit guidelines and enter into transactions only with financial institutions of investment grade or better. We monitor counterparty exposures regularly and review any downgrade in credit rating immediately. If a downgrade in the credit rating of a counterparty were to occur, we have provisions requiring collateral in the form of U.S. government securities for substantially all of our transactions. To mitigate presettlement risk, minimum credit standards become more stringent as the duration of the derivative financial instrument increases. In addition, the Company's master netting agreements reduce credit risk by permitting the Company to net settle for transactions with the same counterparty. To minimize the concentration of credit risk, we enter into derivative transactions with a portfolio of financial institutions. Based on these factors, we consider the risk of counterparty default to be minimal.
Cash Flow Hedging Strategy
The Company uses cash flow hedges to minimize the variability in cash flows of assets or liabilities or forecasted transactions caused by fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates, commodity prices or interest rates. The changes in the fair values of derivatives designated as cash flow hedges are recorded in AOCI and are reclassified into the line item in our consolidated statement of income in which the hedged items are recorded in the same period the hedged items affect earnings. The changes in fair values of hedges that are determined to be ineffective are immediately reclassified from AOCI into earnings. The Company did not discontinue any cash flow hedging relationships during the years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009. The maximum length of time for which the Company hedges its exposure to future cash flows is typically three years.
The Company maintains a foreign currency cash flow hedging program to reduce the risk that our eventual U.S. dollar net cash inflows from sales outside the United States and U.S. dollar net cash outflows from procurement activities will be adversely affected by changes in foreign currency exchange rates. We enter into forward contracts and purchase foreign currency options (principally euros and Japanese yen) and collars to hedge certain portions of forecasted cash flows denominated in foreign currencies. When the U.S. dollar strengthens against the foreign currencies, the decline in the present value of future foreign currency cash flows is partially offset by gains in the fair value of the derivative instruments. Conversely, when the U.S. dollar weakens, the increase in the present value of future foreign currency cash flows is partially offset by losses in the fair value of the derivative instruments. The total notional value of derivatives that have been designated and qualify for the Company's foreign currency cash flow hedging program as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, was $5,158 million and $3,968 million, respectively.
The Company has entered into commodity futures contracts and other derivative instruments on various commodities to mitigate the price risk associated with forecasted purchases of materials used in our manufacturing process. The derivative instruments have been designated and qualify as part of the Company's commodity cash flow hedging program. The objective of this hedging program is to reduce the variability of cash flows associated with future purchases of certain commodities. The total notional value of derivatives that have been designated and qualify for this program as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, was $26 million and $28 million, respectively.
Our Company monitors our mix of short-term debt and long-term debt. From time to time, we manage our risk to interest rate fluctuations through the use of derivative financial instruments. The Company had no outstanding derivative instruments under this cash flow hedging program as of December 31, 2011 and 2010.
100
The following table presents the pretax impact that changes in the fair values of derivatives designated as cash flow hedges had on AOCI and earnings during the years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009 (in millions):
|
Gain (Loss)
Recognized
in Other
Comprehensive
Income ("OCI")
|
Location of Gain (Loss)
Recognized in Income1
|
Gain (Loss)
Reclassified from
AOCI into Income
(Effective Portion)
|
Gain (Loss)
Recognized in Income
(Ineffective Portion and
Amount Excluded from
Effectiveness Testing)
|
|||||||||||
2011 |
||||||||||||||
Foreign currency contracts |
$ |
3 |
Net operating revenues |
$ |
(231 |
) |
$ |
— |
2 |
|||||
Interest rate locks |
(11 |
) |
Interest expense |
(12 |
) |
(1 |
) |
|||||||
Commodity contracts |
(1 |
) |
Cost of goods sold |
— |
— |
|||||||||
Total |
$ |
(9 |
) |
$ |
(243 |
) |
$ |
(1 |
) |
|||||
2010 |
||||||||||||||
Foreign currency contracts |
$ |
(307 |
) |
Net operating revenues |
$ |
(2 |
) |
$ |
(2 |
) |
||||
Interest rate locks |
— |
Interest expense |
(15 |
) |
— |
|||||||||
Commodity contracts |
1 |
Cost of goods sold |
— |
— |
||||||||||
Total |
$ |
(306 |
) |
$ |
(17 |
) |
$ |
(2 |
) |
|||||
2009 |
||||||||||||||
Foreign currency contracts |
$ |
(59 |
) |
Net operating revenues |
$ |
(62 |
) |
$ |
— |
2 |
||||
Interest rate locks |
— |
Interest expense |
(10 |
) |
4 |
|||||||||
Commodity contracts |
— |
Cost of goods sold |
(47 |
) |
— |
|||||||||
Total |
$ |
(59 |
) |
$ |
(119 |
) |
$ |
4 |
||||||
1 |
The Company records gains and losses reclassified from AOCI in income for the effective portion and ineffective portion, if any, to the same line items in our consolidated statements of income. |
2 |
Includes a de minimis amount of ineffectiveness in the hedging relationship. |
As of December 31, 2011, the Company estimates that it will reclassify into earnings during the next 12 months losses of approximately $102 million from the pretax amount recorded in AOCI as the anticipated cash flows occur.
Fair Value Hedging Strategy
The Company uses interest rate swap agreements designated as fair value hedges to minimize exposure to changes in the fair value of fixed-rate debt that results from fluctuations in benchmark interest rates. The changes in fair values of derivatives designated as fair value hedges and the offsetting changes in fair values of the hedged items are recognized in earnings. As of December 31, 2011, such adjustments increased the carrying value of our long-term debt by $231 million. Refer to Note 10. The changes in fair values of hedges that are determined to be ineffective are immediately recognized in earnings. The total notional value of derivatives that were designated and qualified for the Company's fair value hedging program was $5,700 million and $4,750 million as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
101
The following table summarizes the pretax impact that changes in the fair values of derivatives designated as fair value hedges had on earnings during the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2010 (in millions):
Hedging Instruments and Hedged Items |
Location of Gain (Loss)
Recognized in Income
|
Gain (Loss)
Recognized in Income
|
||
2011 |
||||
Interest rate swaps |
Interest expense |
$ |
343 |
|
Fixed-rate debt |
Interest expense |
(333 |
) |
|
Total |
$ |
10 |
||
2010 |
||||
Interest rate swaps |
Interest expense |
$ |
(97 |
) |
Fixed-rate debt |
Interest expense |
102 |
||
Total |
$ |
5 |
||
Hedges of Net Investments in Foreign Operations Strategy
The Company uses forward contracts to protect the value of our investments in a number of foreign subsidiaries. For derivative instruments that are designated and qualify as hedges of net investments in foreign operations, the changes in fair values of the derivative instruments are recognized in net foreign currency translation gain (loss), a component of AOCI, to offset the changes in the values of the net investments being hedged. Any ineffective portions of net investment hedges are reclassified from AOCI into earnings during the period of change. The total notional value of derivatives under this hedging program as of December 31, 2011, was $1,681 million. The Company had no outstanding derivative instruments under this hedging program as of December 31, 2010.
The following table presents the pretax impact that changes in the fair values of derivatives designated as net investment hedges had on AOCI during the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2010 (in millions):
|
Gain (Loss)
Recognized in OCI
|
|||||||
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
|||||
Foreign currency contracts |
$ |
(3 |
) |
$ |
(15 |
) |
|
The Company did not reclassify any deferred gains or losses related to net investment hedges from AOCI to earnings during the years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009. In addition, the Company did not have any ineffectiveness related to net investment hedges during the years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009.
Economic (Non-Designated) Hedging Strategy
In addition to derivative instruments that are designated and qualify for hedge accounting, the Company also uses certain derivatives as economic hedges of foreign currency and commodity exposure. Although these derivatives were not designated and/or did not qualify for hedge accounting, they are effective economic hedges. The changes in fair value of economic hedges are immediately recognized into earnings.
The Company uses foreign currency economic hedges to offset the earnings impact that fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates have on certain monetary assets and liabilities denominated in nonfunctional currencies. The changes in fair value of economic hedges used to offset the monetary assets and liabilities are recognized into earnings in the line item other income (loss) — net in our consolidated statements of income. In addition, we use foreign currency economic hedges to minimize the variability in cash flows associated with changes in foreign currency exchange rates. The changes in fair value of economic hedges used to offset the variability in U.S. dollar net cash flows are recognized into earnings in the line items net operating revenues and cost of goods sold in our consolidated statements of income. The total notional value of derivatives related to our foreign currency economic hedges as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, was $3,629 million and $2,312 million, respectively.
In 2010, the Company initiated certain commodity hedging programs as a result of our acquisition of CCE's North American business. The Company uses these types of derivatives as economic hedges to mitigate the price risk associated with the purchases of materials used in the manufacturing process and for vehicle fuel. The changes in fair values of these economic hedges are immediately recognized into earnings in the line items cost of goods sold and selling, general and administrative
102
expenses in our consolidated statements of income. The total notional value of derivatives related to our economic hedges of this type as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, was $1,165 million and $425 million, respectively.
In connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business, the Company assumed certain interest rate derivatives. The Company did not designate these derivatives as hedges subsequent to the acquisition. These derivatives were originally recorded at fair value as of October 2, 2010. As of December 31, 2010, all interest rate derivatives acquired from CCE were settled and will have no additional impact on future earnings. In 2010, the Company recorded $5 million of losses related to these instruments in interest expense.
The Company entered into interest rate locks that were used as economic hedges to mitigate the interest rate risk associated with the Company's repurchase of certain long-term debt. These hedges were not designated and did not qualify for hedge accounting, but were effective economic hedges. The Company settled these hedges and recognized losses of $104 million in interest expense during 2010. As of December 31, 2010, there were no outstanding interest rate derivatives used as economic hedges.
The following table presents the pretax impact that changes in the fair values of derivatives not designated as hedging instruments had on earnings during the years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009 (in millions):
Gains (Losses) |
|||||||||||||
|
Derivatives Not Designated
as Hedging Instruments
|
Location of Gains (Losses)
Recognized in Income
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
|||||||||||
Foreign currency contracts |
Net operating revenues |
$ |
7 |
$ |
(15 |
) |
$ |
(16 |
) |
||||
Foreign currency contracts |
Other income (loss) — net |
(37 |
) |
(46 |
) |
114 |
|||||||
Foreign currency contracts |
Cost of goods sold |
(12 |
) |
(9 |
) |
— |
|||||||
Commodity contracts |
Cost of goods sold |
(42 |
) |
40 |
12 |
||||||||
Commodity contracts |
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
(11 |
) |
— |
— |
||||||||
Interest rate swaps |
Interest expense |
— |
(5 |
) |
— |
||||||||
Interest rate locks |
Interest expense |
— |
(104 |
) |
— |
||||||||
Other derivative instruments |
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
8 |
21 |
23 |
|||||||||
Total |
$ |
(87 |
) |
$ |
(118 |
) |
$ |
133 |
|||||
NOTE 6: EQUITY METHOD INVESTMENTS
Our consolidated net income includes our Company's proportionate share of the net income or loss of our equity method investees. When we record our proportionate share of net income, it increases equity income (loss) — net in our consolidated statements of income and our carrying value in that investment. Conversely, when we record our proportionate share of a net loss, it decreases equity income (loss) — net in our consolidated statements of income and our carrying value in that investment. The Company's proportionate share of the net income or loss of our equity method investees includes significant operating and nonoperating items recorded by our equity method investees. These items can have a significant impact on the amount of equity income (loss) — net in our consolidated statements of income and our carrying value in those investments. Refer to Note 17 for additional information related to significant operating and nonoperating items recorded by our equity method investees. The carrying values of our equity method investments are also impacted by our proportionate share of items impacting the equity investee's AOCI.
We eliminate from our financial results all significant intercompany transactions, including the intercompany portion of transactions with equity method investees.
Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc.
On October 2, 2010, we completed our acquisition of CCE's North American business and relinquished our indirect ownership interest in CCE's European operations. As a result of this transaction, the Company does not own any interest in New CCE. Refer to Note 2 for additional information related to this acquisition.
103
We accounted for our investment in CCE under the equity method of accounting until our acquisition of CCE's North American business was completed on October 2, 2010. Therefore, our consolidated net income for the year ended December 31, 2010, included equity income from CCE during the first nine months of 2010. The Company owned 33 percent of the outstanding common stock of CCE immediately prior to the acquisition. The following table provides summarized financial information for CCE for the nine months ended October 1, 2010, and for the year ended December 31, 2009 (in millions):
Nine Months Ended |
Year Ended |
||||||
October 1, 2010 |
December 31, 2009 |
||||||
Net operating revenues |
$ |
16,464 |
$ |
21,645 |
|||
Cost of goods sold |
10,028 |
13,333 |
|||||
Gross profit |
$ |
6,436 |
$ |
8,312 |
|||
Operating income (loss) |
$ |
1,369 |
$ |
1,527 |
|||
Net income (loss) |
$ |
677 |
$ |
731 |
|||
The following table provides a summary of our significant transactions with CCE for the nine months ended October 1, 2010, and for the year ended December 31, 2009 (in millions):
Nine Months Ended |
Year Ended |
||||||
October 1, 2010 |
December 31, 2009 |
||||||
Concentrate, syrup and finished product sales to CCE |
$ |
4,737 |
$ |
6,032 |
|||
Syrup and finished product purchases from CCE |
263 |
351 |
|||||
CCE purchases of sweeteners through our Company |
251 |
419 |
|||||
Marketing payments made by us directly to CCE |
314 |
415 |
|||||
Marketing payments made to third parties on behalf of CCE |
106 |
174 |
|||||
Local media and marketing program reimbursements from CCE |
268 |
330 |
|||||
Payments made to CCE for dispensing equipment repair services |
64 |
87 |
|||||
Other payments — net |
19 |
66 |
|||||
Syrup and finished product purchases from CCE represent purchases of fountain syrup in certain territories that have been resold by our Company to major customers and purchases of bottle and can products. Marketing payments made by us directly to CCE represent support of certain marketing activities and our participation with CCE in cooperative advertising and other marketing activities to promote the sale of Company trademark products within CCE territories. These programs were agreed to on an annual basis. Marketing payments made to third parties on behalf of CCE represent support of certain marketing activities and programs to promote the sale of Company trademark products within CCE's territories in conjunction with certain of CCE's customers. Pursuant to cooperative advertising and trade agreements with CCE, we received funds from CCE for local media and marketing program reimbursements. Payments made to CCE for dispensing equipment repair services represent reimbursement to CCE for its costs of parts and labor for repairs on cooler, dispensing or post-mix equipment owned by us or our customers. The other payments — net line in the table above represents payments made to and received from CCE that are individually insignificant.
Our Company had previously entered into programs with CCE designed to help develop cold-drink infrastructure. Under these programs, we paid CCE for a portion of the cost of developing the infrastructure necessary to support accelerated placements of cold-drink equipment. These payments supported a common objective of increased sales of Company Trademark Beverages from increased availability and consumption in the cold-drink channel.
Preexisting Relationships
The Company evaluated all of our preexisting relationships with CCE prior to the close of the transaction. Based on these evaluations, the Company recognized charges of $265 million in 2010 related to preexisting relationships with CCE. These charges were primarily related to the write-off of our investment in cold-drink infrastructure programs with CCE as our investment in these programs did not meet the criteria to be recognized as an asset subsequent to the acquisition. These charges were included in the line item other income (loss) — net in our consolidated statements of income and impacted the Corporate operating segment. Refer to Note 17.
104
Other Equity Method Investments
Our other equity method investments include our ownership interests in Coca-Cola Hellenic, Coca-Cola FEMSA and Coca-Cola Amatil. As of December 31, 2011, we owned approximately 23 percent, 29 percent and 29 percent, respectively, of these companies' common shares. As of December 31, 2011, our investment in our equity method investees in the aggregate exceeded our proportionate share of the net assets of these equity method investees by $1,575 million. This difference is not amortized.
A summary of financial information for our equity method investees in the aggregate, other than CCE, is as follows (in millions):
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
Net operating revenues |
$ |
42,472 |
$ |
38,663 |
$ |
34,292 |
|||||
Cost of goods sold |
26,271 |
23,053 |
20,205 |
||||||||
Gross profit |
$ |
16,201 |
$ |
15,610 |
$ |
14,087 |
|||||
Operating income |
$ |
4,181 |
$ |
4,134 |
$ |
3,657 |
|||||
Consolidated net income |
$ |
2,237 |
$ |
2,659 |
$ |
2,269 |
|||||
Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests |
99 |
89 |
78 |
||||||||
Net income attributable to common shareowners |
$ |
2,138 |
$ |
2,570 |
$ |
2,191 |
|||||
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
|||||
Current assets |
$ |
13,960 |
$ |
12,223 |
|||
Noncurrent assets |
27,152 |
26,524 |
|||||
Total assets |
$ |
41,112 |
$ |
38,747 |
|||
Current liabilities |
$ |
10,545 |
$ |
9,039 |
|||
Noncurrent liabilities |
11,646 |
11,175 |
|||||
Total liabilities |
$ |
22,191 |
$ |
20,214 |
|||
Shareowners' equity |
$ |
18,392 |
$ |
18,046 |
|||
Noncontrolling interest |
529 |
487 |
|||||
Total equity |
$ |
18,921 |
$ |
18,533 |
|||
Company equity investment |
$ |
7,234 |
$ |
6,954 |
|||
Net sales to equity method investees other than CCE, the majority of which are located outside the United States, were $6.9 billion, $6.2 billion and $5.6 billion in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. Total payments, primarily marketing, made to equity method investees other than CCE were $1,147 million, $1,034 million and $878 million in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. In addition, purchases of finished products from equity method investees other than CCE were $430 million, $205 million and $152 million in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
If valued at the December 31, 2011, quoted closing prices of shares actively traded on stock markets, the value of our equity method investments in publicly traded bottlers would have exceeded our carrying value by $6.2 billion.
Net Receivables and Dividends from Equity Method Investees
Total net receivables due from equity method investees were $1,042 million and $899 million as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively. The total amount of dividends received from equity method investees was $421 million, $354 million and $422 million for the years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. Dividends received included a $60 million and $183 million special dividend from Coca-Cola Hellenic during 2011 and 2009, respectively. We classified the receipt of these cash dividends in cash flows from operating activities due to the fact that our cumulative equity in earnings from Coca-Cola Hellenic exceeded the cumulative distributions received; therefore, the dividends were deemed to be a return on our investment and not a return of our investment.
105
NOTE 7: PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT
The following table summarizes our property, plant and equipment (in millions):
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
|||||
Land |
$ |
1,141 |
$ |
1,122 |
|||
Buildings and improvements |
5,240 |
4,883 |
|||||
Machinery, equipment and vehicle fleet |
14,609 |
13,421 |
|||||
Containers |
895 |
826 |
|||||
Construction in progress |
1,266 |
1,454 |
|||||
23,151 |
21,706 |
||||||
Less accumulated depreciation |
8,212 |
6,979 |
|||||
Property, plant and equipment — net |
$ |
14,939 |
$ |
14,727 |
|||
NOTE 8: INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets
The following table summarizes information related to indefinite-lived intangible assets (in millions):
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
|||||
Trademarks1
|
$ |
6,430 |
$ |
6,356 |
|||
Bottlers' franchise rights2
|
7,770 |
7,511 |
|||||
Goodwill3
|
12,219 |
11,665 |
|||||
Other |
113 |
113 |
|||||
Indefinite-lived intangible assets4
|
$ |
26,532 |
$ |
25,645 |
|||
1 |
The increase in 2011 was primarily related to the acquisition of Honest Tea. Refer to Note 2.
|
2 |
The increase in 2011 was primarily related to the reacquisition of Great Plains' rights to distribute Trademark Coca-Cola beverages in specified territories as well as the finalization of purchase accounting for the Company's 2010 acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to Note 2.
|
3 |
The increase in 2011 was primarily related to the acquisition of Great Plains and Honest Tea as well as the finalization of purchase accounting for the Company's 2010 acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to Note 2.
|
4 |
The distribution rights acquired from DPS are the only significant indefinite-lived intangible assets subject to renewal or extension arrangements. Refer to Note 2.
|
106
The following table provides information related to the carrying value of our goodwill by operating segment (in millions):
|
Eurasia &
Africa
|
Europe |
Latin
America
|
North
America
|
Pacific |
Bottling
Investments
|
Total |
|||||||||||||||||||||
2010 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance as of January 1 |
$ |
43 |
$ |
797 |
$ |
320 |
$ |
2,154 |
$ |
110 |
$ |
800 |
$ |
4,224 |
|||||||||||||
Effect of foreign currency translation |
1 |
(102 |
) |
4 |
— |
2 |
(39 |
) |
(134 |
) |
|||||||||||||||||
Acquisitions1
|
— |
— |
54 |
7,746 |
— |
83 |
7,883 |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Adjustments related to the finalization
of purchase accounting
|
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
||||||||||||||||||||
Divestitures, deconsolidations and other1,2
|
— |
— |
(212 |
) |
(39 |
) |
— |
(57 |
) |
(308 |
) |
||||||||||||||||
Balance as of December 31 |
$ |
44 |
$ |
695 |
$ |
166 |
$ |
9,861 |
$ |
112 |
$ |
787 |
$ |
11,665 |
|||||||||||||
2011 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance as of January 1 |
$ |
44 |
$ |
695 |
$ |
166 |
$ |
9,861 |
$ |
112 |
$ |
787 |
$ |
11,665 |
|||||||||||||
Effect of foreign currency translation |
(6 |
) |
15 |
(3 |
) |
— |
2 |
11 |
19 |
||||||||||||||||||
Acquisitions1
|
— |
— |
— |
195 |
— |
— |
195 |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Adjustments related to the finalization
of purchase accounting1
|
— |
— |
— |
304 |
— |
5 |
309 |
||||||||||||||||||||
Divestitures, deconsolidations and other |
— |
— |
— |
155 |
— |
(124 |
) |
31 |
|||||||||||||||||||
Balance as of December 31 |
$ |
38 |
$ |
710 |
$ |
163 |
$ |
10,515 |
$ |
114 |
$ |
679 |
$ |
12,219 |
|||||||||||||
1 |
Refer to Note 2 for information related to the Company's acquisitions and divestitures.
|
2 |
Refer to Note 1 for information related to the deconsolidation of certain entities as a result of the Company's adoption of new accounting guidance issued by the FASB.
|
Definite-Lived Intangible Assets
The following table summarizes information related to definite-lived intangible assets (in millions):
December 31, 2011 |
December 31, 2010 |
||||||||||||||||||
Gross Carrying Amount |
Accumulated Amortization |
Net |
Gross Carrying Amount |
Accumulated Amortization |
Net |
||||||||||||||
Customer relationships |
$ |
619 |
$ |
(126 |
) |
$ |
493 |
$ |
606 |
$ |
(83 |
) |
$ |
523 |
|||||
Bottlers' franchise rights1
|
668 |
(119 |
) |
549 |
605 |
(22 |
) |
583 |
|||||||||||
Trademarks |
99 |
(70 |
) |
29 |
111 |
(67 |
) |
44 |
|||||||||||
Other2
|
196 |
(130 |
) |
66 |
258 |
(144 |
) |
114 |
|||||||||||
Total |
$ |
1,582 |
$ |
(445 |
) |
$ |
1,137 |
$ |
1,580 |
$ |
(316 |
) |
$ |
1,264 |
|||||
1 |
The increase in 2011 was primarily related to the acquisition of Great Plains and the finalization of purchase accounting for the Company's 2010 acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to Note 2.
|
2 |
The decrease in 2011 was primarily related to the finalization of purchase accounting for certain of the Company's acquisitions and other individually insignificant items. |
Total amortization expense for intangible assets subject to amortization was $192 million, $102 million and $63 million in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. Based on the carrying value of definite-lived intangible assets as of December 31, 2011, we estimate our amortization expense for the next five years will be as follows (in millions):
|
Amortization
Expense
|
||||
2012 |
$ |
160 |
||
2013 |
148 |
|||
2014 |
144 |
|||
2015 |
137 |
|||
2016 |
134 |
|||
107
NOTE 9: ACCOUNTS PAYABLE AND ACCRUED EXPENSES
Accounts payable and accrued expenses consisted of the following (in millions):
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
|||||
Accrued marketing |
$ |
2,286 |
$ |
2,250 |
|||
Other accrued expenses |
2,749 |
2,920 |
|||||
Trade accounts payable |
2,172 |
1,887 |
|||||
Accrued compensation |
1,048 |
1,068 |
|||||
Sales, payroll and other taxes |
405 |
401 |
|||||
Container deposits |
349 |
333 |
|||||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
$ |
9,009 |
$ |
8,859 |
|||
NOTE 10: DEBT AND BORROWING ARRANGEMENTS
Short-Term Borrowings
Loans and notes payable consist primarily of commercial paper issued in the United States. As of December 31, 2011 and 2010, we had $12,135 million and $7,535 million, respectively, in outstanding commercial paper borrowings. Our weighted-average interest rates for commercial paper outstanding were approximately 0.2 percent and 0.3 percent per year as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively. In 2010, the Company assumed $266 million of short-term borrowings in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to Note 2.
In addition, we had $5,685 million in lines of credit and other short-term credit facilities as of December 31, 2011, of which $736 million was outstanding. The outstanding amount was primarily related to our international operations.
Included in the credit facilities discussed above, the Company had $4,625 million in lines of credit for general corporate purposes, including commercial paper backup. These backup lines of credit expire at various times from 2012 through 2016. There were no borrowings under these backup lines of credit during 2011. These credit facilities are subject to normal banking terms and conditions. Some of the financial arrangements require compensating balances, none of which is presently significant to our Company.
Long-Term Debt
During 2011, the Company issued $2,979 million of long-term debt. We used $979 million of this newly issued debt and paid a premium of $208 million to exchange $1,022 million of existing long-term debt that was assumed in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. The remaining cash from the issuance was used to reduce the Company's outstanding commercial paper balance and exchange a certain amount of short-term debt.
The general terms of the notes issued during 2011 are as follows:
• |
$1,655 million total principal amount of notes due September 1, 2016, at a fixed interest rate of 1.8 percent; and
|
• |
$1,324 million total principal amount of notes due September 1, 2021, at a fixed interest rate of 3.3 percent.
|
During the fourth quarter of 2011, the Company extinguished long-term debt that had a carrying value of $20 million and was not scheduled to mature until 2012. This debt was outstanding prior to the Company's acquisition of CCE's North American business. In addition, the Company repurchased long-term debt during 2011 that was assumed in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. The repurchased debt included $99 million in unamortized fair value adjustments recorded as part of our purchase accounting for the CCE transaction and was settled throughout the year as follows:
• |
During the first quarter of 2011, the Company repurchased all of our outstanding U.K. pound sterling notes that had a carrying value of $674 million;
|
• |
During the second quarter of 2011, the Company repurchased long-term debt that had a carrying value of $42 million; and
|
• |
During the third quarter of 2011, the Company repurchased long-term debt that had a carrying value of $19 million.
|
The Company recorded a net charge of $9 million in the line item interest expense in our consolidated statement of income during the year ended December 31, 2011. This net charge was due to the exchange, repurchase and/or extinguishment of long-term debt described above.
During 2010, in connection with the Company's acquisition of CCE's North American business, we assumed $7,602 million of long-term debt, which had an estimated fair value of approximately $9,345 million as of the acquisition date. We recorded the
108
assumed debt at its fair value as of the acquisition date. Refer to Note 2.
On November 15, 2010, the Company issued $4,500 million of long-term notes and used some of the proceeds to repurchase $2,910 million of long-term debt. The remaining cash from the issuance was used to reduce our outstanding commercial paper balance. The repurchased debt consisted of $1,827 million of debt assumed in our acquisition of CCE's North American business and $1,083 million of the Company's debt that was outstanding prior to the acquisition. The Company recorded a charge of $342 million in interest expense related to the premiums paid to repurchase the long-term debt and the costs associated with the settlement of treasury rate locks issued in connection with the debt tender offer. The general terms of the notes issued on November 15, 2010, were as follows:
• |
$1,250 million total principal amount of notes due May 15, 2012, at a variable interest rate of 3 month LIBOR plus 0.05 percent;
|
• |
$1,250 million total principal amount of notes due November 15, 2013, at a fixed interest rate of 0.75 percent;
|
• |
$1,000 million total principal amount of notes due November 15, 2015, at a fixed interest rate of 1.5 percent; and
|
• |
$1,000 million total principal amount of notes due November 15, 2020, at a fixed interest rate of 3.15 percent.
|
Subsequent to the repurchase of a portion of the long-term debt assumed from CCE, the general terms of the debt assumed and remaining outstanding as of December 31, 2010, were as follows:
• |
$2,594 million total principal amount of U.S. dollar notes due 2011 to 2037 at an average interest rate of 5.7 percent;
|
• |
$2,288 million total principal amount of U.S. dollar debentures due 2012 to 2098 at an average interest rate of 7.4 percent;
|
• |
$275 million total principal amount of U.S. dollar notes due 2011 at a variable interest rate of 1.0 percent;
|
• |
$544 million total principal amount of U.K. pound sterling notes due 2016 and 2021 at an average interest rate of 6.5 percent;
|
• |
$303 million principal amount of U.S. dollar zero coupon notes due 2020; and
|
• |
$26 million of other long-term debt.
|
On March 6, 2009, the Company issued $2,250 million of long-term notes and used the proceeds to replace a certain amount of commercial paper and short-term debt with long-term debt. The general terms of these notes were as follows:
• |
$900 million total principal amount of notes due March 15, 2014, at a fixed interest rate of 3.625 percent; and
|
• |
$1,350 million total principal amount of notes due March 15, 2019, at a fixed interest rate of 4.875 percent.
|
The Company's long-term debt consisted of the following (in millions, except average rate data):
December 31, 2011 |
December 31, 2010 |
||||||||||||
Amount |
Average
Rate 1
|
Amount |
Average
Rate1
|
||||||||||
U.S. dollar notes due 2012–2093 |
$ |
12,270 |
1.9 |
% |
$ |
11,195 |
1.8 |
% |
|||||
U.S. dollar debentures due 2012–2098 |
2,482 |
4.0 |
2,946 |
3.9 |
|||||||||
U.S. dollar zero coupon notes due 20202
|
130 |
8.4 |
222 |
8.4 |
|||||||||
U.K. pound sterling notes due 2016 and 2021 |
— |
— |
652 |
6.5 |
|||||||||
Other, due through 20983
|
584 |
4.8 |
404 |
5.0 |
|||||||||
Fair value adjustment4
|
231 |
N/A |
(102 |
) |
N/A |
||||||||
Total5,6
|
$ |
15,697 |
2.3 |
% |
$ |
15,317 |
2.6 |
% |
|||||
Less current portion |
2,041 |
1,276 |
|||||||||||
Long-term debt |
$ |
13,656 |
$ |
14,041 |
|||||||||
1 |
These rates represent the weighted-average effective interest rate on the balances outstanding as of year end, as adjusted for the effects of interest rate swap agreements as well as fair value adjustments, if applicable. Refer to Note 5 for a more detailed discussion on interest rate management.
|
2 |
This amount is shown net of unamortized discounts of $41 million and $81 million as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
|
3 |
As of December 31, 2011, the amount shown includes $372 million of debt instruments that are due through 2020.
|
4 |
Refer to Note 5 for additional information about our fair value hedging strategy.
|
5 |
As of December 31, 2011 and 2010, the fair value of our long-term debt, including the current portion, was $16,360 million and $16,218 million, respectively. The fair value of our long-term debt is estimated based on quoted prices for those or similar instruments.
|
6 |
The above notes and debentures include various restrictions, none of which is presently significant to our Company. |
109
The carrying value of the Company's long-term debt included fair value adjustments related to the debt assumed from CCE of $733 million and $994 million as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively. These fair value adjustments will be amortized over a weighted-average period of approximately 16 years, which is equal to the weighted-average maturity of the assumed debt to which these fair value adjustments relate. The amortization of these fair value adjustments will be a reduction of interest expense in future periods, which will typically result in our interest expense being less than the actual interest paid to service the debt. Total interest paid was $573 million, $422 million and $346 million in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
Maturities of long-term debt for the five years succeeding December 31, 2011, are as follows (in millions):
|
Maturities of
Long-Term Debt
|
|||
2012 |
$ |
2,041 |
|
2013 |
1,515 |
||
2014 |
1,690 |
||
2015 |
1,462 |
||
2016 |
1,707 |
||
NOTE 11: COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Guarantees
As of December 31, 2011, we were contingently liable for guarantees of indebtedness owed by third parties of $654 million, of which $321 million was related to VIEs. Refer to Note 1 for additional information related to the Company's maximum exposure to loss due to our involvement with VIEs. Our guarantees are primarily related to third-party customers, bottlers, vendors and container manufacturing operations and have arisen through the normal course of business. These guarantees have various terms, and none of these guarantees was individually significant. The amount represents the maximum potential future payments that we could be required to make under the guarantees; however, we do not consider it probable that we will be required to satisfy these guarantees.
We believe our exposure to concentrations of credit risk is limited due to the diverse geographic areas covered by our operations.
Legal Contingencies
The Company is involved in various legal proceedings. We establish reserves for specific legal proceedings when we determine that the likelihood of an unfavorable outcome is probable and the amount of loss can be reasonably estimated. Management has also identified certain other legal matters where we believe an unfavorable outcome is reasonably possible and/or for which no estimate of possible losses can be made. Management believes that the total liabilities to the Company that may arise as a result of currently pending legal proceedings will not have a material adverse effect on the Company taken as a whole.
During the period from 1970 to 1981, our Company owned Aqua-Chem, Inc., now known as Cleaver-Brooks, Inc. ("Aqua-Chem"). During that time, the Company purchased over $400 million of insurance coverage, which also insures Aqua-Chem for some of its prior and future costs for certain product liability and other claims. A division of Aqua-Chem manufactured certain boilers that contained gaskets that Aqua-Chem purchased from outside suppliers. Several years after our Company sold this entity, Aqua-Chem received its first lawsuit relating to asbestos, a component of some of the gaskets. Aqua-Chem was first named as a defendant in asbestos lawsuits in or around 1985 and currently has approximately 40,000 active claims pending against it. In September 2002, Aqua-Chem notified our Company that it believed we were obligated for certain costs and expenses associated with its asbestos litigations. Aqua-Chem demanded that our Company reimburse it for approximately $10 million for out-of-pocket litigation-related expenses. Aqua-Chem also demanded that the Company acknowledge a continuing obligation to Aqua-Chem for any future liabilities and expenses that are excluded from coverage under the applicable insurance or for which there is no insurance. Our Company disputes Aqua-Chem's claims, and we believe we have no obligation to Aqua-Chem for any of its past, present or future liabilities, costs or expenses. Furthermore, we believe we have substantial legal and factual defenses to Aqua-Chem's claims. The parties entered into litigation in Georgia to resolve this dispute, which was stayed by agreement of the parties pending the outcome of litigation filed in Wisconsin by certain insurers of Aqua-Chem. In that case, five plaintiff insurance companies filed a declaratory judgment action against Aqua-Chem, the Company and 16 defendant insurance companies seeking a determination of the parties' rights and liabilities under policies issued by the insurers and reimbursement for amounts paid by plaintiffs in excess of their obligations. During the course of the Wisconsin insurance coverage litigation, Aqua-Chem and the Company reached settlements with several of the insurers, including plaintiffs, who have or will pay funds into an escrow account for payment of costs arising from the asbestos claims against Aqua-Chem. On
110
July 24, 2007, the Wisconsin trial court entered a final declaratory judgment regarding the rights and obligations of the parties under the insurance policies issued by the remaining defendant insurers, which judgment was not appealed. The judgment directs, among other things, that each insurer whose policy is triggered is jointly and severally liable for 100 percent of Aqua-Chem's losses up to policy limits. The court's judgment concluded the Wisconsin insurance coverage litigation. The Georgia litigation remains subject to the stay agreement. The Company and Aqua-Chem continued to negotiate with various insurers that were defendants in the Wisconsin insurance coverage litigation over those insurers' obligations to defend and indemnify Aqua-Chem for the asbestos-related claims. The Company anticipated that a final settlement with three of those insurers would be finalized in May 2011, but such insurers repudiated their settlement commitments and, as a result, Aqua-Chem and the Company filed suit against them in Wisconsin state court to enforce the coverage-in-place settlement or, in the alternative, to obtain a declaratory judgment validating Aqua-Chem and the Company's interpretation of the court's judgment in the Wisconsin insurance coverage litigation. Whether or not Aqua-Chem and the Company prevail in the coverage-in-place settlement litigation, these three insurance companies will remain subject to the court's judgment in the Wisconsin insurance coverage litigation.
The Company is unable to estimate at this time the amount or range of reasonably possible loss it may ultimately incur as a result of asbestos-related claims against Aqua-Chem. The Company believes that assuming (a) the defense and indemnity costs for the asbestos-related claims against Aqua-Chem in the future are in the same range as during the past five years, and (b) the various insurers that cover the asbestos-related claims against Aqua-Chem remain solvent, regardless of the outcome of the coverage-in-place settlement litigation, there will likely be little defense or indemnity costs that are not covered by insurance over the next five to seven years and, therefore, it is unlikely that Aqua-Chem would seek indemnification from the Company within that period of time. In the event Aqua-Chem and the Company prevail in the coverage-in-place settlement litigation, and based on the same assumptions, the Company believes insurance coverage for substantially all defense and indemnity costs would be available for the next 10 to 12 years.
Indemnifications
At the time we acquire or divest our interest in an entity, we sometimes agree to indemnify the seller or buyer for specific contingent liabilities. Management believes that any liability to the Company that may arise as a result of any such indemnification agreements will not have a material adverse effect on the Company taken as a whole.
Tax Audits
The Company is involved in various tax matters, with respect to some of which the outcome is uncertain. These audits may result in the assessment of additional taxes that are subsequently resolved with authorities or potentially through the courts. Refer to Note 14.
Risk Management Programs
The Company has numerous global insurance programs in place to help protect the Company from the risk of loss. In general, we are self-insured for large portions of many different types of claims; however, we do use commercial insurance above our self-insured retentions to reduce the Company's risk of catastrophic loss. Our reserves for the Company's self-insured losses are estimated through actuarial procedures of the insurance industry and by using industry assumptions, adjusted for our specific expectations based on our claim history. The Company's self-insurance reserves totaled $527 million and $502 million as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
Workforce (Unaudited)
We refer to our employees as "associates." As of December 31, 2011, our Company had approximately 146,200 associates, of which approximately 67,400 associates were located in the United States. Our Company, through its divisions and subsidiaries, is a party to numerous collective bargaining agreements. As of December 31, 2011, approximately 19,000 associates in North America were covered by collective bargaining agreements. These agreements typically have terms of three to five years. We currently expect that we will be able to renegotiate such agreements on satisfactory terms when they expire. The Company believes that its relations with its associates are generally satisfactory.
111
Operating Leases
The following table summarizes our minimum lease payments under noncancelable operating leases with initial or remaining lease terms in excess of one year as of December 31, 2011 (in millions):
Years Ending December 31, |
Operating Lease Payments |
||
2012 |
$ |
241 |
|
2013 |
174 |
||
2014 |
133 |
||
2015 |
101 |
||
2016 |
78 |
||
Thereafter |
270 |
||
Total minimum operating lease payments1
|
$ |
997 |
|
1 |
Income associated with sublease arrangements is not significant. |
NOTE 12: STOCK COMPENSATION PLANS
Our Company grants stock options and restricted stock awards to certain employees of the Company. Total stock-based compensation expense was $354 million, $380 million and $241 million in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively, and was included as a component of selling, general and administrative expenses in our consolidated statements of income. The total income tax benefit recognized in our consolidated statements of income related to stock-based compensation arrangements was $99 million, $110 million and $68 million in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
As of December 31, 2011, we had $516 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to nonvested stock-based compensation arrangements granted under our plans. This cost is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.8 years as stock-based compensation expense. This expected cost does not include the impact of any future stock-based compensation awards.
As a result of our acquisition of CCE's North American business, the Company assumed certain stock-based compensation plans previously sponsored by CCE. Shares from these plans remain available for future grant to current employees who were employees of CCE or its subsidiaries prior to the acquisition or who are hired by the Company or its subsidiaries following the acquisition. The assumed Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. 2001 Stock Option Plan, Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. 2004 Stock Award Plan and Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. 2007 Incentive Award Plan previously sponsored by CCE have approximately 14 million shares available for grant after conversion of CCE common stock into our common stock. The Company has not granted any equity awards from the assumed plans.
Stock Option Plans
The fair value of our stock option grants is amortized over the vesting period, generally four years. The fair value of each option award is estimated on the grant date using a Black-Scholes-Merton option-pricing model. The weighted-average fair value of options granted during the past three years and the weighted-average assumptions used in the Black-Scholes-Merton option-pricing model for such grants were as follows:
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
|||||||||
Fair value of options at grant date |
$ |
9.28 |
$ |
9.39 |
$ |
6.38 |
|||||
Dividend yield1
|
2.7 |
% |
2.9 |
% |
3.4 |
% |
|||||
Expected volatility2
|
19.0 |
% |
20.0 |
% |
20.0 |
% |
|||||
Risk-free interest rate3
|
2.3 |
% |
3.0 |
% |
2.8 |
% |
|||||
Expected term of the option4
|
5 years |
6 years |
6 years |
||||||||
1 |
The dividend yield is the calculated yield on the Company's stock at the time of the grant. |
2 |
Expected volatility is based on implied volatilities from traded options on the Company's stock, historical volatility of the Company's stock and other factors. |
3 |
The risk-free interest rate for the period matching the expected term of the option is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of the grant. |
4 |
The expected term of the option represents the period of time that options granted are expected to be outstanding and is derived by analyzing historic exercise behavior. |
112
Generally, stock options granted from 1999 through July 2003 expire 15 years from the date of grant and stock options granted in December 2003 and thereafter expire 10 years from the date of grant. The shares of common stock to be issued, transferred and/or sold under the stock option plans are made available from authorized and unissued Company common stock or from the Company's treasury shares. In 2007, the Company began issuing common stock under these plans from the Company's treasury shares. The Company had the following active stock option plans as of December 31, 2011:
• |
The Coca-Cola Company 1999 Stock Option Plan (the "1999 Option Plan") was approved by shareowners in April 1999. Under the 1999 Option Plan, a maximum of 120 million shares of our common stock was approved to be issued or transferred, through the grant of stock options, to certain officers and employees.
|
• |
The Coca-Cola Company 2002 Stock Option Plan (the "2002 Option Plan") was approved by shareowners in April 2002. An amendment to the 2002 Option Plan which permitted the issuance of stock appreciation rights was approved by shareowners in April 2003. Under the 2002 Option Plan, a maximum of 120 million shares of our common stock was approved to be issued or transferred, through the grant of stock options or stock appreciation rights, to certain officers and employees. No stock appreciation rights have been issued under the 2002 Option Plan as of December 31, 2011.
|
• |
The Coca-Cola Company 2008 Stock Option Plan (the "2008 Option Plan") was approved by shareowners in April 2008. Under the 2008 Option Plan, a maximum of 140 million shares of our common stock was approved to be issued or transferred to certain officers and employees pursuant to stock options granted under the 2008 Option Plan.
|
• |
As of December 31, 2011, there were 90 million shares available to be granted under the stock option plans discussed above. Options to purchase common stock under all of these plans have generally been granted at fair market value at the date of grant.
|
Stock option activity for all stock option plans for the year ended December 31, 2011, was as follows:
|
Shares
(In millions)
|
Weighted-Average
Exercise Price
|
Weighted-Average
Remaining
Contractual Life
|
Aggregate
Intrinsic Value
(In millions)
|
|||||||||
Outstanding on January 1, 2011 |
171 |
$ |
48.77 |
|||||||||
Granted |
26 |
64.03 |
||||||||||
Exercised |
(32 |
) |
47.96 |
|||||||||
Forfeited/expired |
(3 |
) |
53.77 |
|||||||||
Outstanding on December 31, 20111
|
162 |
$ |
51.23 |
5.93 years |
$ |
3,028 |
||||||
Expected to vest at December 31, 2011 |
160 |
$ |
51.13 |
5.90 years |
$ |
3,009 |
||||||
Exercisable on December 31, 2011 |
106 |
$ |
48.65 |
4.76 years |
$ |
2,266 |
||||||
1 |
Includes 3 million stock option replacement awards in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business in 2010. These options had a weighted-average exercise price of $36.98, which generally vest over three years and expire 10 years from the original date of grant.
|
The total intrinsic value of the options exercised was $631 million, $524 million and $146 million in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. The total shares exercised were 32 million, 37 million and 15 million in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
Restricted Stock Award Plans
Under The Coca-Cola Company 1989 Restricted Stock Award Plan and The Coca-Cola Company 1983 Restricted Stock Award Plan (the "Restricted Stock Award Plans"), 40 million and 24 million shares of restricted common stock, respectively, were originally available to be granted to certain officers and key employees of our Company. As of December 31, 2011, 19 million shares remain available for grant under the Restricted Stock Award Plans. The Company issues restricted stock to employees as a result of performance share unit awards, time-based awards and performance-based awards.
For awards prior to January 1, 2008, under the 1983 Restricted Stock Award Plan, participants are reimbursed by our Company for income taxes imposed on the award, but not for taxes generated by the reimbursement payment. The 1983 Restricted Stock Award Plan has been amended to eliminate this tax reimbursement for awards after January 1, 2008. The shares are subject to certain transfer restrictions and may be forfeited if a participant leaves our Company for reasons other than retirement, disability or death, absent a change in control of our Company.
113
Performance Share Unit Awards
In 2003, the Company established a program to grant performance share units under The Coca-Cola Company 1989 Restricted Stock Award Plan to executives. In 2008, the Company expanded the program to award a mix of stock options and performance share units to eligible employees in addition to executives. The number of shares earned is determined at the end of each performance period, generally three years, based on the actual performance criteria predetermined by the Board of Directors at the time of grant. If the performance criteria are met, the award results in a grant of restricted stock or restricted stock units, which are then generally subject to a holding period in order for the restricted stock to be released. For performance share units granted before 2008, this holding period is generally two years. For performance share units granted in 2008 and after, this holding period is generally one year. Restrictions on such stock generally lapse at the end of the holding period. Performance share units generally do not pay dividends or allow voting rights during the performance period. Participants generally only receive dividends or dividend equivalents once the performance criteria have been certified and the restricted stock or restricted stock units have been issued. Accordingly, the fair value of these units is the quoted market value of the Company stock on the grant date less the present value of the expected dividends not received during the performance period. In the period it becomes probable that the performance criteria specified in the plan will be achieved, we recognize expense for the proportionate share of the total fair value of the performance share units related to the vesting period that has already lapsed. The remaining cost of the grant is expensed on a straight-line basis over the balance of the vesting period.
Performance share units under The Coca-Cola Company 1989 Restricted Stock Award Plan require achievement of certain financial measures, primarily compound annual growth in earnings per share or economic profit. These financial measures are adjusted for certain items approved and certified by the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors. The purpose of these adjustments is to ensure a consistent year to year comparison of the specific performance criteria. Economic profit is our net operating profit after tax less the cost of the capital used in our business. In the event the financial results equal the predefined target, the Company will grant the number of restricted shares equal to the target award in the underlying performance share unit agreements. In the event the financial results exceed the predefined target, additional shares up to the maximum award may be granted. In the event the financial results fall below the predefined target, a reduced number of shares may be granted. If the financial result falls below the threshold award performance level, no shares will be granted. Performance share units are generally settled in stock, except for certain circumstances such as death or disability, where former employees or their beneficiaries are provided a cash equivalent payment. As of December 31, 2011, performance share units of 2,716,000 and 2,967,000 were outstanding for the 2010-2012 and 2011-2013 performance periods, respectively, based on the target award amounts in the performance share unit agreements.
The following table summarizes information about performance share units based on the target award amounts in the performance share unit agreements:
|
Share Units
(In thousands)
|
Weighted-Average
Grant-Date
Fair Value
|
|||||
Outstanding on January 1, 2011 |
5,254 |
$ |
51.60 |
|||
Granted |
3,054 |
51.16 |
||||
Conversions: |
||||||
Restricted stock units1,2
|
(2,311 |
) |
53.08 |
|||
Paid in cash equivalent |
(10 |
) |
53.13 |
|||
Canceled/forfeited |
(304 |
) |
50.56 |
|||
Outstanding on December 31, 20113
|
5,683 |
$ |
50.81 |
|||
1 |
Represents the target amount of performance share units converted to restricted stock units based on the financial results for the 2008-2010 performance period. The vesting of restricted stock units is subject to the terms of the performance share unit agreements. |
2 |
The performance share unit conversions during 2011 are presented at the target award amount. An additional 173,360 restricted stock units were awarded during 2011 based on the financial results of the 2008-2010 performance period.
|
3 |
The outstanding performance share units as of December 31, 2011, at the threshold award and maximum award levels were 2.8 million and 8.5 million, respectively.
|
The Company converted performance share units of 9,731 in 2011, 13,825 in 2010 and 20,958 in 2009 to cash equivalent payments of $0.7 million, $0.7 million and $1.1 million, respectively, to former executives who were ineligible for restricted stock grants due to certain events such as death, disability or termination.
114
The following table summarizes information about the conversions of performance share units to restricted stock and restricted stock units:
|
Share Units
(In thousands)
|
Weighted-Average
Grant-Date
Fair Value1
|
|||||
Nonvested on January 1, 2011 |
797 |
$ |
43.29 |
|||
Granted: |
||||||
Restricted stock units2
|
2,311 |
53.08 |
||||
Vested and released |
(1,024 |
) |
45.72 |
|||
Canceled/forfeited |
(17 |
) |
43.71 |
|||
Nonvested on December 31, 20113
|
2,067 |
$ |
53.05 |
|||
1 |
The weighted-average grant-date fair value is based on the fair values of the performance share units grant fair values. |
2 |
The granted shares are presented at the performance share units target award amount. An additional 173,360 restricted stock units were granted based on the financial results of the 2008-2010 performance period.
|
3 |
The nonvested shares as of December 31, 2011, are presented at the performance share units target award amount. An additional 154,500 shares were outstanding and nonvested as of December 31, 2011.
|
The total intrinsic value of restricted shares that were vested and released was $72 million, $58 million and $66 million in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. The total restricted share units vested and released were 1,042,456 in 2011, which included 1,023,597 of shares released at the target award amount. In 2010 and 2009, the total restricted share units vested and released were 925,233 and 1,269,604, respectively.
Replacement performance share unit awards issued by the Company in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business are not included in the tables or discussions above and were originally granted under the Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. 2007 Incentive Award Plan. Refer to Note 2. These awards were converted into equivalent share units of the Company's common stock on the acquisition date, and entitle the participant to dividend equivalents (which vest, in some cases, only if the restricted share units vest), but not the right to vote. Accordingly, the fair value of these units was the quoted value of the Company's stock at the grant date. The number of shares earned is determined at the end of each performance period, generally one to three years, based on the actual performance criteria predetermined at the time of grant. These performance share units require achievement of certain financial measures, primarily compound annual growth in earnings per share, as adjusted for certain items detailed in the plan documents. In the event the financial results exceed the predefined targets, additional shares up to a maximum of 200 percent of target may be granted. In the event the financial results fall below the predefined targets, a reduced number of shares may be granted. If the financial results fall below the minimum award performance level, no shares will be granted.
On the acquisition date, the Company issued 1.6 million replacement performance share unit awards at target with a weighted average grant-date price of $59.12 per share unit for the 2008-2010, 2009 and 2010 performance periods. The 2008-2010 and the 2010 performance period awards were projected to pay out at 200 percent on the acquisition date and were certified as such in February 2011. The 2009 award was already certified at 200 percent prior to the acquisition date. In accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, the portion of the fair value of the replacement awards related to services provided prior to the business combination was included in the total purchase price. Refer to Note 2. The portion of the fair value associated with future service is recognized as expense over the future service period. However, in the fourth quarter of 2010, the Company modified primarily all of these performance awards to eliminate the remaining holding period after December 31, 2010, which resulted in $74 million of accelerated expense included in the total stock-based compensation expense above. As a result of this modification, the Company released 1.4 million shares at the 200 percent payout for the 2009 performance period award during the fourth quarter of 2010. The intrinsic value of the release of these shares was $91 million. In addition, the Company released 1.5 million shares at the 200 percent payout, primarily related to the 2008-2010 and 2010 performance periods during 2011. The intrinsic value of the release of these shares was $98 million. As of December 31, 2011, the Company had outstanding replacement performance share units of 0.3 million at the 200 percent payout primarily for the 2009 performance period. The majority of the remaining shares are scheduled for release in the second quarter of 2012.
Time-Based and Performance-Based Restricted Stock and Restricted Stock Unit Awards
The Coca-Cola Company 1989 Restricted Stock Award Plan allows for the grant of time-based and performance-based restricted stock and restricted stock units. The performance-based restricted awards are released only upon the achievement of specific measurable performance criteria. These awards pay dividends during the performance period. The majority of awards
115
have specific performance targets for achievement. If the performance targets are not met, the awards will be canceled. In the period it becomes probable that the performance criteria will be achieved, we recognize expense for the proportionate share of the total fair value of the grant related to the vesting period that has already lapsed. The remaining cost of the grant is expensed on a straight-line basis over the balance of the vesting period.
For time-based and performance-based restricted stock awards, participants are entitled to vote and receive dividends on the restricted shares. The Company also awards time-based and performance-based restricted stock units for which participants receive payments of dividend equivalents but are not entitled to vote. As of December 31, 2011, the Company had outstanding nonvested time-based and performance-based restricted stock awards, including restricted stock units, of 367,000 and 130,000, respectively. Time-based and performance-based restricted awards were not significant to our consolidated financial statements.
In 2010, the Company issued time-based restricted stock unit replacement awards in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to Note 2. These awards were converted into equivalent shares of the Company's common stock. These restricted share awards entitle the participant to dividend equivalents (which vest, in some cases, only if the restricted share unit vests), but not the right to vote. As of December 31, 2011, the Company had outstanding nonvested shares of time-based restricted stock unit replacement awards of 309,000. These time-based restricted stock unit awards were not significant to our consolidated financial statements.
NOTE 13: PENSION AND OTHER POSTRETIREMENT BENEFIT PLANS
Our Company sponsors and/or contributes to pension and postretirement health care and life insurance benefit plans covering substantially all U.S. employees. We also sponsor nonqualified, unfunded defined benefit pension plans for certain associates. In addition, our Company and its subsidiaries have various pension plans and other forms of postretirement arrangements outside the United States.
As part of the Company's acquisition of CCE's North American business, we assumed certain liabilities related to pension and other postretirement benefit plans. Refer to Note 2 for additional information related to this acquisition. These liabilities relate to various pension, retiree medical and defined contribution plans (referred to herein as the "assumed plans"). The assumed plans include participation in multi-employer pension plans in the U.S. See discussion of multi-employer plans below.
We refer to the funded defined benefit pension plans in the U.S. that are not associated with collective bargaining organizations as the "primary U.S. plans." The primary U.S. plans include both the Company's existing pension plan as well as one of the pension plans assumed in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. As of December 31, 2011, the primary U.S. plans represented 58 percent and 60 percent of the Company's consolidated projected pension benefit obligation and pension assets, respectively.
116
Obligations and Funded Status
The following table sets forth the changes in benefit obligations and the fair value of plan assets for our benefit plans (in millions):
Pension Benefits
|
Other Benefits
|
||||||||||||||
2011 |
2010 |
2011 |
2010 |
||||||||||||
Benefit obligation at beginning of year1
|
$ |
7,292 |
$ |
3,996 |
$ |
889 |
$ |
483 |
|||||||
Service cost |
249 |
143 |
32 |
24 |
|||||||||||
Interest cost |
391 |
260 |
45 |
30 |
|||||||||||
Foreign currency exchange rate changes |
30 |
(80 |
) |
2 |
— |
||||||||||
Amendments |
(57 |
) |
(6 |
) |
(12 |
) |
— |
||||||||
Actuarial loss (gain) |
773 |
109 |
45 |
1 |
|||||||||||
Benefits paid2
|
(440 |
) |
(249 |
) |
(63 |
) |
(37 |
) |
|||||||
Business combinations3
|
— |
3,163 |
— |
381 |
|||||||||||
Divestitures4
|
— |
(24 |
) |
— |
— |
||||||||||
Settlements |
(24 |
) |
(22 |
) |
— |
— |
|||||||||
Curtailments |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|||||||||||
Special termination benefits |
8 |
— |
3 |
1 |
|||||||||||
Other |
33 |
2 |
12 |
6 |
|||||||||||
Benefit obligation at end of year1
|
$ |
8,255 |
$ |
7,292 |
$ |
953 |
$ |
889 |
|||||||
Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year |
$ |
5,497 |
$ |
3,032 |
$ |
187 |
$ |
173 |
|||||||
Actual return on plan assets |
73 |
445 |
(4 |
) |
16 |
||||||||||
Employer contributions |
1,001 |
77 |
— |
— |
|||||||||||
Foreign currency exchange rate changes |
(1 |
) |
(59 |
) |
— |
— |
|||||||||
Benefits paid |
(374 |
) |
(193 |
) |
(1 |
) |
(6 |
) |
|||||||
Business combinations3
|
— |
2,231 |
— |
— |
|||||||||||
Divestitures4
|
— |
(18 |
) |
— |
— |
||||||||||
Settlements |
(27 |
) |
(20 |
) |
— |
— |
|||||||||
Other |
2 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|||||||||||
Fair value of plan assets at end of year |
$ |
6,171 |
$ |
5,497 |
$ |
185 |
$ |
187 |
|||||||
Net liability recognized |
$ |
(2,084 |
) |
$ |
(1,795 |
) |
$ |
(768 |
) |
$ |
(702 |
) |
|||
1 |
For pension benefit plans, the benefit obligation is the projected benefit obligation. For other benefit plans, the benefit obligation is the accumulated postretirement benefit obligation. The accumulated benefit obligation for our pension plans was $7,958 million and $6,949 million as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
|
2 |
Benefits paid to pension plan participants during 2011 and 2010 included $66 million and $56 million, respectively, in payments related to unfunded pension plans that were paid from Company assets. Benefits paid to participants of other benefit plans during 2011 and 2010 included $62 million and $31 million, respectively, that were paid from Company assets.
|
3 |
Related to the acquisition of CCE's North American business during the fourth quarter of 2010. Refer to Note 2.
|
4 |
Primarily related to the sale of our Norwegian bottling operation to New CCE during the fourth quarter of 2010. Refer to Note 2.
|
Pension and other benefit amounts recognized in our consolidated balance sheets are as follows (in millions):
Pension Benefits
|
Other Benefits
|
||||||||||||||
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2011 |
2010 |
|||||||||||
Noncurrent asset |
$ |
468 |
$ |
66 |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
|||||||
Current liability |
(68 |
) |
(55 |
) |
(21 |
) |
(21 |
) |
|||||||
Long-term liability |
(2,484 |
) |
(1,806 |
) |
(747 |
) |
(681 |
) |
|||||||
Net liability recognized |
$ |
(2,084 |
) |
$ |
(1,795 |
) |
$ |
(768 |
) |
$ |
(702 |
) |
|||
117
Effective January 1, 2010, the Company's existing primary U.S. pension plan was transitioned from a traditional final average pay formula to a cash balance formula. In general, employees may receive credits based on age, service, pay and interest under the new method. The primary pension plan acquired by the Company in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business transitioned to a cash balance formula in 2011.
Certain of our pension plans have projected benefit obligations in excess of the fair value of plan assets. For these plans, the projected benefit obligations and the fair value of plan assets were as follows (in millions):
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
|||||
Projected benefit obligation |
$ |
7,591 |
$ |
7,024 |
|||
Fair value of plan assets |
5,048 |
5,172 |
|||||
Certain of our pension plans have accumulated benefit obligations in excess of the fair value of plan assets. For these plans, the accumulated benefit obligations and the fair value of plan assets were as follows (in millions):
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
|||||
Accumulated benefit obligation |
$ |
7,277 |
$ |
6,503 |
|||
Fair value of plan assets |
4,998 |
4,981 |
|||||
Pension Plan Assets
The following table presents total assets for our U.S. and non-U.S. pension plans (in millions):
U.S. Plans
|
Non-U.S. Plans
|
||||||||||||||
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2011 |
2010 |
|||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ |
104 |
$ |
88 |
$ |
123 |
$ |
38 |
|||||||
Equity securities: |
|||||||||||||||
U.S.-based companies |
1,362 |
1,324 |
33 |
30 |
|||||||||||
International-based companies |
630 |
631 |
323 |
107 |
|||||||||||
Fixed-income securities: |
|||||||||||||||
Government bonds |
358 |
268 |
415 |
163 |
|||||||||||
Corporate bonds and debt securities |
669 |
625 |
49 |
20 |
|||||||||||
Mutual, pooled and commingled funds1
|
323 |
431 |
406 |
700 |
|||||||||||
Hedge funds/limited partnerships |
458 |
415 |
31 |
23 |
|||||||||||
Real estate |
256 |
230 |
14 |
12 |
|||||||||||
Other |
114 |
106 |
503 |
286 |
|||||||||||
Total pension plan assets2
|
$ |
4,274 |
$ |
4,118 |
$ |
1,897 |
$ |
1,379 |
|||||||
1 |
Mutual, pooled and commingled funds include investments in equity securities, fixed-income securities and combinations of both. There are a significant number of mutual and pooled funds from which investors can choose. The selection of the type of fund is dictated by the specific investment objectives and needs of a given plan. These objectives and needs vary greatly between plans. |
2 |
Fair value disclosures related to our pension assets are included in Note 16. Fair value disclosures include, but are not limited to, the levels within the fair value hierarchy on which the fair value measurements in their entirety fall, a reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances of Level 3 assets and information about the valuation techniques and inputs used to measure the fair value of our pension and other postretirement assets.
|
Investment Strategy for U.S. Pension Plans
In 2010, our U.S. pension plan assets increased significantly as a result of our acquisition of CCE's North American business. The Company has since aligned the investment strategy of the combined assets to provide an allocation that supports the Company's investment goals for pension assets. Our investment strategies are described below.
The Company utilizes the services of investment managers to actively manage the pension assets of our primary U.S. plans. We have established asset allocation targets and investment guidelines with each investment manager. Our asset allocation targets promote optimal expected return and volatility characteristics given the long-term time horizon for fulfilling the obligations of the plan. Selection of the targeted asset allocation for U.S. plan assets was based upon a review of the expected return and risk
118
characteristics of each asset class, as well as the correlation of returns among asset classes. Our target allocation is a mix of approximately 51 percent equity investments, 31 percent fixed-income investments and 18 percent in alternative investments. Furthermore, we believe our target allocation will enable us to achieve the following long-term investment objectives:
(1) |
optimize the long-term return on plan assets at an acceptable level of risk; |
(2) |
maintain a broad diversification across asset classes and among investment managers; |
(3) |
maintain careful control of the risk level within each asset class; and |
(4) |
focus on a long-term return objective. |
The guidelines that have been established with each investment manager provide parameters within which the investment managers agree to operate, including criteria that determine eligible and ineligible securities, diversification requirements and credit quality standards, where applicable. Unless exceptions have been approved, investment managers are prohibited from buying or selling commodities, futures or option contracts, as well as from short selling of securities. Additionally, investment managers agree to obtain written approval for deviations from stated investment style or guidelines. As of December 31, 2011, no investment manager was responsible for more than 10 percent of total U.S. plan assets.
Our target allocation of 51 percent equity investments is composed of approximately 39 percent domestic large-cap securities, 33 percent international securities and 28 percent domestic small-cap securities. Optimal returns through our investments in domestic large-cap securities are achieved through security selection and sector diversification. Investments in common stock of our Company accounted for approximately 12 percent of our investments in domestic large-cap securities and approximately 3 percent of total U.S. plan assets. Our investments in international securities are intended to provide equity-like returns, while at the same time helping to diversify our overall equity investment portfolio. Our investments in domestic small-cap securities are expected to experience larger swings in their market value on a periodic basis. Our investments in this asset class are selected based on capital appreciation potential.
Our target allocation of 31 percent fixed-income investments is composed of 71 percent long-duration bonds and 29 percent high-yield bonds. Long-duration bonds provide a stable rate of return through investments in high-quality publicly traded debt securities. Our investments in long-duration bonds are diversified in order to mitigate duration and credit exposure. High-yield bonds are investments in lower-rated and non-rated debt securities, which generally produce higher returns compared to long-duration bonds. Investments in high-yield bonds also help diversify our fixed-income portfolio.
In addition to investments in equity securities and fixed-income investments, we have a target allocation of 18 percent in alternative investments. These alternative investments include hedge funds, private equity limited partnerships, leveraged buyout funds, international venture capital partnerships and real estate. The objective of investing in alternative investments is to provide a higher rate of return than that available from publicly traded equity securities. These investments are inherently illiquid and require a long-term perspective in evaluating investment performance.
Investment Strategy for Non-U.S. Pension Plans
As of December 31, 2011, the long-term target allocation for 42 percent of our international subsidiaries' plan assets, primarily certain of our European plans, is 60 percent equity securities and 40 percent fixed-income securities. The allocation for the remaining 58 percent of the Company's international subsidiaries' plan assets consisted of 36 percent mutual, pooled and commingled funds; 18 percent fixed-income securities; 14 percent equity securities; and 32 percent in other investments. The investment strategies of our international subsidiaries differ greatly, and in some instances are influenced by local law. None of our pension plans outside the United States is individually significant for separate disclosure.
Other Postretirement Benefit Plan Assets
Plan assets associated with other benefits primarily represent funding of the U.S. postretirement benefit plan through a U.S. Voluntary Employee Beneficiary Association ("VEBA"), a tax-qualified trust. The VEBA assets remain segregated from the primary U.S. pension master trust and are primarily invested in liquid assets due to the level of expected future benefit payments.
119
The following table presents total assets for our other postretirement benefit plans (in millions):
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
|||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ |
86 |
$ |
84 |
|||
Equity securities: |
|||||||
U.S.-based companies |
70 |
75 |
|||||
International-based companies |
13 |
14 |
|||||
Fixed-income securities: |
|||||||
Government bonds |
2 |
1 |
|||||
Corporate bonds and debt securities |
6 |
6 |
|||||
Mutual, pooled and commingled funds |
3 |
3 |
|||||
Hedge funds/limited partnerships |
2 |
1 |
|||||
Real estate |
2 |
2 |
|||||
Other |
1 |
1 |
|||||
Total other postretirement benefit plan assets1
|
$ |
185 |
$ |
187 |
|||
1 |
Fair value disclosures related to our other postretirement benefit plan assets are included in Note 16. Fair value disclosures include, but are not limited to, the levels within the fair value hierarchy on which the fair value measurements in their entirety fall, a reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances of Level 3 assets and information about the valuation techniques and inputs used to measure the fair value of our pension and other postretirement assets.
|
Components of Net Periodic Benefit Cost
Net periodic benefit cost for our pension and other postretirement benefit plans consisted of the following (in millions):
Pension Benefits
|
Other Benefits
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
|||||||||||||||||
Service cost |
$ |
249 |
$ |
143 |
$ |
113 |
$ |
32 |
$ |
24 |
$ |
21 |
|||||||||||
Interest cost |
391 |
260 |
213 |
45 |
30 |
29 |
|||||||||||||||||
Expected return on plan assets |
(494 |
) |
(295 |
) |
(214 |
) |
(8 |
) |
(8 |
) |
(8 |
) |
|||||||||||
Amortization of prior service cost (credit) |
5 |
5 |
5 |
(61 |
) |
(61 |
) |
(61 |
) |
||||||||||||||
Amortization of actuarial loss |
87 |
57 |
86 |
2 |
3 |
— |
|||||||||||||||||
Net periodic benefit cost (credit) |
$ |
238 |
$ |
170 |
$ |
203 |
$ |
10 |
$ |
(12 |
) |
$ |
(19 |
) |
|||||||||
Settlement charge |
3 |
6 |
5 |
— |
— |
— |
|||||||||||||||||
Curtailment charge |
— |
— |
1 |
— |
— |
— |
|||||||||||||||||
Special termination benefits1
|
8 |
— |
9 |
3 |
1 |
4 |
|||||||||||||||||
Total cost (credit) recognized in the statements of income |
$ |
249 |
$ |
176 |
$ |
218 |
$ |
13 |
$ |
(11 |
) |
$ |
(15 |
) |
|||||||||
1 |
The special termination benefits primarily relate to the Company's productivity, restructuring and integration initiatives. Refer to Note 18 for additional information related to our productivity, restructuring and integration initiatives.
|
120
The following table sets forth the changes in AOCI for our benefit plans (in millions, pretax):
Pension Benefits
|
Other Benefits
|
||||||||||||||
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2011 |
2010 |
|||||||||||
Beginning balance in AOCI |
$ |
(1,006 |
) |
$ |
(1,119 |
) |
$ |
72 |
$ |
118 |
|||||
Recognized prior service cost (credit) |
5 |
5 |
(61 |
) |
(61 |
) |
|||||||||
Recognized net actuarial loss (gain) |
90 |
63 |
2 |
3 |
|||||||||||
Prior service credit (cost) arising in current year |
57 |
6 |
12 |
— |
|||||||||||
Net actuarial (loss) gain arising in current year |
(1,194 |
) |
41 |
(57 |
) |
8 |
|||||||||
Impact of divestitures1
|
— |
(8 |
) |
— |
— |
||||||||||
Translation gain (loss) |
(7 |
) |
6 |
(2 |
) |
4 |
|||||||||
Ending balance in AOCI |
$ |
(2,055 |
) |
$ |
(1,006 |
) |
$ |
(34 |
) |
$ |
72 |
||||
1 |
Primarily related to the sale of our Norwegian bottling operation to New CCE. Refer to Note 2.
|
The following table sets forth amounts in AOCI for our benefit plans (in millions, pretax):
Pension Benefits
|
Other Benefits
|
||||||||||||||
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2011 |
2010 |
|||||||||||
Prior service credit (cost) |
$ |
14 |
$ |
(49 |
) |
$ |
73 |
$ |
122 |
||||||
Net actuarial loss |
(2,069 |
) |
(957 |
) |
(107 |
) |
(50 |
) |
|||||||
Ending balance in AOCI |
$ |
(2,055 |
) |
$ |
(1,006 |
) |
$ |
(34 |
) |
$ |
72 |
||||
Amounts in AOCI expected to be recognized as components of net periodic pension cost in 2012 are as follows (in millions, pretax):
Pension Benefits |
Other Benefits |
||||||
Amortization of prior service cost (credit) |
$ |
(2 |
) |
$ |
(52 |
) |
|
Amortization of actuarial loss |
137 |
7 |
|||||
$ |
135 |
$ |
(45 |
) |
|||
Assumptions
Certain weighted-average assumptions used in computing the benefit obligations are as follows:
Pension Benefits
|
Other Benefits
|
||||||||||
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2011 |
2010 |
|||||||
Discount rate |
4.75 |
% |
5.50 |
% |
4.75 |
% |
5.25 |
% |
|||
Rate of increase in compensation levels |
3.25 |
% |
4.00 |
% |
N/A |
N/A |
|||||
Certain weighted-average assumptions used in computing net periodic benefit cost are as follows:
Pension Benefits
|
Other Benefits
|
||||||||||||||||
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
|||||||||||
Discount rate |
5.50 |
% |
5.75 |
% |
6.00 |
% |
5.25 |
% |
5.50 |
% |
6.25 |
% |
|||||
Rate of increase in compensation levels |
4.00 |
% |
3.75 |
% |
3.75 |
% |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
||||||||
Expected long-term rate of return on plan assets |
8.25 |
% |
8.00 |
% |
8.00 |
% |
4.75 |
% |
4.75 |
% |
4.75 |
% |
|||||
The expected long-term rate of return assumption for U.S. pension plan assets is based upon the target asset allocation and is determined using forward-looking assumptions in the context of historical returns and volatilities for each asset class, as well as correlations among asset classes. We evaluate the rate of return assumption on an annual basis. The expected long-term rate of
121
return assumption used in computing 2011 net periodic pension cost for the U.S. plans was 8.5 percent. As of December 31, 2011, the 10-year annualized return on plan assets in the primary U.S. plan was 6.0 percent, the 15-year annualized return was 6.4 percent, and the annualized return since inception was 10.9 percent.
The assumed health care cost trend rates are as follows:
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
|||
Health care cost trend rate assumed for next year |
8.00 |
% |
8.50 |
% |
|
Rate to which the cost trend rate is assumed to decline (the ultimate trend rate) |
5.00 |
% |
5.00 |
% |
|
Year that the rate reaches the ultimate trend rate |
2018 |
2018 |
|||
The Company's U.S. postretirement benefit plans are primarily defined dollar benefit plans that limit the effects of medical inflation because the plans have established dollar limits for determining our contributions. As a result, the effect of a 1 percentage point change in the assumed health care cost trend rate would not be significant to the Company.
The discount rate assumptions used to account for pension and other postretirement benefit plans reflect the rates at which the benefit obligations could be effectively settled. Rates for each of our U.S. plans at December 31, 2011, were determined using a cash flow matching technique whereby the rates of a yield curve, developed from high-quality debt securities, were applied to the benefit obligations to determine the appropriate discount rate. For our non-U.S. plans, we base the discount rate on comparable indices within each of the countries. The rate of compensation increase assumption is determined by the Company based upon annual reviews. We review external data and our own historical trends for health care costs to determine the health care cost trend rate assumptions.
Cash Flows
Our estimated future benefit payments for funded and unfunded plans are as follows (in millions):
Year Ended December 31, |
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017–2021 |
|||||||||||||||||
Pension benefit payments |
$ |
486 |
$ |
501 |
$ |
521 |
$ |
537 |
$ |
553 |
$ |
3,042 |
|||||||||||
Other benefit payments1
|
53 |
56 |
59 |
62 |
65 |
342 |
|||||||||||||||||
Total estimated benefit payments |
$ |
539 |
$ |
557 |
$ |
580 |
$ |
599 |
$ |
618 |
$ |
3,384 |
|||||||||||
1 |
The expected benefit payments for our other postretirement benefit plans are net of estimated federal subsidies expected to be received under the Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement and Modernization Act of 2003. Federal subsidies are estimated to be approximately $17 million for the period 2012–2016, and $21 million for the period 2017–2021.
|
On March 23, 2010, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (HR 3590) (the "Act") was signed into law. As a result of this legislation, entities are no longer eligible to receive a tax deduction for the portion of prescription drug expenses reimbursed under the Medicare Part D subsidy. This change resulted in a reduction of our deferred tax assets and a corresponding charge to income tax expense of $14 million during the first quarter of 2010.
The Company anticipates making contributions in 2012 of approximately $953 million, most of which will be allocated to our primary U.S. pension plans. The majority of these contributions are discretionary.
Defined Contribution Plans
Our Company sponsors qualified defined contribution plans covering substantially all U.S. employees. Under the primary U.S. defined contribution plans, we match participants' contributions up to a maximum of 3.0 percent to 3.5 percent of compensation, subject to certain limitations. Company costs related to the U.S. plans were $78 million, $44 million and $27 million in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. We also sponsor defined contribution plans in certain locations outside the United States. Company costs associated with those plans were $31 million, $35 million and $36 million in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
Multi-Employer Plans
As a result of our acquisition of CCE's North American business during the fourth quarter of 2010, the Company now participates in various multi-employer pension plans in the United States. Multi-employer pension plans are designed to cover employees from multiple employers and are typically established under collective bargaining agreements. These plans allow multiple employers to pool their pension resources and realize efficiencies associated with the daily administration of the plan.
122
Multi-employer plans are generally governed by a board of trustees composed of management and labor representatives and are funded through employer contributions.
The Company's expense for U.S. multi-employer pension plans totaled $69 million in 2011, of which $32 million was related to our withdrawal from certain of these plans. The charges of $32 million were included in the costs related to the Company's integration initiatives in North America. Refer to Note 18 for additional information related to these initiatives. The Company's expense for U.S. multi-employer pension plans was $9 million in 2010. The plans we currently participate in have contractual arrangements that extend into 2017. If, in the future, we choose to withdraw from any of the multi-employer pension plans in which we participate, we would need to record the appropriate withdrawal liabilities at that time.
NOTE 14: INCOME TAXES
Income before income taxes consisted of the following (in millions):
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
United States |
$ |
3,010 |
$ |
7,224 |
1 |
$ |
2,691 |
||||
International |
8,429 |
7,019 |
6,255 |
||||||||
$ |
11,439 |
$ |
14,243 |
$ |
8,946 |
||||||
1 |
The increase in 2010 was primarily attributable to a $4,978 million gain due to the remeasurement of our equity investment in CCE to fair value upon our acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to Note 2.
|
Income tax expense consisted of the following for the years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009 (in millions):
United States |
State and Local |
International |
Total |
||||||||||||
2011 |
|||||||||||||||
Current |
$ |
286 |
$ |
66 |
$ |
1,425 |
$ |
1,777 |
|||||||
Deferred |
891 |
27 |
110 |
1,028 |
|||||||||||
2010 |
|||||||||||||||
Current |
$ |
470 |
$ |
85 |
$ |
1,212 |
$ |
1,767 |
|||||||
Deferred |
599 |
2 |
16 |
617 |
|||||||||||
2009 |
|||||||||||||||
Current |
$ |
509 |
$ |
79 |
$ |
1,099 |
$ |
1,687 |
|||||||
Deferred |
322 |
18 |
13 |
353 |
|||||||||||
We made income tax payments of $1,612 million, $1,766 million and $1,534 million in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
123
A reconciliation of the statutory U.S. federal tax rate and our effective tax rate is as follows:
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||
Statutory U.S. federal tax rate |
35.0 |
% |
35.0 |
% |
35.0 |
% |
|||
State and local income taxes — net of federal benefit |
0.9 |
0.6 |
0.7 |
||||||
Earnings in jurisdictions taxed at rates different from the statutory U.S. federal rate |
(9.5 |
) |
1,2.3 |
(5.6 |
) |
11 |
(11.6 |
) |
19 |
Equity income or loss |
(1.4 |
) |
4 |
(1.9 |
) |
12 |
(2.3 |
) |
20 |
CCE transaction |
— |
(12.5 |
) |
13,14 |
— |
||||
Sale of Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations |
— |
5 |
0.4 |
15 |
— |
||||
Other operating charges |
0.3 |
6 |
0.4 |
16 |
0.6 |
21 |
|||
Other — net |
(0.8 |
) |
7,8,9,10 |
0.3 |
17,18 |
0.4 |
22,23 |
||
Effective tax rate |
24.5 |
% |
16.7 |
% |
22.8 |
% |
|||
1 |
Includes a tax benefit of $6 million related to amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties, in various international jurisdictions.
|
2 |
Includes a zero percent effective tax rate on charges due to the impairment of available-for-sale securities. Refer to Note 3 and Note 17.
|
3 |
Includes a tax expense of $299 million (or a 0.7 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to the net gain recognized as a result of the merger of Embotelladoras Arca, S.A.B. de C.V. ("Arca") and Grupo Continental S.A.B. ("Contal"), the gain recognized on the sale of our investment in Embonor and gains the Company recognized as a result of an equity method investee issuing additional shares of its own stock during the year at per share amounts greater than the carrying value of the Company's per share investment. These gains were partially offset by charges associated with certain of the Company's equity method investments in Japan. Refer to Note 17.
|
4 |
Includes a tax benefit of $7 million (or a 0.1 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to our proportionate share of asset impairments and restructuring charges recorded by certain of our equity method investees. Refer to Note 17.
|
5 |
Includes a tax benefit of $2 million related to the finalization of working capital adjustments on the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations. Refer to Note 2 and Note 17.
|
6 |
Includes a tax benefit of $224 million (or a 0.3 percent impact on our effective tax rate) primarily related to the Company's productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives, transaction costs incurred in connection with the merger of Arca and Contal, costs associated with the earthquake and tsunami that devastated northern and eastern Japan and costs associated with the flooding in Thailand. Refer to Note 17.
|
7 |
Includes a tax benefit of $8 million related to the amortization of favorable supply contracts acquired in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business.
|
8 |
Includes a tax benefit of $3 million related to net charges we recognized on the repurchase and/or exchange of certain long-term debt assumed in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business as well as the early extinguishment of certain other long-term debt. Refer to Note 10.
|
9 |
Includes a tax benefit of $14 million on charges due to the impairment of an investment in an entity accounted for under the equity method of accounting. Refer to Note 17.
|
10 |
Includes a tax benefit of $2 million related to amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties, in certain domestic jurisdictions.
|
11 |
Includes tax expense of $265 million (or a 1.9 percent impact on our effective tax rate), primarily related to deferred tax expense on certain current year undistributed foreign earnings that are not considered indefinitely reinvested and amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties.
|
12 |
Includes a tax benefit of $9 million (or a 0.1 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to charges recorded by our equity method investees. Refer to Note 17.
|
13 |
Includes a tax benefit of $34 million (or a reduction of 12.5 percent on our effective tax rate) related to the remeasurement of our equity investment in CCE to fair value upon our acquisition of CCE's North American business. The tax benefit reflects the impact of reversing deferred tax liabilities associated with our equity investment in CCE prior to the acquisition. Refer to Note 2.
|
14 |
Includes a tax benefit of $99 million related to charges associated with the write-off of preexisting relationships with CCE. Refer to Note 2.
|
15 |
Includes a tax expense of $261 million (or a 0.4 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations. Refer to Note 2.
|
16 |
Includes a tax benefit of $223 million (or a 0.4 percent impact on our effective tax rate), primarily related to the Company's productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives, transaction costs and charitable contributions. Refer to Note 17.
|
17 |
Includes a tax benefit of $114 million (or a 0.5 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to charges associated with the repurchase of certain long-term debt and costs associated with the settlement of treasury rate locks issued in connection with the debt tender offer, the loss related to the remeasurement of our Venezuelan subsidiary's net assets, other-than-temporary impairment charges and a donation of preferred shares in one of our equity method investees. Refer to Note 17.
|
124
18 |
Includes a tax expense of $31 million (or a 0.2 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties, and other tax matters in certain domestic jurisdictions.
|
19 |
Includes a tax benefit of $16 million (or a reduction of 0.2 percent on our effective tax rate) related to amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties, in various international jurisdictions.
|
20 |
Includes a tax benefit of $17 million (or a 0.1 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to charges recorded by our equity method investees. Refer to Note 17.
|
21 |
Includes a tax benefit of $16 million (or a 0.6 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to restructuring charges and asset impairments. Refer to Note 17.
|
22 |
Includes a zero percent effective rate (or a reduction of 0.2 percent on our effective tax rate) related to the sale of all or a portion of certain investments. Refer to Note 3.
|
23 |
Includes a zero percent effective rate (or a 0.1 percent impact on our effective tax rate) related to an other-than-temporary impairment of a cost method investment. Refer to Note 17.
|
Our effective tax rate reflects the tax benefits of having significant operations outside the United States, which are generally taxed at rates lower than the U.S. statutory rate of 35 percent. As a result of employment actions and capital investments made by the Company, certain tax jurisdictions provide income tax incentive grants, including Brazil, Costa Rica, Singapore and Swaziland. The terms of these grants range from 2015 to 2020. We expect each of the grants to be renewed indefinitely. Tax incentive grants favorably impacted our income tax expense by $193 million, $145 million and $191 million for the years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. In addition, our effective tax rate reflects the benefits of having significant earnings generated in investments accounted for under the equity method of accounting, which are generally taxed at rates lower than the U.S. statutory rate.
In 2010, the Company recorded a $4,978 million pre-tax remeasurement gain associated with the acquisition of CCE's North American business. This remeasurement gain was not recognized for tax purposes and therefore no tax expense was recorded on this gain. Also, as a result of this acquisition, the Company was required to reverse $34 million of deferred tax liabilities which were associated with our equity investment in CCE prior to the acquisition. In addition, the Company recognized a $265 million charge related to the settlement of preexisting relationships with CCE, and we recorded a tax benefit of 37 percent related to this charge.
The Company or one of its subsidiaries files income tax returns in the U.S. federal jurisdiction and various state and foreign jurisdictions. U.S. tax authorities have completed their federal income tax examinations for all years prior to 2005. With respect to state and local jurisdictions and countries outside the United States, with limited exceptions, the Company and its subsidiaries are no longer subject to income tax audits for years before 2002. For U.S. federal and state tax purposes, the net operating losses and tax credit carryovers acquired in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business that were generated between the years of 1990 through 2010 are subject to adjustments, until the year in which they are actually utilized is no longer subject to examination.
Although the outcome of tax audits is always uncertain, the Company believes that adequate amounts of tax, including interest and penalties, have been provided for any adjustments that are expected to result from those years.
As of December 31, 2011, the gross amount of unrecognized tax benefits was $320 million. If the Company were to prevail on all uncertain tax positions, the net effect would be a benefit to the Company's effective tax rate of $149 million, exclusive of any benefits related to interest and penalties. The remaining $171 million, which was recorded as a deferred tax asset, primarily represents tax benefits that would be received in different tax jurisdictions in the event the Company did not prevail on all uncertain tax positions.
125
A reconciliation of the changes in the gross balance of unrecognized tax benefit amounts is as follows (in millions):
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
Beginning balance of unrecognized tax benefits |
$ |
387 |
$ |
354 |
$ |
369 |
|||||
Increases related to prior period tax positions |
9 |
26 |
49 |
||||||||
Decreases related to prior period tax positions |
(19 |
) |
(10 |
) |
(28 |
) |
|||||
Increases related to current period tax positions |
6 |
33 |
16 |
||||||||
Decreases related to current period tax positions |
(1 |
) |
— |
— |
|||||||
Decreases related to settlements with taxing authorities |
(5 |
) |
— |
(27 |
) |
||||||
Reductions as a result of a lapse of the applicable statute of limitations |
(46 |
) |
(1 |
) |
(73 |
) |
|||||
Increase related to acquisition of CCE's North American business |
— |
6 |
— |
||||||||
Increases (decreases) from effects of foreign currency exchange rates |
(11 |
) |
(21 |
) |
48 |
||||||
Ending balance of unrecognized tax benefits |
$ |
320 |
$ |
387 |
$ |
354 |
|||||
The Company recognizes accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense. The Company had $110 million, $112 million and $94 million in interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits accrued as of December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. Of these amounts, $2 million of benefit, $17 million of expense and $16 million of benefit was recognized through income tax expense in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. If the Company were to prevail on all uncertain tax positions, the reversal of this accrual would also be a benefit to the Company's effective tax rate.
It is expected that the amount of unrecognized tax benefits will change in the next 12 months; however, we do not expect the change to have a significant impact on our consolidated statements of income or consolidated balance sheets. These changes may be the result of settlement of ongoing audits, statute of limitations expiring, or final settlements in transfer pricing matters that are the subject of litigation. At this time, an estimate of the range of the reasonably possible outcomes cannot be made.
As of December 31, 2011, undistributed earnings of the Company's foreign subsidiaries amounted to $23.5 billion. Those earnings are considered to be indefinitely reinvested and, accordingly, no U.S. federal and state income taxes have been provided thereon. Upon distribution of those earnings in the form of dividends or otherwise, the Company would be subject to both U.S. income taxes (subject to an adjustment for foreign tax credits) and withholding taxes payable to the various foreign countries. Determination of the amount of unrecognized deferred U.S. income tax liability is not practical because of the complexities associated with its hypothetical calculation; however, unrecognized foreign tax credits would be available to reduce a portion of the U.S. tax liability.
126
The tax effects of temporary differences and carryforwards that give rise to deferred tax assets and liabilities consist of the following (in millions):
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
||||||
Deferred tax assets: |
||||||||
Property, plant and equipment |
$ |
224 |
$ |
49 |
||||
Trademarks and other intangible assets |
68 |
271 |
||||||
Equity method investments (including translation adjustment) |
278 |
304 |
||||||
Net change in unrealized gain/loss |
43 |
28 |
||||||
Other liabilities |
1,257 |
1,257 |
||||||
Benefit plans |
2,022 |
2,019 |
||||||
Net operating/capital loss carryforwards |
818 |
911 |
||||||
Other |
418 |
683 |
1 |
|||||
Gross deferred tax assets |
$ |
5,128 |
$ |
5,522 |
||||
Valuation allowances |
(859 |
) |
(950 |
) |
||||
Total deferred tax assets2,3
|
$ |
4,269 |
$ |
4,572 |
||||
Deferred tax liabilities: |
||||||||
Property, plant and equipment |
$ |
(2,039 |
) |
$ |
(2,227 |
) |
||
Trademarks and other intangible assets |
(4,201 |
) |
(4,284 |
) |
||||
Equity method investments (including translation adjustment) |
(816 |
) |
(509 |
) |
||||
Net change in unrealized gain/loss |
(129 |
) |
(102 |
) |
||||
Other liabilities |
(129 |
) |
(5 |
) |
||||
Benefit plans |
(445 |
) |
(383 |
) |
||||
Other |
(753 |
) |
(765 |
) |
||||
Total deferred tax liabilities4
|
$ |
(8,512 |
) |
$ |
(8,275 |
) |
||
Net deferred tax liabilities |
$ |
(4,243 |
) |
$ |
(3,703 |
) |
||
1 |
Includes $183 million of tax credit carryforwards acquired in conjunction with our acquisition of CCE's North American business.
|
2 |
Noncurrent deferred tax assets of $243 million and $98 million were included in the line item other assets in our consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
|
3 |
Current deferred tax assets of $227 million and $478 million were included in the line item prepaid expenses and other assets in our consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
|
4 |
Current deferred tax liabilities of $19 million and $18 million were included in the line item accounts payable and accrued expenses in our consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
|
As of December 31, 2011 and 2010, we had $491 million and $445 million, respectively, of net deferred tax liabilities located in countries outside the United States.
As of December 31, 2011, we had $6,297 million of loss carryforwards available to reduce future taxable income. Loss carryforwards of $391 million must be utilized within the next five years and the remainder can be utilized over a period greater than five years.
An analysis of our deferred tax asset valuation allowances is as follows (in millions):
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
Balance at beginning of year |
$ |
950 |
$ |
681 |
$ |
569 |
|||||
Increase due to our acquisition of CCE's North American business |
— |
291 |
— |
||||||||
Additions |
138 |
115 |
178 |
||||||||
Deductions |
(229 |
) |
(137 |
) |
(66 |
) |
|||||
Balance at end of year |
$ |
859 |
$ |
950 |
$ |
681 |
|||||
127
The Company's deferred tax asset valuation allowances are primarily the result of uncertainties regarding the future realization of recorded tax benefits on tax loss carryforwards from operations in various jurisdictions. These valuation allowances were primarily related to deferred tax assets generated from net operating losses. Current evidence does not suggest we will realize sufficient taxable income of the appropriate character (e.g., capital gain versus ordinary income) within the carryforward period to allow us to realize these deferred tax benefits. If we were to identify and implement tax planning strategies to recover these deferred tax assets or generate sufficient income of the appropriate character in these jurisdictions in the future, it could lead to the reversal of these valuation allowances and a reduction of income tax expense. The Company believes that it will generate sufficient future taxable income to realize the tax benefits related to the remaining net deferred tax assets in our consolidated balance sheets.
In 2011, the Company recognized a net decrease of $91 million in its valuation allowances. This decrease was primarily related to the utilization of net operating losses during the normal course of business operations, the reversal of a deferred tax asset and related valuation allowance on certain expiring attributes and the reversal of a deferred tax asset and related valuation allowance on certain equity investments. In addition, the Company recognized an increase in the valuation allowances primarily due to the carryforward of expenses disallowed in the current year and increases in net operating losses during the normal course of business operations.
In 2010, the Company recognized a net increase of $269 million in its valuation allowances. This increase was primarily related to valuation allowances on various tax loss carryforwards acquired in conjunction with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. The Company also recognized an increase in the valuation allowances due to the carryforward of expenses disallowed in the current year and changes to deferred tax assets and a related valuation allowance on certain equity method investments. In addition, the Company recognized a reduction in the valuation allowances primarily due to the reversal of a deferred tax asset and related valuation allowance on certain expiring attributes, the reversal of a deferred tax asset and related valuation allowance related to the deconsolidation of certain entities and the impact of foreign currency fluctuations.
In 2009, the Company recognized a net increase of $112 million in its valuation allowances. This increase was primarily related to asset impairments, increases in net operating losses during the normal course of business operations and the impact of foreign currency fluctuations. In addition, the Company recognized a reduction in the valuation allowances due to the reversal of a deferred tax asset and related valuation allowance on certain equity investments.
NOTE 15: OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
AOCI attributable to shareowners of The Coca-Cola Company is separately presented on our consolidated balance sheets as a component of The Coca-Cola Company's shareowners' equity, which also includes our proportionate share of equity method investees' AOCI. Other comprehensive income (loss) ("OCI") attributable to noncontrolling interests is allocated to, and included in, our balance sheets as part of the line item equity attributable to noncontrolling interests. AOCI attributable to shareowners of The Coca-Cola Company consisted of the following (in millions):
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
|||||
Foreign currency translation adjustment |
$ |
(1,445 |
) |
$ |
(805 |
) |
|
Accumulated derivative net losses |
(53 |
) |
(198 |
) |
|||
Unrealized net gain on available-for-sale securities |
160 |
167 |
|||||
Adjustment to pension and other benefit liabilities |
(1,365 |
) |
(614 |
) |
|||
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) |
$ |
(2,703 |
) |
$ |
(1,450 |
) |
|
128
OCI attributable to shareowners of The Coca-Cola Company, including our proportionate share of equity method investees' OCI, for the years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009, is as follows (in millions):
|
Before-Tax
Amount
|
Income
Tax
|
After-Tax
Amount
|
|||||||||
2011 |
|||||||||||
Net foreign currency translation adjustment |
$ |
(639 |
) |
$ |
(1 |
) |
$ |
(640 |
) |
||
Net gain (loss) on derivatives1
|
240 |
(95 |
) |
145 |
|||||||
Net change in unrealized gain on available-for-sale securities |
6 |
(13 |
) |
(7 |
) |
||||||
Net change in pension and other benefit liabilities |
(1,156 |
) |
405 |
(751 |
) |
||||||
Other comprehensive income (loss) |
$ |
(1,549 |
) |
$ |
296 |
$ |
(1,253 |
) |
|||
2010 |
|||||||||||
Net foreign currency translation adjustment |
$ |
(966 |
) |
$ |
31 |
$ |
(935 |
) |
|||
Net gain (loss) on derivatives1
|
(222 |
) |
102 |
(120 |
) |
||||||
Net change in unrealized gain on available-for-sale securities |
133 |
(31 |
) |
102 |
|||||||
Net change in pension and other benefit liabilities |
396 |
(136 |
) |
260 |
|||||||
Other comprehensive income (loss) |
$ |
(659 |
) |
$ |
(34 |
) |
$ |
(693 |
) |
||
2009 |
|||||||||||
Net foreign currency translation adjustment |
$ |
1,968 |
$ |
(144 |
) |
$ |
1,824 |
||||
Net gain (loss) on derivatives1
|
58 |
(24 |
) |
34 |
|||||||
Net change in unrealized gain on available-for-sale securities2
|
(39 |
) |
(13 |
) |
(52 |
) |
|||||
Net change in pension and other benefit liabilities |
173 |
(62 |
) |
111 |
|||||||
Other comprehensive income (loss) |
$ |
2,160 |
$ |
(243 |
) |
$ |
1,917 |
||||
1 |
Refer to Note 5 for information related to the net gain or loss on derivative instruments designated and qualifying as cash flow hedging instruments.
|
2 |
Includes reclassification adjustments related to divestitures of certain available-for-sale securities. Refer to Note 3 for additional information related to these divestitures.
|
NOTE 16: FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
Accounting principles generally accepted in the United States define fair value as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. Additionally, the inputs used to measure fair value are prioritized based on a three-level hierarchy. This hierarchy requires entities to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The three levels of inputs used to measure fair value are as follows:
• |
Level 1 — Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
• |
Level 2 — Observable inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1. We value assets and liabilities included in this level using dealer and broker quotations, certain pricing models, bid prices, quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data. |
• |
Level 3 — Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets or liabilities. This includes certain pricing models, discounted cash flow methodologies and similar techniques that use significant unobservable inputs. |
Recurring Fair Value Measurements
In accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, certain assets and liabilities are required to be recorded at fair value on a recurring basis. For our Company, the only assets and liabilities that are adjusted to fair value on a recurring basis are investments in equity and debt securities classified as trading or available-for-sale and derivative instruments.
129
Investments in Trading and Available-for-Sale Securities
The fair values of our investments in trading and available-for-sale securities were primarily determined using quoted market prices from daily exchange traded markets. The fair values of instruments using quoted market prices were based on the closing price as of the balance sheet date and were classified as Level 1. The fair values of instruments using other standard valuation models were classified as either Level 2 or Level 3.
Derivative Financial Instruments
The fair values of our futures contracts were primarily determined using quoted contract prices on futures exchange markets. The fair values of these instruments were based on the closing contract price as of the balance sheet date and were classified as Level 1.
The fair values of our derivative instruments other than futures were determined using standard valuation models. The significant inputs used in these models are readily available in public markets or can be derived from observable market transactions, and therefore have been classified as Level 2. Inputs used in these standard valuation models for derivative instruments other than futures include the applicable exchange rates, forward rates, interest rates and discount rates. The standard valuation model for options also uses implied volatility as an additional input. The discount rates are based on the historical U.S. Deposit or U.S. Treasury rates, and the implied volatility specific to options is based on quoted rates from financial institutions.
Included in the fair value of derivative instruments is an adjustment for nonperformance risk. The adjustment is based on the current one-year credit default swap ("CDS") rate applied to each contract, by counterparty. We use our counterparty's CDS rate when we are in an asset position and our own CDS rate when we are in a liability position. The adjustment for nonperformance risk did not have a significant impact on the estimated fair value of our derivative instruments.
The following tables summarize those assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis (in millions):
December 31, 2011 |
|||||||||||||||||||
Level 1 |
Level 2 |
Level 3 |
Netting
Adjustment1
|
Fair Value
Measurements
|
|||||||||||||||
Assets: |
|||||||||||||||||||
Trading securities |
$ |
166 |
$ |
41 |
$ |
4 |
$ |
— |
$ |
211 |
|||||||||
Available-for-sale securities |
1,071 |
214 |
116 |
2 |
— |
1,401 |
|||||||||||||
Derivatives3
|
39 |
467 |
— |
(117 |
) |
389 |
|||||||||||||
Total assets |
$ |
1,276 |
$ |
722 |
$ |
120 |
$ |
(117 |
) |
$ |
2,001 |
||||||||
Liabilities: |
|||||||||||||||||||
Derivatives3
|
$ |
5 |
$ |
201 |
$ |
— |
$ |
(121 |
) |
$ |
85 |
||||||||
Total liabilities |
$ |
5 |
$ |
201 |
$ |
— |
$ |
(121 |
) |
$ |
85 |
||||||||
1 |
Amounts represent the impact of legally enforceable master netting agreements that allow the Company to settle positive and negative positions and also cash collateral held or placed with the same counterparties. |
2 |
Primarily related to long-term debt securities that mature in 2018. |
3 |
Refer to Note 5 for additional information related to the composition of our derivative portfolio. |
December 31, 2010 |
|||||||||||||||||||
Level 1 |
Level 2 |
Level 3 |
Netting
Adjustment1
|
Fair Value
Measurements
|
|||||||||||||||
Assets: |
|||||||||||||||||||
Trading securities |
$ |
183 |
$ |
23 |
$ |
3 |
$ |
— |
$ |
209 |
|||||||||
Available-for-sale securities |
480 |
5 |
— |
— |
485 |
||||||||||||||
Derivatives2
|
19 |
151 |
4 |
(143 |
) |
31 |
|||||||||||||
Total assets |
$ |
682 |
$ |
179 |
$ |
7 |
$ |
(143 |
) |
$ |
725 |
||||||||
Liabilities: |
|||||||||||||||||||
Derivatives2
|
$ |
2 |
$ |
382 |
$ |
— |
$ |
(142 |
) |
$ |
242 |
||||||||
Total liabilities |
$ |
2 |
$ |
382 |
$ |
— |
$ |
(142 |
) |
$ |
242 |
||||||||
1 |
Amounts represent the impact of legally enforceable master netting agreements that allow the Company to settle positive and negative positions and also cash collateral held or placed with the same counterparties. |
2 |
Refer to Note 5 for additional information related to the composition of our derivative portfolio. |
130
Gross realized and unrealized gains and losses on Level 3 assets and liabilities were not significant for the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2010.
The Company recognizes transfers between levels within the hierarchy as of the beginning of the reporting period. Gross transfers between levels within the hierarchy were not significant for the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2010.
Nonrecurring Fair Value Measurements
In addition to assets and liabilities that are recorded at fair value on a recurring basis, the Company records assets and liabilities at fair value on a nonrecurring basis as required by accounting principles generally accepted in the United States. Generally, assets are recorded at fair value on a nonrecurring basis as a result of impairment charges. Assets measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis for the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2010, are summarized below (in millions):
Gains (Losses) |
||||||||
December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
||||||
Exchange of investment in equity securities |
$ |
418 |
1 |
$ |
— |
|||
Valuation of shares in equity method investee |
122 |
2 |
— |
|||||
Equity method investments |
(41 |
) |
3 |
(15 |
) |
6 |
||
Available-for-sale securities |
(17 |
) |
4 |
(26 |
) |
7 |
||
Inventories |
(11 |
) |
5 |
— |
||||
Cold-drink equipment |
(1 |
) |
5 |
— |
||||
Investment in formerly unconsolidated subsidiary |
— |
4,978 |
8 |
|||||
Retained investment in formerly consolidated subsidiary |
— |
12 |
9 |
|||||
Total |
$ |
470 |
$ |
4,949 |
||||
1 |
As a result of the merger of Arca and Contal, the Company recognized a gain on the exchange of the shares we previously owned in Contal for shares in the newly formed entity Arca Contal. The gain represents the difference between the carrying value of the Contal shares we relinquished and the fair value of the Arca Contal shares we received as a result of the transaction. The gain and initial carrying value of our investment were calculated based on Level 1 inputs. Refer to Note 17.
|
2 |
The Company recognized a net gain of $122 million, primarily as a result of an equity method investee issuing additional shares of its own stock at per share amounts greater than the carrying value of the Company's per share investment. Accordingly, the Company is required to treat this type of transaction as if the Company sold a proportionate share of its investment in the equity method investee. The gains the Company recognized as a result of the previous transactions were partially offset by charges associated with certain of the Company's equity method investments in Japan. The gains and charges were determined using Level 1 inputs. Refer to Note 17.
|
3 |
The Company recognized impairment charges of $41 million related to an investment in an entity accounted for under the equity method of accounting. Subsequent to the recognition of these impairment charges, the Company's remaining financial exposure related to this entity is not significant. This charge was determined using Level 3 inputs. Refer to Note 17.
|
4 |
The Company recognized other-than-temporary impairment charges of $17 million on certain available-for-sale securities. The Company determined the fair value of these securities based on Level 1 inputs. Refer to Note 17.
|
5 |
These assets primarily consisted of Company-owned inventory as well as cold-drink equipment that were damaged or lost as a result of the natural disasters in Japan on March 11, 2011. We recorded impairment charges of $11 million and $1 million related to Company-owned inventory and cold-drink equipment, respectively. These charges were determined using Level 3 inputs based on the carrying value of the inventory and cold-drink equipment prior to the disasters. Refer to Note 17.
|
6 |
The Company recognized an other-than-temporary impairment charge of $15 million. The carrying value of the Company's investment prior to recognizing the impairment was $15 million. The Company determined that the fair value of the investment was zero based on Level 3 inputs. Refer to Note 17.
|
7 |
The Company recognized other-than-temporary impairment charges on certain available-for-sale securities. The aggregate carrying value of these securities prior to recognizing the impairment charges was $131 million. The Company determined the fair value of these securities based on Level 1 and Level 2 inputs. The fair value of the Level 2 security was based on a dealer quotation. Refer to Note 17.
|
8 |
The Company recognized a gain on our previously held investment in CCE, which had been accounted for under the equity method of accounting prior to our acquisition of CCE's North American business. Accounting principles generally accepted in the United States require the acquirer to remeasure its previously held noncontrolling equity interest in the acquired entity to fair value as of the acquisition date and recognize any gains or losses in earnings. The Company remeasured our equity interest in CCE based on Level 1 inputs. Refer to Note 2 and Note 17.
|
9 |
The Company sold 50 percent of our investment in Leão Junior, which was a wholly owned subsidiary prior to this transaction. The gain on the transaction consisted of two parts: (1) the difference between the consideration received and 50 percent of the carrying value of our investment and (2) the fair value adjustment for our remaining 50 percent ownership. The gain in the table above represents the portion of the total gain related to the remeasurement of our retained investment in Leão Junior, which was based on Level 3 inputs. Refer to Note 17 for further discussion of this transaction.
|
131
Fair Value Measurements for Pension and Other Postretirement Benefit Plans
The fair value hierarchy discussed above is not only applicable to assets and liabilities that are included in our consolidated balance sheets, but is also applied to certain other assets that indirectly impact our consolidated financial statements. For example, our Company sponsors and/or contributes to a number of pension and other postretirement benefit plans. Assets contributed by the Company become the property of the individual plans. Even though the Company no longer has control over these assets, we are indirectly impacted by subsequent fair value adjustments to these assets. The actual return on these assets impacts the Company's future net periodic benefit cost, as well as amounts recognized in our consolidated balance sheets. Refer to Note 13. The Company uses the fair value hierarchy to measure the fair value of assets held by our various pension and other postretirement plans.
Pension Plan Assets
The following table summarizes the levels within the fair value hierarchy used to determine the fair value of our pension plan assets for our U.S. and non-U.S. pension plans as of December 31, 2011 and 2010 (in millions):
December 31, 2011 |
December 31, 2010 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Level 1 |
Level 2 |
Level 3 |
Total |
Level 1 |
Level 2 |
Level 3 |
Total |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ |
152 |
$ |
75 |
$ |
— |
$ |
227 |
$ |
50 |
$ |
76 |
— |
$ |
126 |
||||||||||||||||
Equity securities: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
U.S.-based companies |
1,366 |
15 |
14 |
1,395 |
1,325 |
14 |
15 |
1,354 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
International-based companies |
865 |
82 |
6 |
953 |
689 |
49 |
— |
738 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Fixed-income securities: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Government bonds |
— |
773 |
— |
773 |
— |
431 |
— |
431 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Corporate bonds and debt securities |
— |
718 |
— |
718 |
— |
645 |
— |
645 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Mutual, pooled and commingled funds |
167 |
557 |
5 |
729 |
248 |
863 |
20 |
1,131 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Hedge funds / limited partnerships |
— |
140 |
349 |
489 |
— |
121 |
317 |
438 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Real estate |
— |
— |
270 |
270 |
— |
— |
242 |
242 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Other |
— |
99 |
518 |
1 |
617 |
3 |
86 |
303 |
1 |
392 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Total |
$ |
2,550 |
$ |
2,459 |
$ |
1,162 |
$ |
6,171 |
$ |
2,315 |
$ |
2,285 |
$ |
897 |
$ |
5,497 |
|||||||||||||||
1 |
Includes $514 million and $299 million of purchased annuity contracts as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
|
132
The following table provides a reconciliation of the beginning and ending balance of Level 3 assets for our U.S. and non-U.S. pension plans for the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2010 (in millions):
|
Corporate
Bonds and
Debt Securities
|
Hedge
Funds/Limited
Partnerships
|
Real Estate |
Equity
Securities
|
Mutual,
Pooled and
Commingled
Funds
|
Other |
Total |
|||||||||||||||||||||
2010 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at beginning of year |
$ |
10 |
$ |
80 |
$ |
153 |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
$ |
45 |
$ |
288 |
|||||||||||||
Actual return on plan assets: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Related to assets still held at the reporting date |
— |
19 |
4 |
5 |
(1 |
) |
10 |
37 |
|||||||||||||||||||
Related to assets sold during the year |
— |
(3 |
) |
— |
— |
1 |
(1 |
) |
(3 |
) |
|||||||||||||||||
Purchases, sales and settlements — net |
(10 |
) |
7 |
(36 |
) |
10 |
(4 |
) |
288 |
255 |
|||||||||||||||||
Business combinations and divestitures — net1
|
— |
213 |
121 |
— |
24 |
5 |
363 |
||||||||||||||||||||
Transfers in or out of Level 3 — net |
— |
1 |
— |
— |
— |
(5 |
) |
(4 |
) |
||||||||||||||||||
Translation |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
(39 |
) |
(39 |
) |
||||||||||||||||||
Balance at end of year |
$ |
— |
$ |
317 |
$ |
242 |
$ |
15 |
$ |
20 |
$ |
303 |
2 |
$ |
897 |
||||||||||||
2011 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at beginning of year |
$ |
— |
$ |
317 |
$ |
242 |
$ |
15 |
$ |
20 |
$ |
303 |
$ |
897 |
|||||||||||||
Actual return on plan assets: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Related to assets still held at the reporting date |
— |
9 |
35 |
4 |
(5 |
) |
61 |
104 |
|||||||||||||||||||
Related to assets sold during the year |
— |
(3 |
) |
(5 |
) |
— |
6 |
— |
(2 |
) |
|||||||||||||||||
Purchases, sales and settlements — net |
— |
26 |
(2 |
) |
(1 |
) |
(16 |
) |
146 |
153 |
|||||||||||||||||
Business combinations and divestitures — net |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
||||||||||||||||||||
Transfers in or out of Level 3 — net |
— |
1 |
— |
2 |
— |
2 |
5 |
||||||||||||||||||||
Translation |
— |
(1 |
) |
— |
— |
— |
6 |
5 |
|||||||||||||||||||
Balance at end of year |
$ |
— |
$ |
349 |
$ |
270 |
$ |
20 |
$ |
5 |
$ |
518 |
2 |
$ |
1,162 |
||||||||||||
1 |
Primarily related to our acquisition of CCE's North American business and the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE. Refer to Note 2. |
2 |
Includes $514 million and $299 million of purchased annuity contracts as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
|
Other Postretirement Benefit Plan Assets
The following table summarizes the levels within the fair value hierarchy used to determine the fair value of our other postretirement benefit plan assets as of December 31, 2011 and 2010 (in millions):
December 31, 2011 |
December 31, 2010 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Level 1 |
Level 2 |
Level 3 1
|
Total |
Level 1 |
Level 2 |
Level 3 1
|
Total |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ |
— |
$ |
86 |
$ |
— |
$ |
86 |
$ |
— |
$ |
84 |
$ |
— |
$ |
84 |
|||||||||||||||
Equity securities: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
U.S.-based companies |
70 |
— |
— |
70 |
75 |
— |
— |
75 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
International-based companies |
13 |
— |
— |
13 |
14 |
— |
— |
14 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Fixed-income securities: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Government bonds |
— |
2 |
— |
2 |
— |
1 |
— |
1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Corporate bonds and debt securities |
— |
6 |
— |
6 |
— |
6 |
— |
6 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Mutual, pooled and commingled funds |
— |
3 |
— |
3 |
— |
3 |
— |
3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Hedge funds / limited partnerships |
— |
— |
2 |
2 |
— |
— |
1 |
1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Real estate |
— |
— |
2 |
2 |
— |
— |
2 |
2 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Other |
— |
1 |
— |
1 |
— |
1 |
— |
1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Total |
$ |
83 |
$ |
98 |
$ |
4 |
$ |
185 |
$ |
89 |
$ |
95 |
$ |
3 |
$ |
187 |
|||||||||||||||
1 |
Level 3 assets are not a significant portion of other postretirement benefit plan assets. |
133
Fair Value of Other Financial Instruments
The carrying amounts of cash and cash equivalents; short-term investments; receivables; accounts payable and accrued expenses; and loans and notes payable approximate their fair values because of the relatively short-term maturities of these financial instruments.
NOTE 17: SIGNIFICANT OPERATING AND NONOPERATING ITEMS
Other Operating Items
On March 11, 2011, a major earthquake struck off the coast of Japan, resulting in a tsunami that devastated the northern and eastern regions of the country. As a result of these events, the Company made a donation to a charitable organization to establish the Coca-Cola Japan Reconstruction Fund, which will help rebuild schools and community facilities across the impacted areas of the country.
The Company recorded total charges of $84 million related to these events during the year ended December 31, 2011. These charges were recorded in various line items in our consolidated statement of income, including charges of $23 million in deductions from revenue, $11 million in cost of goods sold and $50 million in other operating charges. Refer to Note 19 for the impact these charges had on our operating segments.
The charges of $23 million recorded in deductions from revenue were primarily related to funds we provided our local bottling partners to enable them to continue producing and distributing our beverage products in the affected regions. This support not only helped restore our business operations in the impacted areas, but it also assisted our bottling partners in meeting the evolving customer and consumer needs as the recovery and rebuilding efforts advanced. The charges of $11 million in cost of goods sold were primarily related to Company-owned inventory that was destroyed or lost. The $50 million of other operating charges were primarily related to the donation discussed above and a $1 million impairment charge related to certain Company-owned fixed assets. These fixed assets primarily consisted of Company-owned vending equipment and coolers that were damaged or lost as a result of these events. Refer to Note 16 for the fair value disclosures related to the inventory and fixed asset charges described above.
Other Operating Charges
In 2011, the Company incurred other operating charges of $732 million, which primarily consisted of $633 million associated with the Company's ongoing productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives; $50 million related to the events in Japan described above; $35 million of costs associated with the merger of Arca and Contal; and $10 million associated with the floods in Thailand that impacted the Company's supply chain operations in the region. Refer to Note 18 for additional information on our productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives. Refer to the discussion of the merger of Arca and Contal below for additional information on the transaction. Refer to Note 19 for the impact these charges had on our operating segments.
In 2010, the Company incurred other operating charges of $819 million, which consisted of $478 million associated with the Company's ongoing productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives; $250 million related to charitable contributions; $81 million due to transaction costs incurred in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business and the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE; and $10 million of charges related to bottling activities in Eurasia. Refer to Note 18 for additional information on our productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives. The charitable contributions were primarily attributable to a cash donation to The Coca-Cola Foundation. Refer to Note 2 for additional information related to the transaction costs. Refer to Note 19 for the impact these charges had on our operating segments.
In 2009, the Company incurred other operating charges of $313 million, which consisted of $273 million related to the Company's ongoing productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives and $40 million due to asset impairments. Refer to Note 18 for additional information on our productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives. The impairment charges were related to a $23 million impairment of an intangible asset and a $17 million impairment of a building. The impairment of the intangible asset was due to a change in the expected useful life of the asset, which was previously determined to have an indefinite life. The $17 million impairment was due to a change in disposal strategy related to a building that is no longer occupied. The Company had originally intended to sell the building along with the related land. However, we determined that the maximum potential sales proceeds would likely be realized through the sale of vacant land. As a result, the building was removed. The land was not considered held-for-sale, primarily due to the fact that it was not probable a sale would be completed within one year. Refer to Note 16 for the related fair value disclosures of the impairments. Refer to Note 19 for the impact these charges had on our operating segments.
Other Nonoperating Items
Equity Income (Loss) — Net
In 2011, the Company recorded charges of $53 million in equity income (loss) — net. These charges primarily represent the
134
Company's proportionate share of asset impairments and restructuring charges recorded by equity method investees. Refer to Note 19 for the impact these charges had on our operating segments.
In 2010, the Company recorded a net charge of $66 million in equity income (loss) — net. This net charge primarily represents the Company's proportionate share of unusual tax charges, asset impairments, restructuring charges and transaction costs recorded by equity method investees. The unusual tax charges primarily relate to an additional tax liability recorded by Coca-Cola Hellenic as a result of the Extraordinary Social Contribution Tax levied by the Greek government. The transaction costs represent our proportionate share of certain costs incurred by CCE in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business and the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE. Refer to Note 2 for additional information related to these transactions. These charges were partially offset by our proportionate share of a foreign currency remeasurement gain recorded by an equity method investee. The components of the net charge were individually insignificant. Refer to Note 19 for the impact these charges had on our operating segments.
During 2009, the Company recorded charges of $86 million in equity income (loss) — net. These charges primarily represent the Company's proportionate share of asset impairments and restructuring charges recorded by equity method investees. Refer to Note 19 for the impact these charges had on our operating segments.
Other Income (Loss) — Net
In 2011, the Company recognized a net gain of $417 million in other income (loss) — net, primarily as a result of the merger of Arca and Contal, two bottling partners headquartered in Mexico, into a combined entity known as Arca Contal. Prior to this transaction the Company held an investment in Contal that we accounted for under the equity method of accounting. The merger of the two companies was a non-cash transaction that resulted in Contal shareholders exchanging their existing Contal shares for new shares in Arca Contal at a specified exchange rate. Refer to Note 16 for additional information on the measurement of the gain. As a result, the Company now holds an investment in Arca Contal that we account for as an available-for-sale security. This net gain impacted the Corporate operating segment.
The Company also recognized a net gain of $122 million during 2011, primarily as a result of an equity method investee issuing additional shares of its own stock at per share amounts greater than the carrying value of the Company's per share investment. Accordingly, the Company is required to treat this type of transaction as if the Company sold a proportionate share of its investment in the equity method investee. The gains the Company recognized as a result of the previous transactions were partially offset by charges associated with certain of the Company's equity method investments in Japan. In addition, the Company recognized a gain of $102 million during 2011 related to the sale of our investment in Embonor. Refer to Note 2 for additional information. Refer to Note 19 for the impact these items had on our operating segments.
During 2011, the Company recorded charges of $41 million due to the impairment of an investment in an entity accounted for under the equity method of accounting and $17 million due to other-than-temporary declines in the fair value of certain of the Company's available-for-sale securities. Refer to Note 16 for additional fair value information related to these impairments. The Company also recorded a charge of $5 million related to the finalization of working capital adjustments associated with the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish Bottling operations to New CCE during the fourth quarter of 2010. This charge reduced the amount of our previously reported gain on the sale of these bottling operations. Refer to Note 19 for the impact these charges had on our operating segments.
In 2010, the Company recognized gains of $4,978 million related to the remeasurement of our equity investment in CCE to fair value; $597 million due to the sale of all our ownership interests in our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE; and $23 million as a result of the sale of 50 percent of our investment in Leão Junior, which was a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company prior to this transaction. Refer to Note 2 for additional information related to our acquisition of CCE's North American business and the sale of all our ownership interests in our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE. The gain on the Leão Junior transaction consisted of two parts: (1) the difference between the consideration received and 50 percent of the carrying value of our investment and (2) the fair value adjustment for our remaining 50 percent ownership. We have accounted for our remaining investment in Leão Junior under the equity method of accounting since the close of this transaction. The gains related to these transactions were recorded in other income (loss) — net and impacted our Corporate operating segment. Refer to Note 16 for fair value disclosures related to these transactions.
During 2010, in addition to the transaction gains, the Company recorded charges of $265 million related to preexisting relationships with CCE and $103 million due to the remeasurement of our Venezuelan subsidiary's net assets. The charges related to preexisting relationships with CCE were primarily due to the write-off of our investment in infrastructure programs with CCE. Refer to Note 6 for additional information related to our preexisting relationships with CCE. The remeasurement loss related to our Venezuelan subsidiary's net assets was due to the Venezuelan government announcing a currency devaluation and Venezuela becoming a hyperinflationary economy subsequent to December 31, 2009. As a result, our local subsidiary was required to use the U.S. dollar as its functional currency, and the remeasurement gains and losses were recorded in other income (loss) — net. This charge impacted the Corporate operating segment.
Also during 2010, the Company recorded charges of $48 million in other income (loss) — net related to other-than-temporary
135
impairments of available-for-sale securities and an equity method investment and a donation of preferred shares in one of our equity method investees. Refer to Note 16 for fair value disclosures related to these impairments. Refer to Note 19 for the impact these charges had on our operating segments.
During 2009, the Company realized a gain of $44 million in other income (loss) — net on the sale of equity securities that were classified as available-for-sale. In 2008, the Company recognized an other-than-temporary impairment on these same securities, primarily due to the length of time the market value had been less than our cost basis, and the lack of intent to retain the investment for a period of time sufficient to allow for recovery in market value. The gain on the sale of these securities represents the appreciation in market value since the impairment was recognized and impacted the Corporate operating segment.
Also during 2009, the Company recorded a charge of $27 million in other income (loss) — net due to an other-than-temporary decline in the fair value of a cost method investment. As of December 31, 2008, the estimated fair value of this investment approximated the Company's carrying value in the investment. However, during the first quarter of 2009, the Company was informed by the investee of its intent to reorganize its capital structure in 2009, which would result in the Company's shares in the investee being canceled. As a result, the Company determined that the decline in fair value of this cost method investment was other than temporary. This impairment charge impacted the Corporate operating segment. Refer to Note 16 for fair value disclosures related to this impairment.
NOTE 18: PRODUCTIVITY, INTEGRATION AND RESTRUCTURING INITIATIVES
Productivity Initiatives
During 2008, the Company announced a transformation effort centered on productivity initiatives that will provide additional flexibility to invest for growth. In 2011, we completed this program. The initiatives impacted a number of areas, including aggressively managing operating expenses supported by lean techniques; redesigning key processes to drive standardization and effectiveness; better leveraging our size and scale; and driving savings in indirect costs through the implementation of a "procure-to-pay" program.
The Company incurred total pretax expenses of $508 million related to these productivity initiatives since they commenced in the first quarter of 2008. These expenses were recorded in the line item other operating charges. Refer to Note 19 for the impact these charges had on our operating segments. Other direct costs included both internal and external costs associated with the development, communication, administration and implementation of these initiatives and accelerated depreciation on certain fixed assets.
The following table summarizes the balance of accrued expenses related to productivity initiatives and the changes in the accrued amounts (in millions):
|
Severance Pay
and Benefits
|
Outside Services1
|
Other
Direct Costs
|
Total |
||||||||||||
2009 |
|||||||||||||||
Accrued balance as of January 1 |
$ |
14 |
$ |
3 |
$ |
— |
$ |
17 |
|||||||
Costs incurred |
41 |
47 |
19 |
107 |
|||||||||||
Payments |
(37 |
) |
(41 |
) |
(12 |
) |
(90 |
) |
|||||||
Noncash and exchange |
— |
— |
(3 |
) |
(3 |
) |
|||||||||
Accrued balance as of December 31 |
$ |
18 |
$ |
9 |
$ |
4 |
$ |
31 |
|||||||
2010 |
|||||||||||||||
Costs incurred |
$ |
71 |
$ |
58 |
$ |
61 |
$ |
190 |
|||||||
Payments |
(30 |
) |
(61 |
) |
(54 |
) |
(145 |
) |
|||||||
Noncash and exchange |
— |
— |
(2 |
) |
(2 |
) |
|||||||||
Accrued balance as of December 31 |
$ |
59 |
$ |
6 |
$ |
9 |
$ |
74 |
|||||||
2011 |
|||||||||||||||
Costs incurred |
$ |
59 |
$ |
17 |
$ |
80 |
$ |
156 |
|||||||
Payments |
(50 |
) |
(21 |
) |
(71 |
) |
(142 |
) |
|||||||
Noncash and exchange |
(20 |
) |
1 |
(9 |
) |
(28 |
) |
||||||||
Accrued balance as of December 31 |
$ |
48 |
$ |
3 |
$ |
9 |
$ |
60 |
|||||||
1 |
Primarily relate to expenses in connection with legal, outplacement and consulting activities. |
136
Integration Initiatives
Integration of CCE's North American Business
In 2010, we acquired CCE's North American business and began an integration initiative to develop, design and implement our future operating framework. Upon completion of the CCE transaction, we combined the management of the acquired North American business with the management of our existing foodservice business; Minute Maid and Odwalla juice businesses; North America supply chain operations; and Company-owned bottling operations in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, into a unified bottling and customer service organization called Coca-Cola Refreshments, or CCR. In addition, we reshaped our remaining CCNA operations into an organization that primarily provides franchise leadership and consumer marketing and innovation for the North American market. As a result of the transaction and related reorganization, our North American businesses operate as aligned and agile organizations with distinct capabilities, responsibilities and strengths.
The Company incurred total pretax expenses of $358 million and $135 million during 2011 and 2010, respectively, related to this initiative. Other direct costs were primarily related to internal and external costs associated with the development, design and implementation of our future operating framework. Other direct costs also included, among other items, contract termination fees and relocation costs and were recorded in the line item other operating charges. Refer to Note 19 for the impact these charges had on our operating segments. In 2011, we completed this program.
The following table summarizes the balance of accrued expenses related to these integration initiatives and the changes in the accrued amounts since the commencement of the plan (in millions):
|
Severance Pay
and Benefits
|
Outside Services1
|
Other
Direct Costs
|
Total |
||||||||||||
2010 |
|||||||||||||||
Costs incurred |
$ |
45 |
$ |
42 |
$ |
48 |
$ |
135 |
|||||||
Payments |
(1 |
) |
(33 |
) |
(34 |
) |
(68 |
) |
|||||||
Noncash and exchange |
4 |
— |
(2 |
) |
2 |
||||||||||
Accrued balance as of December 31 |
$ |
48 |
$ |
9 |
$ |
12 |
$ |
69 |
|||||||
2011 |
|||||||||||||||
Costs incurred |
$ |
40 |
$ |
91 |
$ |
227 |
$ |
358 |
|||||||
Payments |
(40 |
) |
(89 |
) |
(210 |
) |
(339 |
) |
|||||||
Noncash and exchange |
— |
— |
3 |
3 |
|||||||||||
Accrued balance as of December 31 |
$ |
48 |
$ |
11 |
$ |
32 |
$ |
91 |
|||||||
1 |
Primarily relate to expenses in connection with legal, outplacement and consulting activities. |
Integration of Our German Bottling and Distribution Operations
In 2008, the Company began an integration initiative related to the 18 German bottling and distribution operations acquired in 2007. The Company incurred $67 million, $94 million and $110 million of expenses related to this initiative in 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. The Company has incurred total pretax expenses of $292 million related to this initiative since it commenced, which were recorded in the line item other operating charges and impacted the Bottling Investments operating segment. The expenses recorded in connection with these integration activities have been primarily due to involuntary terminations. The Company had $30 million and $34 million accrued related to these integration costs as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
The Company is currently reviewing other integration and restructuring opportunities within the German bottling and distribution operations, which if implemented will result in additional charges in future periods. However, as of December 31, 2011, the Company has not finalized any additional plans.
Restructuring Initiatives
The Company incurred charges of $52 million, $59 million and $51 million related to other restructuring initiatives during 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. These other restructuring initiatives were outside the scope of the productivity, integration and streamlining initiatives discussed above and were related to individually insignificant activities throughout many of our business units. These charges were recorded in the line item other operating charges. Refer to Note 19 for the impact these charges had on our operating segments.
137
NOTE 19: OPERATING SEGMENTS
As of December 31, 2011, our organizational structure consisted of the following operating segments: Eurasia and Africa; Europe; Latin America; North America; Pacific; Bottling Investments; and Corporate.
Segment Products and Services
The business of our Company is nonalcoholic beverages. Our geographic operating segments (Eurasia and Africa; Europe; Latin America; North America; and Pacific) derive a majority of their revenues from the manufacture and sale of beverage concentrates and syrups and, in some cases, the sale of finished beverages. Our Bottling Investments operating segment is comprised of our Company-owned or consolidated bottling operations, regardless of the geographic location of the bottler, except for bottling operations managed by CCR, which are included in our North America operating segment, and equity income from the majority of our equity method investments. Company-owned or consolidated bottling operations derive the majority of their revenues from the sale of finished beverages. Subsequent to our acquisition of CCE's North American business on October 2, 2010, our North America operating segment began to derive the majority of its net operating revenues from the sale of finished beverages. Refer to Note 2. Generally, bottling and finished products operations produce higher net revenues but lower gross profit margins compared to concentrate and syrup operations.
The following table sets forth the percentage of total net operating revenues related to concentrate operations and finished products operations:
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
|||||
Concentrate operations1
|
39 |
% |
51 |
% |
54 |
% |
||
Finished products operations2,3
|
61 |
49 |
46 |
|||||
Net operating revenues |
100 |
% |
100 |
% |
100 |
% |
||
1 |
Includes concentrates sold by the Company to authorized bottling partners for the manufacture of fountain syrups. The bottlers then typically sell the fountain syrups to wholesalers or directly to fountain retailers. |
2 |
Includes fountain syrups manufactured by the Company, including consolidated bottling operations, and sold to fountain retailers or to authorized fountain wholesalers or bottling partners who resell the fountain syrups to fountain retailers. |
3 |
Includes net operating revenues related to the acquired CCE North American business from October 2, 2010. |
Method of Determining Segment Income or Loss
Management evaluates the performance of our operating segments separately to individually monitor the different factors affecting financial performance. Our Company manages income taxes and certain treasury-related items, such as interest income and expense, on a global basis within the Corporate operating segment. We evaluate segment performance based on income or loss before income taxes.
Geographic Data
The following table provides information related to our net operating revenues (in millions):
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
United States |
$ |
18,699 |
$ |
10,629 |
$ |
8,011 |
|||||
International |
27,843 |
24,490 |
22,979 |
||||||||
Net operating revenues |
$ |
46,542 |
$ |
35,119 |
$ |
30,990 |
|||||
The following table provides information related to our property, plant and equipment — net (in millions):
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
United States |
$ |
8,043 |
$ |
8,251 |
$ |
3,115 |
|||||
International |
6,896 |
6,476 |
6,446 |
||||||||
Property, plant and equipment — net |
$ |
14,939 |
$ |
14,727 |
$ |
9,561 |
|||||
138
Information about our Company's operations by operating segment for the years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009, is as follows (in millions):
|
Eurasia &
Africa
|
Europe |
Latin
America
|
North
America
|
Pacific |
Bottling
Investments
|
Corporate |
Eliminations |
Consolidated |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2011 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net operating revenues: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Third party |
$ |
2,689 |
$ |
4,777 |
$ |
4,403 |
$ |
20,559 |
$ |
5,454 |
1 |
$ |
8,501 |
$ |
159 |
$ |
— |
$ |
46,542 |
||||||||||||||||
Intersegment |
152 |
697 |
287 |
12 |
384 |
90 |
— |
(1,622 |
) |
— |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total net revenues |
2,841 |
5,474 |
4,690 |
20,571 |
5,838 |
8,591 |
159 |
(1,622 |
) |
46,542 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating income (loss) |
1,091 |
3,090 |
2,815 |
2,318 |
2,151 |
224 |
(1,535 |
) |
— |
10,154 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest income |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
483 |
— |
483 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest expense |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
417 |
— |
417 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization |
39 |
109 |
63 |
1,065 |
106 |
403 |
169 |
— |
1,954 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Equity income (loss) — net |
(3 |
) |
33 |
20 |
6 |
1 |
646 |
(13 |
) |
— |
690 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Income (loss) before income taxes |
1,089 |
3,134 |
2,832 |
2,325 |
2,154 |
897 |
(992 |
) |
— |
11,439 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Identifiable operating assets2
|
1,245 |
3,204 |
3 |
2,446 |
33,422 |
2,085 |
8,905 |
3 |
20,293 |
— |
71,600 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Investments4
|
284 |
243 |
475 |
26 |
133 |
7,140 |
73 |
— |
8,374 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Capital expenditures |
86 |
38 |
105 |
1,364 |
92 |
1,039 |
196 |
— |
2,920 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2010 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net operating revenues: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Third party |
$ |
2,426 |
$ |
4,424 |
$ |
3,880 |
$ |
11,140 |
$ |
4,941 |
1 |
$ |
8,216 |
$ |
92 |
$ |
— |
$ |
35,119 |
||||||||||||||||
Intersegment |
130 |
825 |
241 |
65 |
330 |
97 |
— |
(1,688 |
) |
— |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total net revenues |
2,556 |
5,249 |
4,121 |
11,205 |
5,271 |
8,313 |
92 |
(1,688 |
) |
35,119 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating income (loss) |
980 |
2,976 |
2,405 |
1,520 |
2,048 |
227 |
(1,707 |
) |
— |
8,449 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest income |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
317 |
— |
317 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest expense |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
733 |
— |
733 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization |
31 |
106 |
54 |
575 |
101 |
430 |
146 |
— |
1,443 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Equity income (loss) — net |
18 |
33 |
24 |
(4 |
) |
1 |
971 |
(18 |
) |
— |
1,025 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Income (loss) before income taxes |
1,000 |
3,020 |
2,426 |
1,523 |
2,049 |
1,205 |
3,020 |
— |
14,243 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Identifiable operating assets2
|
1,278 |
2,724 |
3 |
2,298 |
32,793 |
1,827 |
8,398 |
3 |
16,018 |
— |
65,336 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Investments4
|
291 |
243 |
379 |
57 |
123 |
6,426 |
66 |
— |
7,585 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Capital expenditures |
59 |
33 |
94 |
711 |
101 |
942 |
275 |
— |
2,215 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2009 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net operating revenues: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Third party |
$ |
1,977 |
$ |
4,308 |
$ |
3,700 |
$ |
8,191 |
$ |
4,533 |
1 |
$ |
8,193 |
$ |
88 |
$ |
— |
$ |
30,990 |
||||||||||||||||
Intersegment |
220 |
895 |
182 |
80 |
342 |
127 |
— |
(1,846 |
) |
— |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total net revenues |
2,197 |
5,203 |
3,882 |
8,271 |
4,875 |
8,320 |
88 |
(1,846 |
) |
30,990 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating income (loss) |
810 |
2,946 |
2,042 |
1,699 |
1,887 |
179 |
(1,332 |
) |
— |
8,231 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest income |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
249 |
— |
249 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest expense |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
355 |
— |
355 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization |
27 |
132 |
52 |
365 |
95 |
424 |
141 |
— |
1,236 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Equity income (loss) — net |
(1 |
) |
20 |
(4 |
) |
(1 |
) |
(23 |
) |
785 |
5 |
— |
781 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Income (loss) before income taxes |
810 |
2,976 |
2,039 |
1,701 |
1,866 |
980 |
(1,426 |
) |
— |
8,946 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Identifiable operating assets2
|
1,155 |
3,047 |
3 |
2,480 |
10,941 |
1,929 |
9,140 |
3 |
13,224 |
— |
41,916 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Investments4
|
331 |
214 |
248 |
8 |
82 |
5,809 |
63 |
— |
6,755 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Capital expenditures |
70 |
68 |
123 |
458 |
91 |
826 |
357 |
— |
1,993 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 |
Net operating revenues in Japan represented approximately 8 percent of consolidated net operating revenues in 2011, 9 percent in 2010 and 10 percent in 2009.
|
2 |
Principally cash and cash equivalents, trade accounts receivable, inventories, goodwill, trademarks and other intangible assets and property, plant and equipment — net. |
3 |
Property, plant and equipment — net in Germany represented approximately 10 percent of consolidated property, plant and equipment — net in 2011, 10 percent in 2010 and 18 percent in 2009.
|
4 |
Principally equity method investments, available-for-sale securities and nonmarketable investments in bottling companies. |
139
In 2011, the results of our operating segments were impacted by the following items:
• |
Operating income (loss) and income (loss) before income taxes were reduced by $12 million for Eurasia and Africa, $25 million for Europe, $4 million for Latin America, $374 million for North America, $4 million for Pacific, $89 million for Bottling Investments and $164 million for Corporate, primarily due to the Company's ongoing productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives as well as costs associated with the merger of Arca and Contal. Refer to Note 18 for additional information on our productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives. Refer to Note 17 for additional information related to the merger of Arca and Contal.
|
• |
Operating income (loss) and income (loss) before income taxes were reduced by $82 million for Pacific and $2 million for North America due to charges associated with the earthquake and tsunami that devastated northern and eastern Japan on March 11, 2011. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Operating income (loss) and income (loss) before income taxes were reduced by $10 million for Corporate due to charges associated with the floods in Thailand that impacted the Company's supply chain operations in the region. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Equity income (loss) — net and income (loss) before income taxes were reduced by $53 million for Bottling Investments, primarily attributable to the Company's proportionate share of asset impairments and restructuring charges recorded by certain of our equity method investees. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Income (loss) before income taxes was increased by a net $417 million for Corporate, primarily due to the gain the Company recognized as a result of the merger of Arca and Contal. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Income (loss) before income taxes was increased by a net $122 million for Corporate, primarily due to gains the Company recognized as a result of an equity method investee issuing additional shares of its own stock during the year at per share amounts greater than the carrying value of the Company's per share investment. These gains were partially offset by charges associated with certain of the Company's equity method investments in Japan. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Income (loss) before income taxes was increased by $102 million for Corporate, primarily due to the gain on the sale of our investment in Embonor, a bottling partner with operations primarily in Chile. Prior to this transaction, the Company accounted for our investment in Embonor under the equity method of accounting. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Income (loss) before income taxes was reduced by $41 million for Corporate due to the impairment of an investment in an entity accounted for under the equity method of accounting. Refer to Note 16 and Note 17.
|
• |
Income (loss) before income taxes was reduced by $17 million for Corporate due to other-than-temporary impairments of certain available-for-sale securities. Refer to Note 16 and Note 17.
|
• |
Income (loss) before income taxes was reduced by $9 million for Corporate due to the net charge we recognized on the repurchase and/or exchange of certain long-term debt assumed in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business as well as the early extinguishment of certain other long-term debt. Refer to Note 10.
|
• |
Income (loss) before income taxes was reduced by $5 million for Corporate due to the finalization of working capital adjustments related to the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE. Refer to Note 2 and Note 17.
|
In 2010, the results of our operating segments were impacted by the following items:
• |
Operating income (loss) and income (loss) before income taxes were reduced by $7 million for Eurasia and Africa, $50 million for Europe, $133 million for North America, $22 million for Pacific, $122 million for Bottling Investments and $485 million for Corporate, primarily due to the Company's ongoing productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives; charitable donations; transaction costs incurred in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business and the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE; and other charges related to bottling activities in Eurasia. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Operating income (loss) and income (loss) before income taxes were reduced by $74 million for North America due to the acceleration of expense associated with certain share-based replacement awards issued in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to Note 12.
|
• |
Equity income (loss) — net and income (loss) before income taxes were reduced by $66 million for Bottling Investments. This net charge was primarily attributable to the Company's proportionate share of unusual tax charges, asset impairments, restructuring charges and transaction costs recorded by equity method investees, which were partially offset by our proportionate share of a foreign currency remeasurement gain recorded by an equity method investee. The components of the net charge were individually insignificant. Refer to Note 17.
|
140
• |
Income (loss) before income taxes was reduced by $23 million for Bottling Investments and $25 million for Corporate due to other-than-temporary impairments and a donation of preferred shares in one of our equity method investees. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Income (loss) before income taxes was increased by $4,978 million for Corporate due to the remeasurement of our equity investment in CCE to fair value upon the close of the transaction. Refer to Note 2.
|
• |
Income (loss) before income taxes was increased by $597 million for Corporate due to the gain on the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE. Refer to Note 2.
|
• |
Income (loss) before income taxes was reduced by $342 million for Corporate related to the premiums paid to repurchase the long-term debt and the costs associated with the settlement of treasury rate locks issued in connection with the debt tender offer. Refer to Note 10.
|
• |
Income (loss) before income taxes was reduced by $265 million for Corporate due to charges related to preexisting relationships with CCE. These charges primarily related to the write-off of our investment in infrastructure programs with CCE. Refer to Note 2.
|
• |
Income (loss) before income taxes was reduced by $103 million for Corporate due to the remeasurement of our Venezuelan subsidiary's net assets. Refer to Note 1.
|
• |
Income (loss) before income taxes was increased by $23 million for Corporate due to the gain on the sale of 50 percent of our investment in Leão Junior. Refer to Note 17.
|
In 2009, the results of our operating segments were impacted by the following items:
• |
Operating income (loss) and income (loss) before income taxes were reduced by $4 million for Eurasia and Africa, $7 million for Europe, $31 million for North America, $1 million for Pacific, $141 million for Bottling Investments and $129 million for Corporate, primarily as a result of the Company's ongoing productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives and asset impairments. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Equity income (loss) — net and income (loss) before income taxes were reduced by $84 million for Bottling Investments and $2 million for Corporate, primarily attributable to the Company's proportionate share of asset impairment and restructuring charges recorded by certain of our equity method investees. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Income (loss) before income taxes was increased by $44 million for Corporate due to realized gains on the sale of equity securities that were classified as available-for-sale. In 2008, the Company recognized an other-than-temporary impairment related to these securities. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Income (loss) before income taxes was reduced by $27 million for Corporate due to an other-than-temporary impairment of a cost method investment. Refer to Note 17.
|
NOTE 20: NET CHANGE IN OPERATING ASSETS AND LIABILITIES
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities attributable to the net change in operating assets and liabilities is composed of the following (in millions):
Year Ended December 31, |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
||||||||
(Increase) decrease in trade accounts receivable |
$ |
(562 |
) |
$ |
(41 |
) |
$ |
(404 |
) |
||
(Increase) decrease in inventories |
(447 |
) |
182 |
(50 |
) |
||||||
(Increase) decrease in prepaid expenses and other assets |
(350 |
) |
(148 |
) |
(332 |
) |
|||||
Increase (decrease) in accounts payable and accrued expenses |
63 |
656 |
319 |
||||||||
Increase (decrease) in accrued taxes |
(132 |
) |
(266 |
) |
81 |
||||||
Increase (decrease) in other liabilities |
(465 |
) |
(13 |
) |
(178 |
) |
|||||
Net change in operating assets and liabilities |
$ |
(1,893 |
) |
$ |
370 |
$ |
(564 |
) |
|||
141
REPORT OF MANAGEMENT
Management's Responsibility for the Financial Statements
Management of the Company is responsible for the preparation and integrity of the consolidated financial statements appearing in our annual report on Form 10-K. The financial statements were prepared in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles appropriate in the circumstances and, accordingly, include certain amounts based on our best judgments and estimates. Financial information in this annual report on Form 10-K is consistent with that in the financial statements.
Management of the Company is responsible for establishing and maintaining a system of internal controls and procedures to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of the consolidated financial statements. Our internal control system is supported by a program of internal audits and appropriate reviews by management, written policies and guidelines, careful selection and training of qualified personnel and a written Code of Business Conduct adopted by our Company's Board of Directors, applicable to all officers and employees of our Company and subsidiaries. In addition, our Company's Board of Directors adopted a written Code of Business Conduct for Non-Employee Directors which reflects the same principles and values as our Code of Business Conduct for officers and employees but focuses on matters of relevance to non-employee Directors.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements and, even when determined to be effective, can only provide reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management of the Company is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 ("Exchange Act"). Management assessed the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2011. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission ("COSO") in Internal Control — Integrated Framework. Based on this assessment, management believes that the Company maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2011.
The Company's independent auditors, Ernst & Young LLP, a registered public accounting firm, are appointed by the Audit Committee of the Company's Board of Directors, subject to ratification by our Company's shareowners. Ernst & Young LLP has audited and reported on the consolidated financial statements of The Coca-Cola Company and subsidiaries and the Company's internal control over financial reporting. The reports of the independent auditors are contained in this annual report.
142
Audit Committee's Responsibility
The Audit Committee of our Company's Board of Directors, composed solely of Directors who are independent in accordance with the requirements of the New York Stock Exchange listing standards, the Exchange Act, and the Company's Corporate Governance Guidelines, meets with the independent auditors, management and internal auditors periodically to discuss internal controls and auditing and financial reporting matters. The Audit Committee reviews with the independent auditors the scope and results of the audit effort. The Audit Committee also meets periodically with the independent auditors and the chief internal auditor without management present to ensure that the independent auditors and the chief internal auditor have free access to the Audit Committee. Our Audit Committee's Report can be found in the Company's 2012 Proxy Statement.
 |
 |
|
Muhtar Kent |
Kathy N. Waller |
|
|
Chairman of the Board of Directors,
Chief Executive Officer and President
February 23, 2012
|
Vice President and Controller
February 23, 2012
|
|
 |
||
|
Gary P. Fayard
Executive Vice President
and Chief Financial Officer
February 23, 2012
|
||
143
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Board of Directors and Shareowners
The Coca-Cola Company
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of The Coca-Cola Company and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, and the related consolidated statements of income, shareowners' equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2011. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of The Coca-Cola Company and subsidiaries at December 31, 2011 and 2010, and the consolidated results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2011, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), The Coca-Cola Company and subsidiaries' internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2011, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated February 23, 2012 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.

Atlanta, Georgia
February 23, 2012
144
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Board of Directors and Shareowners
The Coca-Cola Company
We have audited The Coca-Cola Company and subsidiaries' internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2011, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (the COSO criteria). The Coca-Cola Company and subsidiaries' management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, The Coca-Cola Company and subsidiaries maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2011, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of The Coca-Cola Company and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2011 and 2010, and the related consolidated statements of income, shareowners' equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2011, and our report dated February 23, 2012 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.

Atlanta, Georgia
February 23, 2012
145
Quarterly Data (Unaudited)
|
First
Quarter
|
Second
Quarter
|
Third
Quarter
|
Fourth
Quarter
|
Full Year |
||||||||||||||||
(In millions except per share data) |
||||||||||||||||||||
2011 |
||||||||||||||||||||
Net operating revenues |
$ |
10,517 |
$ |
12,737 |
$ |
12,248 |
$ |
11,040 |
$ |
46,542 |
||||||||||
Gross profit |
6,568 |
7,748 |
7,373 |
6,637 |
28,326 |
|||||||||||||||
Net income attributable to shareowners of The Coca-Cola Company |
1,900 |
2,797 |
2,221 |
1,654 |
8,572 |
|||||||||||||||
Basic net income per share |
$ |
0.83 |
$ |
1.22 |
$ |
0.97 |
$ |
0.73 |
$ |
3.75 |
||||||||||
Diluted net income per share |
$ |
0.82 |
$ |
1.20 |
$ |
0.95 |
$ |
0.72 |
$ |
3.69 |
||||||||||
2010 |
||||||||||||||||||||
Net operating revenues |
$ |
7,525 |
$ |
8,674 |
$ |
8,426 |
$ |
10,494 |
1 |
$ |
35,119 |
1 |
||||||||
Gross profit |
4,984 |
5,719 |
5,508 |
6,215 |
1 |
22,426 |
1 |
|||||||||||||
Net income attributable to shareowners of The Coca-Cola Company |
1,614 |
2,369 |
2,055 |
5,771 |
1 |
11,809 |
1 |
|||||||||||||
Basic net income per share |
$ |
0.70 |
$ |
1.03 |
$ |
0.89 |
$ |
2.50 |
1 |
$ |
5.12 |
1 |
||||||||
Diluted net income per share |
$ |
0.69 |
$ |
1.02 |
$ |
0.88 |
$ |
2.46 |
1 |
$ |
5.06 |
1,2 |
||||||||
1 |
Amounts include the impacts of our acquisition of CCE's North American business and the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE. Refer to Note 2. |
2 |
The sum of the quarterly diluted net income per share amounts does not agree to the full year diluted net income per share. We calculate net income per share based on the weighted-average number of outstanding shares during the reporting period. The average number of shares fluctuates throughout the year and can therefore produce a full year result that does not agree to the sum of the individual quarters. |
Our reporting period ends on the Friday closest to the last day of the quarterly calendar period. Our fiscal year ends on December 31 regardless of the day of the week on which December 31 falls.
The Company's first quarter 2011 results were impacted by one less shipping day compared to the first quarter of 2010. Furthermore, the Company recorded the following transactions which impacted results:
• |
Charges of $1 million for Eurasia and Africa, $1 million for Europe, $111 million for North America, $1 million for Pacific, $21 million for Bottling Investments and $27 million for Corporate due to the Company's ongoing productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives. Refer to Note 17 and Note 18.
|
• |
Gain of $102 million for Corporate due to the sale of our investment in Embonor, a bottling partner with operations primarily in Chile. Prior to this transaction, the Company accounted for our investment in Embonor under the equity method of accounting. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Charge of $79 million for Pacific associated with the earthquake and tsunami that devastated northern and eastern Japan on March 11, 2011. This charge was primarily related to the Company's charitable donations in support of relief and rebuilding efforts in Japan and funds provided to certain bottling partners in the affected regions. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Charge of $19 million for North America due to the amortization of favorable supply contracts acquired in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Charge of $4 million for Corporate related to premiums paid to repurchase certain long-term debt assumed in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to Note 10.
|
• |
Charge of $4 million for Bottling Investments, primarily attributable to the Company's proportionate share of restructuring charges recorded by an equity method investee. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
A net tax charge of $3 million related to amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties. Refer to Note 14.
|
In the second quarter of 2011, the Company recorded the following transactions which impacted results:
• |
Charges of $8 million for Eurasia and Africa, $2 million for Europe, $1 million for Latin America, $66 million for North
|
146
America, $23 million for Bottling Investments and $47 million for Corporate, primarily due to the Company's ongoing productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives as well as costs associated with the merger of Arca and Contal. Refer to Note 17 and Note 18.
• |
A net gain of $417 million for Corporate, primarily due to the merger of Arca and Contal. Refer to Note 16 and Note 17.
|
• |
Charge of $38 million for Corporate due to the impairment of an investment in an entity accounted for under the equity method of accounting. Refer to Note 16 and Note 17.
|
• |
Charge of $4 million for Pacific due to the earthquake and tsunami that devastated northern and eastern Japan on March 11, 2011. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
A net gain of $1 million for Corporate related to the repurchase of certain long-term debt we assumed in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to Note 10.
|
• |
A net tax charge of $16 million related to amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties. Refer to Note 14.
|
In the third quarter of 2011, the Company recorded the following transactions which impacted results:
• |
Charges of $2 million for Europe, $2 million for Latin America, $52 million for North America, $2 million for Pacific, $14 million for Bottling Investments and $26 million for Corporate, due to the Company's ongoing productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives as well as costs associated with the merger of Arca and Contal. Refer to Note 17 and Note 18.
|
• |
Charge of $36 million for Bottling Investments, primarily attributable to the Company's proportionate share of asset impairments and restructuring charges recorded by certain of our equity method investees. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
A net charge of $5 million for Corporate due to the repurchase and/or exchange of certain long-term debt assumed in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to Note 10.
|
• |
Charge of $5 million for Corporate due to the finalization of working capital adjustments related to the sale of all our ownership interests in our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Charge of $3 million for Corporate due to the impairment of an investment in an entity accounted for under the equity method of accounting. Refer to Note 16 and Note 17.
|
• |
A net charge of $1 million associated with the earthquake and tsunami that devastated northern and eastern Japan on March 11, 2011. This net charge included a charge of $2 million for North America and a benefit of $1 million for Pacific. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
A net tax benefit of $4 million related to amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties. Refer to Note 14.
|
The Company's fourth quarter 2011 results were impacted by one additional shipping day compared to the fourth quarter of 2010. Furthermore, the Company recorded the following transactions which impacted results:
• |
Charges of $3 million for Eurasia and Africa, $20 million for Europe, $1 million for Latin America, $145 million for North America, $1 million for Pacific, $31 million for Bottling Investments and $64 million for Corporate, primarily due to the Company's ongoing productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives. Refer to Note 17 and Note 18.
|
• |
A net gain of $122 million for Corporate, primarily due to gains the Company recognized as a result of an equity method investee issuing additional shares of its own stock during the period at per share amounts greater than the carrying value of the Company's per share investment. These gains were partially offset by charges associated with certain of the Company's equity method investments in Japan. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Charge of $17 million for Corporate due to other-than-temporary impairments of certain available-for-sale securities. Refer to Note 16 and Note 17.
|
• |
Charge of $13 million for Bottling Investments, primarily attributable to the Company's proportionate share of asset impairments and restructuring charges recorded by certain of our equity method investees. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Charge of $10 million for Corporate due to the floods in Thailand that impacted the Company's supply chain operations in the region. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Charge of $1 million for Corporate due to the early extinguishment of certain long-term debt. This debt existed prior to the Company's acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to Note 10.
|
• |
A net tax benefit of $22 million related to amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties. Refer to Note 14.
|
147
In the first quarter of 2010, the Company recorded the following transactions which impacted results:
• |
Charges of $1 million for Eurasia and Africa, $28 million for Europe, $4 million for North America, $33 million for Bottling Investments and $30 million for Corporate, primarily due to the Company's ongoing productivity initiatives, restructuring charges and transaction costs. Refer to Note 17 and Note 18.
|
• |
Charge of $103 million for Corporate due to the remeasurement of our Venezuelan subsidiary's net assets. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Charge of $29 million for Bottling Investments, primarily attributable to the Company's proportionate share of asset impairment charges and restructuring costs recorded by equity method investees. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Charges of $23 million for Bottling Investments and $3 million for Corporate, primarily due to other-than-temporary impairments of available-for-sale securities. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
A tax charge of $14 million related to new legislation that changed the tax treatment of Medicare Part D subsidies. Refer to Note 14.
|
• |
A net tax benefit of $1 million related to amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties. Refer to Note 14.
|
In the second quarter of 2010, the Company recorded the following transactions which impacted results:
• |
Charges of $2 million for Eurasia and Africa, $2 million for Europe, $6 million for North America, $5 million for Pacific, $11 million for Bottling Investments and $52 million for Corporate, primarily due to the Company's ongoing productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives and transaction costs. Refer to Note 17 and Note 18.
|
• |
Charge of $16 million for Bottling Investments, primarily attributable to the Company's proportionate share of unusual tax charges and transaction costs recorded by equity method investees. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
A net tax charge of $16 million related to amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties. Refer to Note 14.
|
In the third quarter of 2010, the Company recorded the following transactions which impacted results:
• |
Charges of $1 million for Eurasia and Africa, $13 million for Europe, $8 million for Pacific, $12 million for Bottling Investments and $68 million for Corporate, primarily due to the Company's ongoing productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives and transaction costs incurred in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business and the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE. These charges were partially offset by a $2 million benefit for North America due to the refinement of previously established restructuring accruals. Refer to Note 17 and Note 18.
|
• |
Charge of $10 million for Bottling Investments. This net charge was primarily attributable to the Company's proportionate share of transaction costs recorded by CCE, which was partially offset by our proportionate share of a foreign currency remeasurement gain recorded by an equity method investee. The components of the net charge were individually insignificant. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Gain of $23 million for Corporate due to the sale of 50 percent of our investment in Leão Junior. Refer to Note 2 and Note 17.
|
• |
A net tax charge of $13 million related to amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties. Refer to Note 14.
|
In the fourth quarter of 2010, the Company recorded the following transactions which impacted results:
• |
Charges of $3 million for Eurasia and Africa, $7 million for Europe, $125 million for North America, $9 million for Pacific, $66 million for Bottling Investments and $335 million for Corporate, primarily due to the Company's productivity, integration and restructuring initiatives, charitable donations, transaction costs incurred in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business and the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE and other charges related to bottling activities in Eurasia. Refer to Note 17 and Note 18.
|
• |
Benefit of $4,978 million for Corporate due to the remeasurement of our equity investment in CCE to fair value upon the close of the transaction. Refer to Note 2 and Note 17.
|
• |
Gain of $597 million for Corporate due to the sale of our Norwegian and Swedish bottling operations to New CCE. Refer to Note 2 and Note 17.
|
• |
Charge of $342 million for Corporate related to the premiums paid to repurchase certain long-term debt and the costs associated with the settlement of treasury rate locks issued in connection with the debt tender offer. Refer to Note 10.
|
148
• |
Charge of $265 million for Corporate due to expenses related to preexisting relationships with CCE. These expenses primarily related to the write-off of our investment in infrastructure programs with CCE. Refer to Note 2 and Note 17.
|
• |
Charge of $74 million for North America due to the acceleration of expense associated with certain share-based replacement awards issued in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Charge of $22 million for Corporate due to an other-than-temporary impairment of an equity method investment and a donation of preferred shares in one of our equity method investees. Refer to Note 16 and Note 17.
|
• |
Charge of $20 million for North America due to the amortization of favorable supply contracts acquired in connection with our acquisition of CCE's North American business. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
Charge of $11 million for Bottling Investments, primarily attributable to the Company's proportionate share of restructuring charges recorded by equity method investees. Refer to Note 17.
|
• |
A tax charge of $260 million primarily related to deferred tax expense on certain current year undistributed foreign earnings that are not considered indefinitely reinvested. Refer to Note 14.
|
• |
A tax benefit of $44 million primarily due to the impact that tax rate changes had on certain deferred tax assets. Refer to Note 14.
|
• |
A net tax charge of $38 million related to amounts required to be recorded for changes to our uncertain tax positions, including interest and penalties. Refer to Note 14.
|
149
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
Not applicable.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The Company, under the supervision and with the participation of its management, including the Chief Executive Officer and the Chief Financial Officer, evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of the Company's "disclosure controls and procedures" (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Exchange Act")) as of the end of the period covered by this report. Based on that evaluation, the Chief Executive Officer and the Chief Financial Officer concluded that the Company's disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of December 31, 2011.
Report of Management on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting and Attestation Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The report of management on our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2011 and the attestation report of our independent registered public accounting firm on our internal control over financial reporting are set forth in Part II, "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" in this report.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There have been no changes in the Company's internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2011 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company's internal control over financial reporting.
Additional Information
The Company is in the process of several productivity and transformation initiatives that include redesigning several key business processes in a number of areas. As business processes change related to these transformation initiatives, the Company identifies, documents and evaluates controls to ensure controls over our financial reporting remain strong.
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
Not applicable.
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
The information under the principal headings "ELECTION OF DIRECTORS" and "SECTION 16(A) BENEFICIAL OWNERSHIP REPORTING COMPLIANCE," the information under the subheading "Codes of Business Conduct" under the principal heading "CORPORATE GOVERNANCE," and the information regarding the Audit Committee under the subheading “Board Meetings and Committees” under the principal heading "CORPORATE GOVERNANCE," in the Company's 2012 Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference. See Item X in Part I of this report for information regarding executive officers of the Company.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The information under the principal headings "DIRECTOR COMPENSATION," "COMPENSATION DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS," "REPORT OF THE COMPENSATION COMMITTEE," "COMPENSATION COMMITTEE INTERLOCKS AND INSIDER PARTICIPATION" and "EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION" in the Company's 2012 Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
The information under the principal headings "EQUITY COMPENSATION PLAN INFORMATION" and "OWNERSHIP OF EQUITY SECURITIES OF THE COMPANY" in the Company's 2012 Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
150
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
The information under the subheading "Independence and Related Person Transactions" under the principal heading "CORPORATE GOVERNANCE" in the Company's 2012 Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES
The information under the subheadings "Audit Fees and All Other Fees" and "Audit Committee Pre-Approval of Audit and Permissible Non-Audit Services of Independent Auditors" below the principal heading "RATIFICATION OF THE APPOINTMENT OF ERNST & YOUNG LLP AS INDEPENDENT AUDITORS" in the Company's 2012 Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
(a) |
The following documents are filed as part of this report: |
1.Financial Statements:
Consolidated Statements of Income — Years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009.
Consolidated Balance Sheets — December 31, 2011 and 2010.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows — Years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009.
Consolidated Statements of Shareowners' Equity — Years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting.
2.Financial Statement Schedules:
The schedules for which provision is made in the applicable accounting regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC") are not required under the related instructions or are inapplicable and, therefore, have been omitted.
3.Exhibits
In reviewing the agreements included as exhibits to this report, please remember they are included to provide you with information regarding their terms and are not intended to provide any other factual or disclosure information about the Company or the other parties to the agreements. The agreements contain representations, warranties, covenants and conditions by or of each of the parties to the applicable agreement. These representations, warranties, covenants and conditions have been made solely for the benefit of the other parties to the applicable agreement and:
• |
should not in all instances be treated as categorical statements of fact, but rather as a way of allocating the risk to one of the parties if those statements prove to be inaccurate; |
• |
may have been qualified by disclosures that were made to the other party in connection with the negotiation of the applicable agreement, which disclosures are not necessarily reflected in the agreement; |
• |
may apply standards of materiality in a way that is different from what may be viewed as material to you or other investors; and |
• |
were made only as of the date of the applicable agreement or such other date or dates as may be specified in the agreement and are subject to more recent developments. |
Accordingly, these representations and warranties may not describe the actual state of affairs as of the date they were made or at any other time. Additional information about the Company may be found elsewhere in this report and the Company's other public filings, which are available without charge through the SEC's website at http://www.sec.gov.
151
Exhibit No.
(With regard to applicable cross-references in the list of exhibits below, the Company's Current, Quarterly and Annual Reports are filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the "SEC") under File No. 001-02217; and Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc.'s (formerly known as Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc.) Current, Quarterly and Annual Reports are filed with the SEC under File No. 01-09300).
2.1.1 |
Business Separation and Merger Agreement, dated as of February 25, 2010, by and among Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc., International CCE, Inc., The Coca-Cola Company and Cobalt Subsidiary LLC. |
||
Exhibit I |
Tax Sharing Agreement |
||
Exhibit II |
Employee Matters Agreement |
||
Exhibit III |
Form of Corporate Name Letter |
||
Exhibit IV |
Form of Transition Services Agreement |
||
Exhibit V-1 |
Bottler's Agreement Jurisdictions |
||
Exhibit V-2 |
Form of Bottler's Agreement |
||
— incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 2.1 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 3, 2010. In accordance with Item 601(b)(2) of Regulation S-K, certain schedules have not been filed. The Company hereby agrees to furnish supplementally a copy of any omitted schedule to the SEC upon request. |
|||
2.1.2 |
Amendment No. 1, dated as of September 6, 2010, to the Business Separation and Merger Agreement, dated as of February 25, 2010, by and among Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc., International CCE Inc., the Company and Cobalt Subsidiary LLC — incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on September 7, 2010. |
||
2.2 |
Tax Sharing Agreement, dated as of February 25, 2010, by and among The Coca-Cola Company, Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. and International CCE, Inc. (included as Exhibit I to the Business Separation and Merger Agreement) — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 2.2 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 3, 2010. |
||
2.3 |
Employee Matters Agreement, dated as of February 25, 2010, by and among The Coca-Cola Company, Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. and International CCE, Inc. (included as Exhibit II to the Business Separation and Merger Agreement) — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 2.3 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 3, 2010. |
||
2.4 |
Letter Agreement, dated as of February 25, 2010, by and between the Company and Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 2.4 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 3, 2010. |
||
2.5 |
Share Purchase Agreement, dated as of March 20, 2010, by and among The Coca-Cola Company, Bottling Holdings (Luxembourg) s.a.r.l., Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. and International CCE, Inc. |
||
Exhibit I |
Form of Corporate Name Letter |
||
Exhibit II |
Form of Bottler's Agreement |
||
— incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 2.1 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 22, 2010. In accordance with Item 601(b)(2) of Regulation S-K, certain schedules have not been filed. The Company hereby agrees to furnish supplementally a copy of any omitted schedule to the SEC upon request. |
|||
3.1 |
Certificate of Incorporation of the Company, including Amendment of Certificate of Incorporation, effective May 1, 1996 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3 of the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 1996. |
||
3.2 |
By-Laws of the Company, as amended and restated through April 17, 2008 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.2 of the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 27, 2008. |
||
4.1 |
As permitted by the rules of the SEC, the Company has not filed certain instruments defining the rights of holders of long-term debt of the Company or consolidated subsidiaries under which the total amount of securities authorized does not exceed 10 percent of the total assets of the Company and its consolidated subsidiaries. The Company agrees to furnish to the SEC, upon request, a copy of any omitted instrument. |
||
4.2 |
Amended and Restated Indenture, dated as of April 26, 1988, between the Company and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as successor to Bankers Trust Company, as trustee — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company's Registration Statement on Form S-3 (Registration No. 33-50743) filed on October 25, 1993. |
||
152
4.3 |
First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of February 24, 1992, to Amended and Restated Indenture, dated as of April 26, 1988, between the Company and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as successor to Bankers Trust Company, as trustee — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Company's Registration Statement on Form S-3 (Registration No. 33-50743) filed on October 25, 1993. |
||
4.4 |
Second Supplemental Indenture, dated as of November 1, 2007, to Amended and Restated Indenture, dated as of April 26, 1988, as amended, between the Company and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as successor to Bankers Trust Company, as trustee — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.3 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 5, 2009. |
||
4.5 |
Form of Note for 5.350% Notes due November 15, 2017 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed October 31, 2007. |
||
4.6 |
Form of Note for 3.625% Notes due March 15, 2014 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.4 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 5, 2009. |
||
4.7 |
Form of Note for 4.875% Notes due March 15, 2019 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.5 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 5, 2009. |
||
4.8 |
Form of Note for Floating Rate Notes due May 15, 2012 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.4 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed November 18, 2010. |
||
4.9 |
Form of Note for 0.750% Notes due November 15, 2013 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.5 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed November 18, 2010. |
||
4.10 |
Form of Note for 1.500% Notes due November 15, 2015 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.6 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed November 18, 2010. |
||
4.10.1 |
Form of Note for 1.500% Notes due November 15, 2015 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.7 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed November 18, 2010. |
||
4.11 |
Form of Exchange and Registration Rights Agreement among the Company, the representatives of the initial purchasers of the Notes and the other parties named therein — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed August 8, 2011. |
||
4.12 |
Form of Note for 1.80% Notes due September 1, 2016 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.13 to the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2011. |
||
4.13 |
Form of Note for 3.30% Notes due September 1, 2021 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.14 to the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2011. |
||
10.1 |
Supplemental Disability Plan of the Company, as amended and restated effective January 1, 2003 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2002.* |
||
10.2 |
Performance Incentive Plan of the Company, as amended and restated as of February 16, 2011 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.7 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 17, 2011.* |
||
10.3.1 |
1999 Stock Option Plan of the Company, as amended and restated through February 16, 2011 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 17, 2011.*
|
||
10.3.2 |
Form of Stock Option Agreement in connection with the 1999 Stock Option Plan of the Company — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 99.1 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 14, 2007.* |
||
10.3.3 |
Form of Stock Option Agreement in connection with the 1999 Stock Option Plan of the Company, as adopted December 12, 2007 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.8 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 21, 2008.* |
||
10.3.4 |
Form of Stock Option Agreement in connection with the 1999 Stock Option Plan of the Company, as adopted February 18, 2009 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.5 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 18, 2009.* |
||
10.4.1 |
2002 Stock Option Plan of the Company, amended and restated through February 18, 2009 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 18, 2009.* |
||
10.4.2 |
Form of Stock Option Agreement in connection with the 2002 Stock Option Plan, as amended — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 99.1 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 8, 2004.* |
||
10.4.3 |
Form of Stock Option Agreement in connection with the 2002 Stock Option Plan, as adopted December 12, 2007 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.9 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on February 21, 2008.* |
||
153
10.4.4 |
Form of Stock Option Agreement in connection with the 2002 Stock Option Plan, as adopted February 18, 2009 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.6 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on February 18, 2009.* |
||
10.5.1 |
2008 Stock Option Plan of the Company, as amended and restated, effective February 16, 2011 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on February 17, 2011.*
|
||
10.5.2 |
Form of Stock Option Agreement for grants under the Company's 2008 Stock Option Plan — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed July 16, 2008.* |
||
10.5.3 |
Form of Stock Option Agreement for grants under the Company's 2008 Stock Option Plan, as adopted February 18, 2009 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.7 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 18, 2009.* |
||
10.6 |
1983 Restricted Stock Award Plan of the Company, as amended and restated through February 16, 2011 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.3 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on February 17, 2011.* |
||
10.7.1 |
1989 Restricted Stock Award Plan of the Company, as amended and restated through February 16, 2011 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 17, 2011.*
|
||
10.7.2 |
Form of Restricted Stock Agreement (Performance Share Unit Agreement) in connection with the 1989 Restricted Stock Award Plan of the Company, as adopted December 12, 2007 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.5 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 21, 2008.* |
||
10.7.3 |
Form of Restricted Stock Agreement (Performance Share Unit Agreement) for France in connection with the 1989 Restricted Stock Award Plan of the Company, as adopted December 12, 2007 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.6 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 21, 2008.* |
||
10.7.4 |
Form of Restricted Stock Agreement in connection with The Coca-Cola Company 1989 Restricted Stock Award Plan, as adopted February 17, 2010 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on February 18, 2010. * |
||
10.7.5 |
Form of Restricted Stock Agreement (Performance Share Unit Agreement) in connection with The Coca-Cola Company 1989 Restricted Stock Award Plan, as adopted February 17, 2010 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on February 18, 2010.* |
||
10.7.6 |
Form of Restricted Stock Agreement (Performance Share Unit Agreement) for France in connection with The Coca-Cola Company 1989 Restricted Stock Award Plan, as adopted February 17, 2010 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.3 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on February 18, 2010.* |
||
10.7.7 |
Form of Restricted Stock Agreement (Performance Share Unit Agreement) in connection with the 1989 Restricted Stock Award Plan of the Company, as adopted February 16, 2011 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.5 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 17, 2011.* |
||
10.7.8 |
Form of Restricted Stock Agreement (Performance Share Unit Agreement) for France in connection with the 1989 Restricted Stock Award Plan of the Company, as adopted February 16, 2011 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.6 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 17, 2011.* |
||
10.8.1 |
Compensation Deferral & Investment Program of the Company, as amended, including Amendment Number Four, dated November 28, 1995 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.13 of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 1995.* |
||
10.8.2 |
Amendment Number Five to the Compensation Deferral & Investment Program of the Company, effective as of January 1, 1998 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.8.2 of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 1997.* |
||
10.8.3 |
Amendment Number Six to the Compensation Deferral & Investment Program of the Company, dated as of January 12, 2004, effective January 1, 2004 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.9.3 of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2003.* |
||
10.9 |
[RESERVED] |
||
10.10 |
Supplemental Pension Plan, Amended and Restated Effective January 1, 2010 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.10.6 of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2009.* |
||
10.11 |
The Coca-Cola Company Supplemental 401(k) Plan (f/k/a the Supplemental Thrift Plan of the Company), Amended and Restated Effective January 1, 2012, dated December 14, 2011.* |
||
10.12 |
The Coca-Cola Company Supplemental Cash Balance Plan, effective January 1, 2012.* |
||
154
10.13 |
The Coca-Cola Company Compensation and Deferred Compensation Plan for Non-Employee Directors, effective January 1, 2009 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.8 of the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended April 3, 2009.* |
||
10.14 |
Long-Term Performance Incentive Plan of the Company, as amended and restated effective December 13, 2006 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.14 of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010.* |
||
10.15 |
Executive Incentive Plan of the Company, adopted as of February 14, 2001 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.19 of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2000.* |
||
10.16 |
Deferred Compensation Plan of the Company, as amended and restated December 8, 2010 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.16 of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010.* |
||
10.17 |
The Coca-Cola Export Corporation Employee Share Plan, effective as of March 13, 2002 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.31 of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2002.* |
||
10.18 |
Employees' Savings and Share Ownership Plan of Coca-Cola Ltd., effective as of January 1, 1990 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.32 of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2002.* |
||
10.19 |
Share Purchase Plan — Denmark, effective as of 1991 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.33 of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2002.* |
||
10.20.1 |
The Coca-Cola Company Benefits Plan for Members of the Board of Directors, as amended and restated through April 14, 2004 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2004.* |
||
10.20.2 |
Amendment Number One to the Company's Benefits Plan for Members of the Board of Directors, dated December 16, 2005 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.31.2 of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005.* |
||
10.21 |
Employment Agreement, dated as of February 20, 2003, between the Company and José Octavio Reyes — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.43 of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2004.* |
||
10.22 |
The Coca-Cola Company Severance Pay Plan, As Amended and Restated Effective January 1, 2012, dated December 14, 2011.* |
||
10.23 |
Order Instituting Cease and Desist Proceedings, Making Findings and Imposing a Cease-and-Desist Order Pursuant to Section 8A of the Securities Act of 1933 and Section 21C of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 99.2 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 18, 2005. |
||
10.24 |
Offer of Settlement of The Coca-Cola Company — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 99.2 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 18, 2005. |
||
10.25 |
Employment Agreement, effective as of May 1, 2005, between Refreshment Services S.A.S. and Dominique Reiniche, dated September 7, 2006 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 99.1 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on September 12, 2006.* |
||
10.26 |
Refreshment Services S.A.S. Defined Benefit Plan, dated September 25, 2006 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.3 of the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 29, 2006.* |
||
10.27 |
Share Purchase Agreement among Coca-Cola South Asia Holdings, Inc. and San Miguel Corporation, San Miguel Beverages (L) Pte Limited and San Miguel Holdings Limited in connection with the Company's purchase of Coca-Cola Bottlers Philippines, Inc., dated December 23, 2006 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 99.1 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 29, 2006. |
||
10.28 |
Cooperation Agreement between Coca-Cola South Asia Holdings, Inc. and San Miguel Corporation in connection with the Company's purchase of Coca-Cola Bottlers Philippines, Inc., dated December 23, 2006 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 99.2 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 29, 2006. |
||
10.29.1 |
Offer Letter, dated July 20, 2007, from the Company to Joseph V. Tripodi, including Agreement on Confidentiality, Non-Competition and Non-Solicitation, dated July 20, 2007 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 28, 2007.* |
||
10.29.2 |
Agreement between the Company and Joseph V. Tripodi, dated December 15, 2008 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.47.2 of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008.* |
||
155
10.30 |
Letter, dated July 17, 2008, to Muhtar Kent — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed July 21, 2008.* |
||
10.31 |
Separation Agreement between the Company and Robert Leechman, dated February 24, 2009, including form of Full and Complete Release and Agreement on Competition, Trade Secrets and Confidentiality — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.9 of the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended April 3, 2009.* |
||
10.32 |
Separation Agreement between the Company and Cynthia McCague, dated June 22, 2009 (effective as of July 22, 2009), including form of Full and Complete Release and Agreement on Competition, Trade Secrets and Confidentiality and summary of anticipated consulting agreement — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended October 2, 2009.* |
||
10.33 |
Letter of Understanding between the Company and Ceree Eberly, dated October 26, 2009, including Agreement on Confidentiality, Non-Competition and Non-Solicitation, dated November 1, 2009 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.47 of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2009.* |
||
10.34.1 |
The Coca-Cola Export Corporation Overseas Retirement Plan, as amended and restated, effective October 1, 2007 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.55 of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008.* |
||
10.34.2 |
Amendment Number One to The Coca-Cola Export Corporation Overseas Retirement Plan, as Amended and Restated Effective October 1, 2007, dated September 29, 2011.* |
||
10.34.3 |
Amendment Number Two to The Coca-Cola Export Corporation Overseas Retirement Plan, as Amended and Restated Effective October 1, 2007, dated November 14, 2011.* |
||
10.35.1 |
The Coca-Cola Export Corporation International Thrift Plan, as amended and restated, effective January 1, 2011 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.8 of the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended April 1, 2011.* |
||
10.35.2 |
Amendment Number One to The Coca-Cola Export Corporation International Thrift Plan, as Amended and Restated, Effective January 1, 2011, dated September 20, 2011.* |
||
10.36 |
Letter Agreement, dated as of June 7, 2010, between The Coca-Cola Company and Dr Pepper Seven-Up, Inc. — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 7, 2010. |
||
10.37 |
[RESERVED] |
||
10.38 |
Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. Stock Deferral Plan — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to the Company's Registration Statement on Form S-3 (Registration No. 333-169724) filed on October 1, 2010.* |
||
10.39 |
Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. 1997 Stock Option Plan — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to the Company's Registration Statement on Form S-8 (Registration No. 333-169722) filed on October 1, 2010.* |
||
10.40 |
Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. 1999 Stock Option Plan — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to the Company's Registration Statement on Form S-8 (Registration No. 333-169722) filed on October 1, 2010.* |
||
10.41 |
Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. 2001 Restricted Stock Award Plan — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 99.3 to the Company's Registration Statement on Form S-8 (Registration No. 333-169722) filed on October 1, 2010.* |
||
10.42 |
Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. 2001 Stock Option Plan — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 99.4 to the Company's Registration Statement on Form S-8 (Registration No. 333-169722) filed on October 1, 2010.* |
||
10.43 |
Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. 2004 Stock Award Plan — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 99.5 to the Company's Registration Statement on Form S-8 (Registration No. 333-169722) filed on October 1, 2010.* |
||
10.44.1 |
Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. 2007 Incentive Award Plan — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 99.6 to the Company's Registration Statement on Form S-8 (Registration No. 333-169722) filed on October 1, 2010.* |
||
10.44.2 |
Form of 2007 Stock Option Agreement (Senior Officers) under the Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. 2007 Incentive Award Plan — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.32 to Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc.'s (formerly known as Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc.) Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2007.* |
||
10.44.3 |
Form of Stock Option Agreement (Chief Executive Officer and Senior Officers) under the Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. 2007 Incentive Award Plan for Awards after October 29, 2008 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.16.4 to Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc.'s (formerly known as Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc.) Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008.* |
||
156
10.44.4 |
Form of 2007 Restricted Stock Unit Agreement (Senior Officers) under the Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. 2007 Incentive Award Plan — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.16.7 to Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc.'s (formerly known as Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc.) Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008.* |
||
10.44.5 |
Form of 2007 Performance Share Unit Agreement (Senior Officers) under the Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. 2007 Incentive Award Plan — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.16.10 to Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc.'s (formerly known as Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc.) Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008.* |
||
10.44.6 |
Form of Performance Share Unit Agreement (Chief Executive Officer and Senior Officers) under the Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc. 2007 Incentive Award Plan for Awards after October 29, 2008 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.16.12 to Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc.'s (formerly known as Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc.) Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008.* |
||
10.45.1 |
Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc. Supplemental Matched Employee Savings and Investment Plan (Amended and Restated Effective January 1, 2010) — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc.'s (formerly known as Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc.) Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2009.* |
||
10.45.2 |
First Amendment to the Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc. Supplemental Matched Employee Savings and Investment Plan (Amended and Restated Effective January 1, 2010), dated September 24, 2010 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.45.2 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010.* |
||
10.45.3 |
Second Amendment to the Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc. Supplemental Matched Employee Savings and Investment Plan (Amended and Restated Effective January 1, 2010), dated November 3, 2010 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.45.3 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010.* |
||
10.45.4 |
Third Amendment to the Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc. Supplemental Matched Employee Savings and Investment Plan, Effective January 1, 2010), dated February 15, 2011.* |
||
10.45.5 |
Fourth Amendment to the Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc. Supplemental Matched Employee Savings and Investment Plan, effective December 31, 2011, dated December 14, 2011.* |
||
10.46.1 |
Coca-Cola Refreshments Executive Pension Plan, dated December 13, 2010 (Amended and Restated Effective January 1, 2011) — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.46 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010.* |
||
10.46.2 |
Amendment Number One to the Coca-Cola Refreshments Executive Pension Plan (Amended and Restated Effective January 1, 2011), dated as of July 14, 2011— incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2011.* |
||
10.46.3 |
Amendment Number Two to the Coca-Cola Refreshments Executive Pension Plan, effective December 31, 2011, dated December 14, 2011.* |
||
10.47 |
Summary Plan Description for Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc. Executive Long-Term Disability Plan — incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.18 of Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc.'s (formerly known as Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc.) Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2006.* |
||
10.48.1 |
Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc. Executive Severance Plan (Amended and Restated Effective December 31, 2008) — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.5.4 to Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc.'s (formerly known as Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc.) Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008.* |
||
10.48.2 |
First Amendment to the Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc. Executive Severance Plan (Amended and Restated Effective December 31, 2008), dated as of November 3, 2010 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.48.2 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010.* |
||
10.48.3 |
Form Agreement in connection with the Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc. Executive Severance Plan (Amended and Restated Effective September 25, 2008) — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.5.5 to Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc.'s (formerly known as Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc.) Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008.* |
||
10.48.4 |
Amendment Number Two to the Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc. Executive Severance Plan (Amended and Restated Effective December 31, 2008), dated as of July 14, 2011 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2011.* |
||
10.49 |
Amendment to certain Coca-Cola Refreshments USA, Inc.'s (formerly known as Coca-Cola Enterprises Inc.) Employee Benefit Plans and Equity Plans, effective December 6, 2010 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.49 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010.* |
||
157
10.50 |
Offer Letter, dated October 21, 2010, from the Company to Steven A. Cahillane, including Agreement on Confidentiality, Non-Competition and Non-Solicitation, dated November 10, 2010 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.50 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010.* |
||
10.51 |
Offer Letter, dated January 5, 2011, from the Company to Guy Wollaert, including Agreement on Confidentiality, Non-Competition and Non-Solicitation, dated June 23, 2008 — incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.9 of the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended April 1, 2011.* |
||
12.1 |
Computation of Ratios of Earnings to Fixed Charges for the years ended December 31, 2011, 2010, 2009, 2008 and 2007. |
||
21.1 |
List of subsidiaries of the Company as of December 31, 2011. |
||
23.1 |
Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. |
||
24.1 |
Powers of Attorney of Officers and Directors signing this report. |
||
31.1 |
Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a) Certification, executed by Muhtar Kent, Chairman of the Board of Directors, Chief Executive Officer and President of The Coca-Cola Company. |
||
31.2 |
Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a) Certification, executed by Gary P. Fayard, Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of The Coca-Cola Company. |
||
32.1 |
Certifications required by Rule 13a-14(b) or Rule 15d-14(b) and Section 1350 of Chapter 63 of Title 18 of the United States Code (18 U.S.C. 1350), executed by Muhtar Kent, Chairman of the Board of Directors, Chief Executive Officer and President of The Coca-Cola Company and by Gary P. Fayard, Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of The Coca-Cola Company. |
||
101 |
The following financial information from The Coca-Cola Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011, formatted in XBRL (eXtensible Business Reporting Language): (i) Consolidated Statements of Income, (ii) Consolidated Balance Sheets, (iii) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, (iv) Consolidated Statements of Shareowners' Equity and (v) the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
|
||
_________________________________
* |
Management contracts and compensatory plans and arrangements required to be filed as exhibits pursuant to Item 15(b) of this report. |
158
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
THE COCA-COLA COMPANY |
|||||
(Registrant) |
|||||
By: |
/s/ Muhtar Kent |
||||
|
Muhtar Kent
Chairman of the Board of Directors,
Chief Executive Officer and President
|
|||||
Date: |
February 23, 2012 |
||||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
/s/ Muhtar Kent |
* |
|
|
Muhtar Kent
Chairman of the Board of Directors,
Chief Executive Officer,
President and a Director
(Principal Executive Officer)
|
Richard M. Daley
Director
|
|
February 23, 2012 |
February 23, 2012 |
|
/s/ Gary P. Fayard |
* |
|
Gary P. Fayard Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) |
Barry Diller
Director
|
|
February 23, 2012 |
February 23, 2012 |
|
/s/ Kathy N. Waller |
* |
|
|
Kathy N. Waller
Vice President and Controller
(Principal Accounting Officer)
|
Evan G. Greenberg
Director
|
|
February 23, 2012 |
February 23, 2012 |
|
* |
* |
|
|
Herbert A. Allen
Director
|
Alexis M. Herman
Director
|
|
February 23, 2012 |
February 23, 2012 |
|
* |
* |
|
|
Ronald W. Allen
Director
|
Donald R. Keough
Director
|
|
February 23, 2012 |
February 23, 2012 |
|
* |
* |
|
|
Howard G. Buffett
Director
|
Robert A. Kotick Director |
|
February 23, 2012 |
February 23, 2012 |
|
159
* |
* |
|
|
Maria Elena Lagomasino
Director
|
Peter V. Ueberroth
Director
|
|
February 23, 2012 |
February 23, 2012 |
|
* |
* |
|
|
Donald F. McHenry
Director
|
Jacob Wallenberg
Director
|
|
February 23, 2012 |
February 23, 2012 |
|
* |
* |
|
|
Sam Nunn
Director
|
James B. Williams
Director
|
|
February 23, 2012 |
February 23, 2012 |
|
* |
||
|
James D. Robinson III
Director
|
||
February 23, 2012 |
||
*By: |
/s/ Gloria K. Bowden |
|
|
Gloria K. Bowden
Attorney-in-fact
|
||
February 23, 2012 |
||
160